In today’s digital era, cloud computing has become an essential component of modern businesses, enabling organizations to scale their operations, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation. Microsoft Azure, a leading cloud computing platform, has emerged as a dominant force, empowering businesses to leverage the power of the cloud for their digital transformation journeys. As we are into 2023, the Microsoft Azure career path is evolving rapidly, offering exciting opportunities for professionals seeking to build a rewarding and future-proof career.
The purpose of this blog is to provide an overview of the new Microsoft Azure career path in 2023, highlighting the growing demand for Azure professionals and the skills required to excel in this dynamic field. We will explore the diverse career opportunities within the Azure ecosystem, delve into the essential technical skills and certifications needed to succeed and discuss the resources available for learning and upskilling in Azure. Additionally, we will showcase success stories of professionals who have carved a successful path in the Azure domain, and we’ll touch upon the emerging trends that will shape the future of Microsoft Azure.
Whether you are an aspiring IT professional looking to enter the cloud computing space or an experienced professional seeking to pivot your career towards Azure, this blog will serve as a valuable resource to help you navigate the new Microsoft Azure career path in 2023. Let’s dive in and discover the exciting possibilities that lie ahead in this ever-expanding field.
Overview of Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services and solutions to businesses of all sizes. It provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings, enabling organizations to build, deploy, and manage applications and services with ease. Azure offers a global network of data centers, ensuring scalability, reliability, and high availability for businesses operating in various regions.
Azure’s services span across multiple domains, including compute, storage, networking, databases, artificial intelligence, analytics, and more. Organizations can leverage Azure to host websites and web applications, store and analyze vast amounts of data, deploy virtual machines, develop and deploy machine learning models, and integrate various tools and services for seamless operations.
Major industries and sectors leveraging Azure for digital transformation:
- Enterprise IT: Organizations are migrating their on-premises infrastructure to Azure to reduce costs, improve scalability, and enhance security.
- E-commerce and Retail: Azure enables businesses to handle high-traffic demands during peak periods, implement personalized shopping experiences, and leverage data analytics for customer insights.
- Healthcare: Azure facilitates secure data storage, interoperability of health records, and the development of AI-powered healthcare solutions for improved patient care.
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions utilize Azure for regulatory compliance, fraud detection, risk analysis, and developing scalable applications.
- Manufacturing: Azure enables manufacturers to optimize their supply chain, monitor equipment performance, and implement predictive maintenance using IoT and AI capabilities.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Azure provides the infrastructure for cloud gaming, streaming services, and content delivery, ensuring a seamless and immersive user experience.
Emerging Career Opportunities in Microsoft Azure
As the adoption of Microsoft Azure continues to soar, an array of exciting and in-demand career opportunities has emerged within the Azure ecosystem. These roles require specialized skills and expertise in leveraging Azure’s robust infrastructure, services, and tools to drive digital transformation and deliver innovative solutions. Let’s explore some of the prominent career paths in Microsoft Azure:
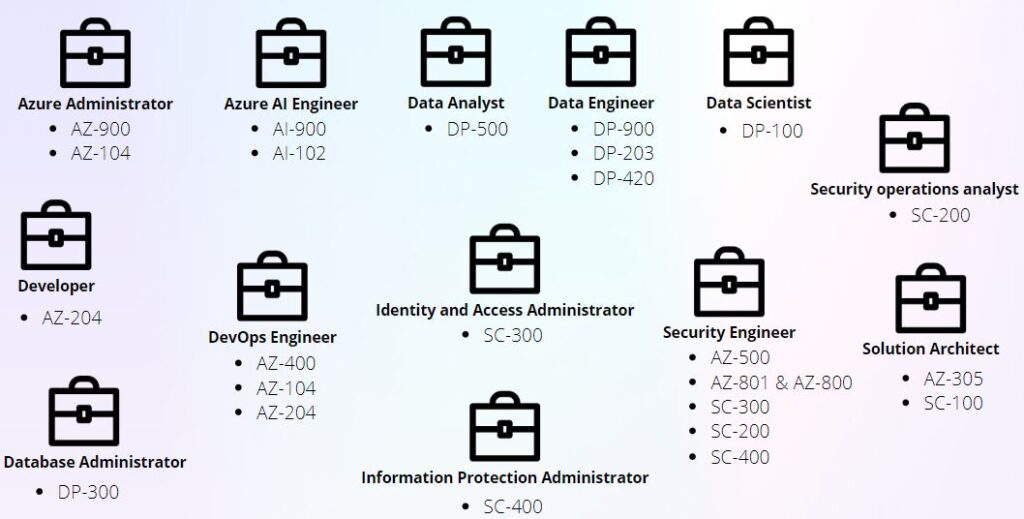
Azure Administrator
Azure Administrators play a crucial role in implementing, managing, and monitoring an organization’s Microsoft Azure environment. They possess subject matter expertise in various aspects of Azure, including identity management, storage, compute, virtual networks, security, and governance. Working as part of a larger team dedicated to cloud infrastructure, Azure Administrators are responsible for provisioning resources, ensuring proper sizing, monitoring performance, and making necessary adjustments.
Exam AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
Candidates taking this exam should possess a solid understanding of cloud services and their implementation using Microsoft Azure. The exam is designed for individuals who are either new to cloud-based solutions and services or are just beginning to work with Azure.
The Azure Fundamentals exam serves as a valuable opportunity to demonstrate knowledge in various areas, including cloud concepts, Azure services, Azure workloads, security and privacy within Azure, as well as Azure pricing and support. Candidates should have a grasp of fundamental technology concepts, encompassing networking, storage, compute, application support, and application development.
While Azure Fundamentals can be utilized as a preparation tool for other Azure role-based or specialty certifications, it is not mandatory as a prerequisite for any of them.
