Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a wide range of security features to help protect your applications and data from cyber threats. With the increasing risk of cyber attacks, it’s essential to ensure that your data and systems are secure. This blog will explore some of the key security features in GCP, including identity and access management, network security, data encryption, and threat detection. By understanding these features, you can better protect your applications and data and ensure the security of your GCP environment.
Google Cloud Platform Glossary
Here are some key terms and definitions related to Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): A suite of cloud computing services offered by Google, including computing, storage, networking, and more.
- Virtual Machine (VM): A software-based emulation of a physical computer that can run applications and operating systems just like a physical computer.
- Load Balancing: A technique used to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to improve performance and availability.
- Cloud Storage: A cloud-based data storage service that allows users to store and access data from anywhere in the world using an internet connection.
- Big Data: A term used to describe large, complex data sets that are difficult to process using traditional data processing tools.
- Kubernetes: An open-source container orchestration platform used to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Firewall: A network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Compute Engine: A GCP service that allows users to run virtual machines on Google’s infrastructure.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): A GCP service that allows users to manage access control and permissions for GCP resources.
- Machine Learning: A type of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. GCP offers several machine learning services, such as TensorFlow and AutoML.
Google Security features
Let’s begin by reviewing what we get straight by virtue of practicing the GCP. These are safety protections that we would not be capable to engineer for ourselves. So, let’s go for some of the various layers of the security given by the GCP.