Skill Measured:
- Describe cloud concepts (25–30%)
- Describe Azure architecture and services (35–40%)
- Describe Azure management and governance (30–35%)
Exam AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
To pursue a career as an Azure Administrator, candidates can follow the path of acquiring the AZ-104 certification: Microsoft Azure Administrator. This certification validates the candidate’s knowledge and skills in implementing, managing, and monitoring Azure environments. It covers various topics such as virtual networks, storage, compute, identity, security, and governance.
Azure Administrators often collaborate with other roles within the organization to deliver networking, security, database, application development, and DevOps solutions on the Azure platform. Their responsibilities extend beyond the technical aspects and include coordinating with different teams to ensure the successful implementation of Azure solutions.
Professionals aspiring to become Azure Administrators should have a solid understanding of operating systems, networking, servers, and virtualization. Additionally, experience with tools like PowerShell, Azure CLI, Azure Resource Manager templates (ARM templates), and Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is essential for effectively managing Azure environments.
By obtaining the AZ-104 certification and developing the necessary skills, individuals can embark on a rewarding career as Azure Administrators, contributing to the successful implementation and management of cloud solutions for organizations.
Skill Measured:
- Manage Azure identities and governance (15–20%)
- Implement and manage storage (15–20%)
- Deploy and manage Azure compute resources (20–25%)
- Configure and manage virtual networking (20-25%)
- Monitor and maintain Azure resources (10–15%)
Azure AI Engineer
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineers play a pivotal role in the development and implementation of AI systems that mimic human intelligence. They are responsible for programming, training, and fine-tuning complex algorithms that power AI applications. This multifaceted role requires expertise in software development, programming, data science, and data engineering.
While there is overlap with data engineering, AI Engineers typically focus on the higher-level tasks of model development and implementation rather than writing the code for scalable data sharing. Their primary responsibilities include sourcing and integrating data from various sources, designing and testing machine learning models, and utilizing APIs or embedded code to build and deploy AI applications.
AI Engineers operate in various environments, including cloud or hybrid setups, and leverage their expertise to develop and deploy cognitive services, machine learning algorithms, and knowledge mining solutions. By harnessing the power of AI, these professionals enable organizations to gain a competitive edge, automate processes, and extract valuable insights from data.
The role of AI Engineers is integral to the advancement of technology and its application across industries. As AI continues to evolve and shape the future, AI Engineers will play a crucial role in driving innovation, enhancing customer experiences, and enabling organizations to stay ahead of the game.
AI-900: Azure AI Fundamentals
Acquiring a strong foundation in artificial intelligence (AI) can serve as a launching pad for your career and open up a world of technical opportunities within Azure. The realm of AI offers possibilities that were once considered science fiction but are now within reach. By harnessing AI, you can create innovative solutions, enhance applications, and drive advancements in various fields such as healthcare, finance, and environmental protection.
If you aspire to showcase your AI skills and contribute to building a better world, pursuing the Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Fundamentals certification could be the perfect fit. This certification allows you to demonstrate your understanding of common AI and machine learning workloads and how Azure services can address them effectively. It serves as a solid foundation for your career, validating your knowledge of essential machine learning and AI concepts, as well as relevant Azure services.
While having some general programming knowledge or experience is recommended, it is not mandatory to pursue the Azure AI Fundamentals certification. This certification can also reinforce your foundational understanding of other Azure role-based certifications, such as Azure Data Scientist Associate, Azure AI Engineer Associate, or Azure Developer Associate. However, it is not a prerequisite for these certifications.
By obtaining the Azure AI Fundamentals certification, you establish a strong foothold in the world of AI and position yourself for further growth within Azure’s certification paths. This certification demonstrates your commitment to expanding your AI knowledge and provides a solid framework for pursuing more advanced Azure certifications.
Skills Measured:
- Describe Artificial Intelligence workloads and considerations
- Describe the fundamental principles of machine learning on Azure
- Describe features of computer vision workloads on Azure
- Describe features of Natural Language Processing (NLP) workloads on Azure
Exam AI-102: Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
Microsoft Azure AI engineers play a crucial role in designing, managing, and deploying AI solutions that leverage the power of Azure Cognitive Services and other Azure services. Their responsibilities encompass the entire lifecycle of AI solution development, starting from requirements gathering and design, all the way to development, deployment, integration, maintenance, performance optimization, and monitoring.
Collaborating closely with solution architects, Azure AI engineers translate the architectural vision into practical implementation. They work alongside data scientists, data engineers, IoT specialists, infrastructure administrators, and fellow software developers to build comprehensive end-to-end AI solutions.
Proficiency in programming languages like Python or C# is essential for Azure AI engineers. They utilize REST-based APIs and software development kits (SDKs) to create secure solutions for image processing, video processing, natural language processing (NLP), knowledge mining, and conversational AI on the Azure platform. They possess a deep understanding of various AI implementation techniques and are well-versed in the components comprising the Azure AI portfolio, as well as the available data storage options.
Responsible AI principles are integral to the work of Azure AI engineers. They have a solid grasp of ethical considerations and are equipped to apply responsible AI practices in their solutions. This ensures that the AI systems they build are fair, transparent, and trustworthy.
Skills Measured:
- Plan and manage an Azure AI solution
- Implement image and video processing solutions
- Implement natural language processing solutions
- Implement knowledge-mining solutions
- Implement conversational AI solutions
Data Analyst
Data analysts play a vital role in helping businesses extract maximum value from their data assets by utilizing visualization and reporting tools. They are responsible for tasks such as profiling, cleaning, and transforming data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. Additionally, data analysts design and construct scalable data models that enable effective analysis, and they implement advanced analytics capabilities within reports to uncover valuable insights.
Collaborating with relevant stakeholders, data analysts identify the necessary data and reporting requirements that align with business objectives. They work closely with teams to understand their needs and then use their expertise to transform raw data into meaningful and relevant insights.
A key aspect of a data analyst’s role is to simplify complex data by designing and building data models. These models facilitate the interpretation and understanding of data, ultimately driving valuable business outcomes. By transforming data into actionable insights, data analysts empower organizations to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge.
Exam DP-500: Designing and Implementing Enterprise-Scale Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Azure and Microsoft Power BI
To excel in DP-500 exam, candidates should possess comprehensive expertise in designing, creating, and deploying data analytics solutions tailored for enterprise-scale environments.
The responsibilities of this role encompass a wide range of advanced data analytics tasks, including data cleaning and transformation, designing and constructing enterprise data models, integrating advanced analytics capabilities, connecting with IT infrastructure, and applying development lifecycle practices. These professionals play a crucial role in collecting enterprise-level requirements for data analytics solutions that leverage Azure and Microsoft Power BI. They also provide guidance on data governance and configuration settings for Power BI administration, monitor data usage, and optimize the performance of data analytics solutions.
Azure enterprise data analysts collaborate closely with other roles such as solution architects, data engineers, data scientists, AI engineers, database administrators, and Power BI data analysts. Their expertise is vital in aligning data analytics solutions with the broader organizational objectives and integrating seamlessly with other stakeholders.
Candidates aspiring to succeed in this exam should possess advanced skills in Power BI. This includes proficiency in managing data repositories and processing data both in the cloud and on-premises, as well as utilizing Power Query and Data Analysis Expressions (DAX). Additionally, candidates should be adept at consuming data from Azure Synapse Analytics, have experience in querying relational databases using Transact-SQL (T-SQL), and possess strong data visualization capabilities.
Skills Measured:
- Implement and manage a data analytics environment (25–30%)
- Query and transform data (20–25%)
- Implement and manage data models (25–30%)
- Explore and visualize data (20–25%)
Data Engineer
A data engineer plays a critical role in integrating, transforming, and consolidating data from diverse structured and unstructured data systems. Their primary objective is to create data structures that are well-suited for building robust analytics solutions. Additionally, data engineers are responsible for designing and supporting data pipelines and data stores that exhibit high performance, efficiency, organization, and reliability, all while adhering to specific business requirements and constraints.
By leveraging their expertise, data engineers ensure that data from various sources can be seamlessly integrated and transformed into a unified format. This consolidated data can then be utilized for analytics purposes, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
In addition to data integration and transformation, data engineers also focus on designing and implementing data pipelines and data stores. These pipelines serve as efficient channels for data flow, facilitating the movement of data between different systems and stages of processing. Data stores, on the other hand, provide secure and reliable storage for processed and transformed data.
To meet specific business requirements and constraints, data engineers collaborate closely with stakeholders to understand their needs and ensure that the data engineering solutions align with organizational goals. They work in tandem with data architects, data scientists, and other professionals to create a robust data infrastructure that supports analytics initiatives.
Exam DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
This exam provides candidates with the chance to showcase their understanding of essential data concepts and the relevant Microsoft Azure data services. Prior familiarity with the self-paced or instructor-led learning material for Exam DP-900 is highly recommended for individuals interested in taking this exam.
The exam is specifically designed for candidates who are at the initial stages of working with data in the cloud. It assesses their knowledge and comprehension of fundamental data concepts, including both relational and non-relational data models. Candidates should also have a good understanding of different data workloads, such as transactional and analytical processes.
While preparing for the Azure Data Fundamentals exam, candidates can also use the opportunity to lay the foundation for pursuing other Azure role-based certifications, such as Azure Database Administrator Associate or Azure Data Engineer Associate. However, it is important to note that the Azure Data Fundamentals certification is not a prerequisite for these advanced certifications.
Skill Measured:
- Describe core data concepts (25-30%)
- Identify considerations for relational data on Azure (20-25%)
- Describe considerations for working with non-relational data on Azure (15-20%)
- Describe an analytics workload on Azure (25-30%)
Exam DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
To excel in this exam, candidates should possess comprehensive subject matter expertise in integrating, transforming, and consolidating data from diverse structured, unstructured, and streaming data systems. Azure data engineers play a crucial role in helping stakeholders gain insights from data through exploration. They are responsible for building and maintaining secure and compliant data processing pipelines using a variety of tools and techniques.
Using various Azure data services and frameworks, data engineers store and generate cleansed and enhanced datasets for analysis. The design of the data store depends on specific business requirements and can follow architectural patterns such as modern data warehouse (MDW), big data, or lakehouse architecture.
Data engineers also contribute to the high-performance, efficient, organized, and reliable operationalization of data pipelines and data stores, considering the constraints and requirements of the business. They identify and troubleshoot operational and data quality issues, ensuring smooth data flow. Additionally, data engineers design, implement, monitor, and optimize data platforms to support the data pipelines effectively.
Candidates preparing for this exam must possess a solid understanding of data processing languages, including SQL, Python, and Scala. They should be proficient in parallel processing and have knowledge of data architecture patterns. Mastery of Azure Data Factory, Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Stream Analytics, Azure Event Hubs, Azure Data Lake Storage, and Azure Databricks is essential for creating efficient and effective data processing solutions.
Skill Measured:
- Design and implement data storage (15–20%)
- Develop data processing (40–45%)
- Secure, monitor, and optimize data storage and data processing (30–35%)
Exam DP-420: Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
To succeed in this exam, candidates should possess expertise in designing, implementing, and monitoring cloud-native applications that are responsible for storing and managing data.
The key responsibilities for this role include designing and implementing data models and data distribution strategies, loading data into an Azure Cosmos DB database, and optimizing and maintaining the solution. These professionals are adept at integrating the solution with other Azure services to create a comprehensive application ecosystem. They prioritize considerations such as security, availability, resilience, and performance when designing, implementing, and monitoring solutions.
A successful candidate for this exam must demonstrate strong knowledge and hands-on experience in developing applications for Azure, particularly leveraging Azure Cosmos DB database technologies. They should be proficient in developing applications that utilize the Azure Cosmos DB NoSQL API. This entails being able to write efficient SQL queries for the API and create suitable indexing policies. Additionally, candidates should have experience in creating server-side objects using JavaScript. They should possess familiarity with provisioning and managing resources in Azure, interpreting JSON, reading C# or Java code, and utilizing PowerShell.
Skill Measured:
- Design and implement data models (35–40%)
- Design and implement data distribution (5–10%)
- Integrate an Azure Cosmos DB solution (5–10%)
- Optimize an Azure Cosmos DB solution (15–20%)
- Maintain an Azure Cosmos DB solution (25–30%)
Data Scientist
A data scientist is a skilled professional in the field of data analysis who plays a crucial role in collecting, analyzing, and interpreting vast amounts of data to address complex business challenges. By combining expertise in statistics, computer science, and business acumen, data scientists assist organizations in gaining deeper insights and achieving their objectives. Their work often revolves around handling large and unstructured datasets sourced from various channels and devising effective strategies to extract meaningful information from the data.
Data scientists leverage advanced techniques such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and statistical analysis to uncover hidden patterns, identify trends, and challenge prevailing assumptions. They are skilled in developing models and algorithms that enable accurate predictions, valuable insights, and informed decision-making. Their expertise allows them to transform raw data into actionable recommendations, thereby providing organizations with a competitive edge.
The role of a data scientist involves applying a wide range of analytical tools and programming languages to extract knowledge from complex datasets. They are proficient in data wrangling, feature engineering, and data visualization techniques. Additionally, data scientists possess strong problem-solving abilities and possess excellent communication skills, enabling them to effectively convey their findings and insights to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Exam DP-100: Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
To excel in this exam, candidates should possess in-depth subject matter expertise in the application of data science and machine learning to implement and execute machine learning workloads on the Azure platform.
The responsibilities associated with this role encompass designing and establishing an appropriate working environment for data science workloads, performing data exploration, training machine learning models, implementing pipelines, executing jobs to prepare for production, and managing, deploying, and monitoring scalable machine learning solutions.
A successful candidate for this exam should demonstrate strong knowledge and practical experience in data science, specifically utilizing Azure Machine Learning and MLflow. They should be proficient in leveraging these tools and platforms to develop and implement machine learning solutions effectively.
Skill Measured:
- Design and prepare a machine learning solution (20–25%)
- Explore data and train models (35–40%)
- Prepare a model for deployment (20–25%)
- Deploy and retrain a model (10–15%)
Developer
As a developer, you play a critical role in leveraging your comprehensive technical expertise in large-scale distributed systems. This expertise encompasses various aspects such as infrastructure, code, inter- and intra-service dependencies, and operations. Your primary objective is to develop and enhance the reliability, performance, efficiency, latency, and scalability of services and products that operate at scale. This involves proactively and continuously improving these aspects throughout the entire development and operational lifecycle.
Within this role, you provide guidance and recommendations on code optimization, drawing from your experience and insights gained from working with related services or products. Additionally, you actively participate in incident response, addressing issues and ensuring the smooth functioning of the systems and products you work on.
A key aspect of your role is the development of code, scripts, systems, and tools that automate complex and repetitive tasks. These automation efforts help reduce the operational burden and enable product engineering teams to deploy changes to production at an increased velocity, all while maintaining safety and reliability. Furthermore, you monitor and assess the impact of these changes across various systems, services, and products, ensuring their seamless integration.
Exam AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
As an Azure developer, you play a crucial role in the end-to-end development process, encompassing various phases such as requirements gathering, design, development, deployment, security, maintenance, performance tuning, and monitoring. Your responsibilities include being well-versed in Azure technologies such as SDKs, data storage options, data connections, APIs, app authentication/authorization, compute/container deployment, and debugging.
Collaboration is essential in this role, as you partner with cloud solution architects, database administrators (DBAs), DevOps professionals, infrastructure administrators, and other stakeholders to implement effective solutions. By working closely with these teams, you ensure seamless integration and optimal performance of the solutions you develop.
To excel in this role, candidates should possess a minimum of 2 years of professional development experience, along with hands-on experience working with Azure. Proficiency in programming languages supported by Azure is essential, and candidates should be skilled in utilizing tools such as Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, and other relevant tools for efficient development.
Skill Measured:
- Develop Azure compute solutions (25-30%)
- Develop for Azure storage (15-20%)
- Implement Azure security (20-25%)
- Monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize Azure solutions (15-20%)
- Connect to and consume Azure services and third-party services (15-20%)
DevOps Engineer
A DevOps engineer is a versatile professional with expertise in both development and infrastructure administration. Their primary focus is on enabling the continuous delivery of value within organizations by effectively managing people, processes, and products. They play a pivotal role in designing and implementing strategies across various areas, including collaboration, code management, infrastructure management, source control, security, compliance, continuous integration, testing, delivery, monitoring, and feedback.
Collaboration is a key aspect of the DevOps engineer’s role, as they work closely with development teams, operations teams, and other stakeholders to establish efficient workflows and foster effective communication. They facilitate seamless collaboration between different teams involved in the software development lifecycle.
In addition, the DevOps engineer contributes to the design and implementation of infrastructure and deployment strategies that ensure the availability, scalability, and reliability of applications and systems. They employ best practices to automate processes, implement security measures, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Continuous integration, testing, and delivery are critical components of the DevOps engineer’s responsibilities. They establish and maintain systems and processes for automated testing and integration, enabling frequent and reliable software releases. Monitoring and feedback mechanisms are also implemented to identify and address issues promptly, ensuring optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Exam AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
DevOps engineers are highly skilled professionals who possess expertise in both development and infrastructure administration. They play a critical role in enabling organizations to achieve continuous delivery of value by effectively collaborating with people, optimizing processes, and leveraging relevant products and technologies.
The primary responsibilities of a DevOps engineer encompass designing and implementing strategies across various domains, including collaboration, code management, infrastructure management, source control, security, compliance, continuous integration, testing, delivery, monitoring, and feedback. By establishing efficient workflows and fostering effective communication, they facilitate seamless collaboration among different teams involved in the software development lifecycle.
DevOps engineers work closely with developers, site reliability engineers, and Azure administrators as part of cross-functional teams. They bring their expertise to the table to ensure smooth integration of development and operations, enabling organizations to achieve their goals efficiently and effectively.
To excel in this role, DevOps engineers must have hands-on experience with administering and developing in Azure. They should possess strong skills in at least one of the key areas mentioned earlier and be well-versed in using Azure DevOps and GitHub as essential tools for managing code, collaboration, and version control.
Skills Measured:
- Configure processes and communications (10-15%)
- Design and implement source control (15-20%)
- Design and implement build and release pipelines (40-45%)
- Develop a security and compliance plan (10-15%)
- Implement an instrumentation strategy (10-15%)
Exam AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
To succeed in this exam, candidates should possess in-depth expertise in implementing, managing, and monitoring an organization’s Microsoft Azure environment. This includes proficiency in various aspects such as virtual networks, storage, compute, identity, security, and governance.
As an Azure administrator, you will play a vital role as part of a dedicated team responsible for implementing and maintaining the organization’s cloud infrastructure. Collaboration with other roles within the team is crucial to deliver comprehensive Azure solutions, covering areas such as networking, security, database management, application development, and DevOps practices.
Candidates for this exam should have a solid understanding of operating systems, networking principles, server administration, and virtualization technologies. Moreover, professionals in this role should be experienced in utilizing tools and technologies like PowerShell, Azure CLI, the Azure portal, Azure Resource Manager templates (ARM templates), and Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), which is a part of the Microsoft 365 suite.
By demonstrating your expertise and knowledge in these areas, you can establish yourself as a competent Azure administrator, capable of effectively managing and optimizing an organization’s Azure infrastructure to drive business success.
Skill Measured:
- Manage Azure identities and governance (15–20%)
- Implement and manage storage (15–20%)
- Deploy and manage Azure compute resources (20–25%)
- Configure and manage virtual networking (20-25%)
- Monitor and maintain Azure resources (10–15%)
Exam AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
To succeed in this exam, candidates should have a wide range of skills and experience in various aspects of the development lifecycle. They are responsible for actively participating in all phases of development, including requirements gathering, design, development, deployment, security, maintenance, performance tuning, and monitoring.
Proficiency in Azure is crucial for candidates, including familiarity with Azure Software Development Kits (SDKs), data storage options, data connections, APIs, application authentication/authorization, compute/container deployment, and debugging techniques.
Collaboration is key, as candidates are expected to partner with cloud solution architects, database administrators (DBAs), DevOps professionals, infrastructure administrators, and other stakeholders to implement effective solutions.
Candidates should have at least 2 years of professional development experience, along with hands-on experience working with Azure. They should be capable of programming in an Azure-supported language and be proficient in using tools such as Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, and other related technologies.
Skill Measured:
- Develop Azure compute solutions (25-30%)
- Develop for Azure storage (15-20%)
- Implement Azure security (20-25%)
- Monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize Azure solutions (15-20%)
- Connect to and consume Azure services and third-party services (15-20%)
Identity and access administrator
The role of an identity and access administrator is to automate the authentication and authorization processes for various identities, including users, devices, Azure resources, and applications within an environment. This automation facilitates a seamless user experience and provides self-service management capabilities for all users.
One of the key responsibilities of an identity and access administrator is to ensure that all identities are explicitly verified, following the principles of Zero Trust. This approach focuses on continuously validating and verifying identities, regardless of their location or context, to enhance security and mitigate potential risks.
By implementing efficient authentication and authorization mechanisms, the identity and access administrator plays a critical role in maintaining a secure and controlled access environment, while enabling users to securely interact with resources and applications. Their efforts contribute to a seamless and efficient user experience while upholding the highest standards of security and compliance.
Exam SC-300: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
The role of a Microsoft identity and access administrator involves designing, implementing, and operating the identity and access management systems within an organization using Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), which is part of Microsoft Entra. They are responsible for configuring and managing authentication and authorization processes for users, devices, Azure resources, and applications.
In order to provide seamless user experiences and self-service management capabilities, the identity and access administrator ensures that identities are explicitly verified, aligning with the principles of Zero Trust. They leverage automation through PowerShell to manage Azure AD and utilize Kusto Query Language (KQL) to analyze events. Additionally, they are accountable for troubleshooting, monitoring, and reporting within the identity and access environment.
The identity and access administrator collaborates with various other roles in the organization to drive strategic identity projects, modernize identity solutions, implement hybrid identity solutions, and establish identity governance. They should possess a strong familiarity with Azure and Microsoft 365 services and workloads.
By fulfilling their responsibilities, the identity and access administrator plays a vital role in ensuring secure and efficient identity management, while enabling users to seamlessly access resources and applications. Their expertise and collaboration contribute to enhancing the organization’s overall identity and access management capabilities.
Skill Measured:
- Implement identities in Azure AD (20–25%)
- Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
- Implement access management for applications (15–20%)
- Plan and implement identity governance in Azure AD (20–25%)
Information Protection Administrator
The role of a Microsoft information protection administrator involves planning and implementing controls that align with the information protection and governance requirements of an organization, utilizing Microsoft 365 information protection services. They are tasked with translating these requirements and controls into technical implementations.
The information protection administrator plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and compliance of organizational data. They work closely with stakeholders to understand the information protection needs and design strategies to address them effectively. They leverage Microsoft 365 information protection services to implement solutions that safeguard sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and enforce data governance policies.
By implementing appropriate controls and configurations, the information protection administrator helps to protect the organization’s valuable information assets from unauthorized disclosure, data loss, and other security risks. They collaborate with various teams, such as compliance officers, security teams, and IT administrators, to ensure that the implemented information protection measures are aligned with the organization’s overall security and governance framework.
Exam SC-400: Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
The role of a Microsoft information protection administrator involves planning and implementing controls that align with the information protection and governance requirements of an organization, utilizing Microsoft 365 information protection services. They are responsible for translating information protection requirements and controls into technical implementations.
In addition to this, the information protection administrator works closely with various stakeholders, including IT personnel, business application owners, human resources, and legal teams, to implement technology solutions that support policies and controls necessary for regulatory compliance. They collaborate with security and governance leadership, such as chief compliance officers, chief data officers, and security officers, to assess enterprise risk and develop appropriate policies.
The information protection administrator defines relevant requirements and evaluates IT processes and operations to ensure compliance with policies and controls. They are tasked with creating policies and rules for content classification, data loss prevention, governance, and protection. By establishing these policies, they help enforce security measures and mitigate risks associated with sensitive data.
Skill Measured:
- Implement information protection (35–40%)
- Implement data loss prevention (30–35%)
- Implement information governance (25–30%)
Security Engineer
Security engineers play a crucial role in safeguarding organizations and their systems from vulnerabilities, security incidents, and persistent threats. Their responsibilities encompass a wide range of functions aimed at ensuring the security and resilience of network infrastructure and systems.
One of their primary tasks is to design and deploy secure network solutions that protect against potential threats. This involves implementing robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols, to defend against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Security engineers also play a critical role in incident response. They promptly investigate and respond to security escalations, identifying the root cause of incidents and implementing appropriate remediation measures to mitigate the impact and prevent future occurrences.
To proactively identify vulnerabilities, security engineers conduct assessments and penetration testing. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, they assess the resilience of systems and applications, identify weaknesses, and recommend security enhancements to address potential risks.
Exam AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
Candidates preparing for this exam specialize in implementing, managing, and monitoring security measures for resources deployed in Azure, multi-cloud, and hybrid environments. They are responsible for ensuring comprehensive security across the entire infrastructure, recommending appropriate security components and configurations to protect identity and access, data, applications, and networks.
As Azure security engineers, their key responsibilities include managing the overall security posture, proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, conducting threat modeling exercises, and implementing robust threat protection mechanisms. They may also play a role in responding to security incidents, working alongside incident response teams to mitigate risks and minimize the impact of security breaches.
Collaboration is crucial in this role, as Azure security engineers work closely with architects, administrators, and developers to design and implement security solutions that align with organizational security and compliance requirements.
To excel in this role, candidates should possess practical experience in administering Microsoft Azure and hybrid environments. They should have a strong command of compute, network, and storage concepts in Azure, along with a deep understanding of Azure Active Directory, which is a critical component of Microsoft Entra.
Skill Measured:
- Manage identity and access (25–30%)
- Secure networking (20–25%)
- Secure compute, storage, and databases (20–25%)
- Manage security operations (25–30%)
Microsoft Certified: Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate
Exam Required:
- Exam AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- Exam AZ-801: Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
Candidates pursuing the Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate certification should possess in-depth knowledge and expertise in configuring and managing Windows Server environments across on-premises, hybrid, and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) platforms.
In this role, candidates are responsible for seamlessly integrating Windows Server environments with Azure services and effectively managing Windows Server within on-premises networks. They are also tasked with managing and maintaining Windows Server workloads in Azure IaaS, as well as migrating and deploying workloads to the Azure cloud.
Collaboration is essential for this role, as Windows Server Hybrid Administrators frequently work alongside Azure administrators, enterprise architects, Microsoft 365 administrators, and network engineers to achieve organizational goals.
Candidates pursuing this certification demonstrate their proficiency in administering both core and advanced Windows Server workloads and services, leveraging a combination of on-premises, hybrid, and cloud technologies. They possess expertise in implementing and managing various aspects of on-premises and hybrid solutions, including identity management, compute, networking, storage, security, migration, monitoring, high availability, troubleshooting, and disaster recovery.
These professionals are adept at utilizing administrative tools and technologies such as Windows Admin Center, PowerShell, Azure Arc, and IaaS virtual machine administration. Additionally, they are well-versed in utilizing Azure services like Azure Automation Update Management, Microsoft Defender for Identity, Azure Security Center, Azure Migrate, and Azure Monitor to enhance their administrative capabilities.
Exam SC-300: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
The role of a Microsoft identity and access administrator involves designing, implementing, and operating the identity and access management systems within an organization using Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), which is part of Microsoft Entra. They are responsible for configuring and managing authentication and authorization processes for users, devices, Azure resources, and applications.
In order to provide seamless user experiences and self-service management capabilities, the identity and access administrator ensures that identities are explicitly verified, aligning with the principles of Zero Trust. They leverage automation through PowerShell to manage Azure AD and utilize Kusto Query Language (KQL) to analyze events. Additionally, they are accountable for troubleshooting, monitoring, and reporting within the identity and access environment.
The identity and access administrator collaborates with various other roles in the organization to drive strategic identity projects, modernize identity solutions, implement hybrid identity solutions, and establish identity governance. They should possess a strong familiarity with Azure and Microsoft 365 services and workloads.
By fulfilling their responsibilities, the identity and access administrator plays a vital role in ensuring secure and efficient identity management, while enabling users to seamlessly access resources and applications. Their expertise and collaboration contribute to enhancing the organization’s overall identity and access management capabilities.
Skill Measured:
- Implement identities in Azure AD (20–25%)
- Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
- Implement access management for applications (15–20%)
- Plan and implement identity governance in Azure AD (20–25%)
Exam SC-200: Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
Microsoft security operations analysts play a crucial role in minimizing organizational risk by promptly addressing active attacks, providing recommendations for enhancing threat protection practices and reporting policy violations to the appropriate stakeholders. They perform various tasks including triage, incident response, vulnerability management, threat hunting, and analysis of cyber threat intelligence.
In the dynamic landscape of multi-cloud environments, Microsoft security operations analysts are responsible for monitoring, identifying, investigating, and responding to threats. They leverage tools such as Microsoft Sentinel, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft 365 Defender, and third-party security solutions. Collaborating with business stakeholders, architects, identity administrators, Azure administrators, and endpoint administrators, these analysts work towards securing IT systems across the organization.
Candidates pursuing this role should have a strong familiarity with Microsoft 365, Azure cloud services, as well as Windows and Linux operating systems. They should possess the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively utilize these platforms and systems in order to ensure robust security measures are in place.
Skill Measured:
- Mitigate threats by using Microsoft 365 Defender (25–30%)
- Mitigate threats by using Defender for Cloud (15–20%)
- Mitigate threats by using Microsoft Sentinel (50–55%)
Exam SC-400: Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
The role of a Microsoft information protection administrator involves planning and implementing controls that align with the information protection and governance requirements of an organization, utilizing Microsoft 365 information protection services. They are responsible for translating information protection requirements and controls into technical implementations.
In addition to this, the information protection administrator works closely with various stakeholders, including IT personnel, business application owners, human resources, and legal teams, to implement technology solutions that support policies and controls necessary for regulatory compliance. They collaborate with security and governance leadership, such as chief compliance officers, chief data officers, and security officers, to assess enterprise risk and develop appropriate policies.
The information protection administrator defines relevant requirements and evaluates IT processes and operations to ensure compliance with policies and controls. They are tasked with creating policies and rules for content classification, data loss prevention, governance, and protection. By establishing these policies, they help enforce security measures and mitigate risks associated with sensitive data.
Skill Measured:
- Implement information protection (35–40%)
- Implement data loss prevention (30–35%)
- Implement information governance (25–30%)
Security operations analyst
A security operations analyst is dedicated to threat management, monitoring, and response by investigating security threats using tools such as Microsoft Sentinel, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft 365 Defender, and third-party security products.
Collaborating with stakeholders across the organization, the Microsoft security operations analyst focuses on securing information technology systems. Their primary objective is to mitigate organizational risk by promptly addressing active attacks, providing recommendations for enhancing threat protection practices, and reporting policy violations to the relevant stakeholders.
Exam SC-200: Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
Microsoft security operations analysts play a crucial role in minimizing organizational risk by promptly addressing active attacks, providing recommendations for enhancing threat protection practices and reporting policy violations to the appropriate stakeholders. They perform various tasks including triage, incident response, vulnerability management, threat hunting, and analysis of cyber threat intelligence.
In the dynamic landscape of multi-cloud environments, Microsoft security operations analysts are responsible for monitoring, identifying, investigating, and responding to threats. They leverage tools such as Microsoft Sentinel, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft 365 Defender, and third-party security solutions. Collaborating with business stakeholders, architects, identity administrators, Azure administrators, and endpoint administrators, these analysts work towards securing IT systems across the organization.
Candidates pursuing this role should have a strong familiarity with Microsoft 365, Azure cloud services, as well as Windows and Linux operating systems. They should possess the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively utilize these platforms and systems in order to ensure robust security measures are in place.
Skill Measured:
- Mitigate threats by using Microsoft 365 Defender (25–30%)
- Mitigate threats by using Defender for Cloud (15–20%)
- Mitigate threats by using Microsoft Sentinel (50–55%)
Solutions Architect
Solutions architects play a pivotal customer-facing role, taking ownership of the technical relationship and strategy between the organization and the customer. They lead architectural design sessions, create a proof of concepts/pilots, implement projects, and continuously refine and enhance solutions.
The key responsibilities of solutions architects include providing guidance to stakeholders and translating business requirements into secure, scalable, and reliable solution designs. They collaborate closely with the customer to ensure that the proposed solutions meet their specific needs and align with industry best practices.
Exam AZ-305: Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
Candidates aiming to pass this exam must possess extensive expertise in designing cloud and hybrid solutions specifically tailored for Microsoft Azure. This expertise should cover various aspects such as compute, network, storage, monitoring, and security.
As an Azure solutions architect, responsibilities include providing valuable advice to stakeholders and effectively translating their business requirements into designs that prioritize security, scalability, and reliability within Azure solutions.
Collaboration with developers, administrators, and other relevant roles involved in the implementation of Azure solutions is a crucial part of the Azure solutions architect’s role.
To excel in this exam, candidates should demonstrate advanced knowledge and hands-on experience in IT operations, encompassing networking, virtualization, identity management, security practices, business continuity, disaster recovery, data platforms, and governance. Professionals in this role should possess the ability to analyze how decisions in each area impact the overall solution. Additionally, expertise in Azure administration, Azure development, and familiarity with DevOps processes is expected.
Skill Measured:
- Design identity, governance, and monitoring solutions (25-30%)
- Design data storage solutions (25-30%)
- Design business continuity solutions (10-15%)
- Design infrastructure solutions (25-30%)
Exam SC-100: Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
Candidates undertaking this exam are Microsoft cybersecurity architects responsible for translating a cybersecurity strategy into tangible capabilities that safeguard an organization’s assets, business operations, and overall security posture. They excel in designing, implementing, and maintaining security solutions that adhere to Zero Trust principles and industry best practices. This includes devising strategies for securing identity, devices, data, applications, network, infrastructure, and DevOps environments. They also specialize in developing solutions for Governance and Risk Compliance (GRC), security operations, and security posture management.
Collaboration with leaders and practitioners in IT security, privacy, and other relevant roles is an ongoing aspect of the cybersecurity architect’s responsibilities. Together, they plan and execute a cybersecurity strategy that aligns with the organization’s business objectives.
Candidates pursuing this exam should possess hands-on experience in implementing or administering solutions across various domains, including identity and access, platform protection, security operations, data security, application security, and hybrid/multicloud infrastructures. They are expected to demonstrate expert-level proficiency in at least one of these areas. Additionally, candidates should have extensive experience in designing security solutions that leverage Microsoft’s suite of security technologies.
Skill Measured:
- Design solutions that align with security best practices and priorities (20–25%)
- Design security operations, identity, and compliance capabilities (30–35%)
- Design security solutions for infrastructure (20–25%)
- Design security solutions for applications and data (20–25%)
Database Administrator
The Azure database administrator specializes in implementing and managing the operational aspects of cloud-native and hybrid data platform solutions built on SQL Server and SQL database services. Their expertise encompasses a wide range of methods and tools used for day-to-day operations, with a strong emphasis on leveraging T-SQL and other administrative management tools for efficient and automated workflows.
In this role, professionals are accountable for overseeing the management, availability, security, and performance optimization of database solutions. They actively monitor and fine-tune the performance of databases, while also ensuring their security and availability. Additionally, they play a critical role in evaluating and executing migration strategies for seamless movement of databases between Azure and on-premises environments. Collaboration with Azure data engineers, solution architects, developers, data scientists, and other relevant professionals is a common practice to effectively manage the operational aspects of data platform solutions.
Exam DP-300: Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
Candidates preparing for this exam should possess comprehensive expertise in constructing robust database solutions capable of supporting diverse workloads utilizing both on-premises SQL Server and Azure SQL database services.
The exam is specifically designed for aspiring database administrators responsible for managing databases across on-premises and cloud environments, utilizing SQL Server and SQL database services.
Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in various Azure database services, including Azure SQL Edge, Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, as well as SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines for both Windows and Linux operating systems.
Skill Measured:
- Plan and implement data platform resources (20–25%)
- Implement a secure environment (15–20%)
- Monitor, configure, and optimize database resources (20–25%)
- Configure and manage automation of tasks (15–20%)
- Plan and configure a high availability and disaster recovery (HA/DR) environment (20–25%)
Embracing the Future of Microsoft Azure
As we look ahead, it is evident that the future of Microsoft Azure is filled with immense possibilities and exciting advancements. Azure continues to evolve and innovate, enabling organizations to stay at the forefront of technology and drive their digital transformation journeys. Here are some key aspects that showcase the promising future of Microsoft Azure:
Continued Growth and Market Dominance:
Microsoft Azure has been experiencing remarkable growth and market dominance in the cloud computing space. With a wide range of services, global data centers, and a strong customer base, Azure is positioned as a leading player in the industry. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud solutions, Azure is likely to maintain its upward trajectory, offering abundant career opportunities for Azure professionals.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Capabilities:
Azure’s hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities are shaping the future of cloud computing. Azure provides seamless integration and interoperability between on-premises infrastructure and the cloud, enabling organizations to adopt a hybrid approach that combines the best of both worlds. Additionally, Azure’s multi-cloud support allows businesses to leverage multiple cloud providers, harnessing the strengths and specialized services of each platform.
Advanced AI and Machine Learning:
Azure is at the forefront of AI and machine learning advancements, empowering organizations to build intelligent solutions. With Azure’s AI services, including Azure Cognitive Services and Azure Machine Learning, businesses can leverage natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics to gain valuable insights, automate processes, and deliver personalized experiences. As AI continues to revolutionize industries, Azure’s AI capabilities will play a vital role in shaping the future.
Internet of Things (IoT) Enablement:
Azure provides robust tools and services for IoT enablement, allowing organizations to connect, monitor, and analyze data from a multitude of devices. Azure IoT Hub, Azure IoT Edge, and Azure IoT Central enable businesses to build scalable IoT solutions, leverage edge computing capabilities, and derive actionable insights from sensor data. As the IoT ecosystem expands, Azure’s IoT offerings will be instrumental in driving innovation and transforming industries.
Data Analytics and Insights:
Data is increasingly recognized as a valuable asset, and Azure offers a comprehensive suite of data analytics services. Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, and Azure Data Factory enable organizations to ingest, process, and analyze large volumes of data to uncover valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. As organizations strive to derive meaningful insights from their data, Azure’s data analytics capabilities will continue to play a critical role.
Final Words
The new Microsoft Azure career path in 2023 presents exciting opportunities for professionals seeking to thrive in the ever-evolving world of cloud computing. Azure’s extensive services, global reach, and continuous innovation make it a dominant force in the industry, driving digital transformation across various sectors.
In this blog, we have explored the emerging career paths within the Azure landscape, including Azure Solution Architects, Azure DevOps Engineers, Azure Data Engineers, and Azure AI Engineers. These roles require specialized skills and expertise in leveraging Azure’s capabilities to design, develop, and deploy scalable and intelligent solutions.
To succeed in the Azure domain, professionals must acquire core technical skills, such as proficiency in Azure services, networking, security, and data management. Azure certifications provide a valuable validation of these skills, helping professionals stand out in the job market and enhance their career prospects.


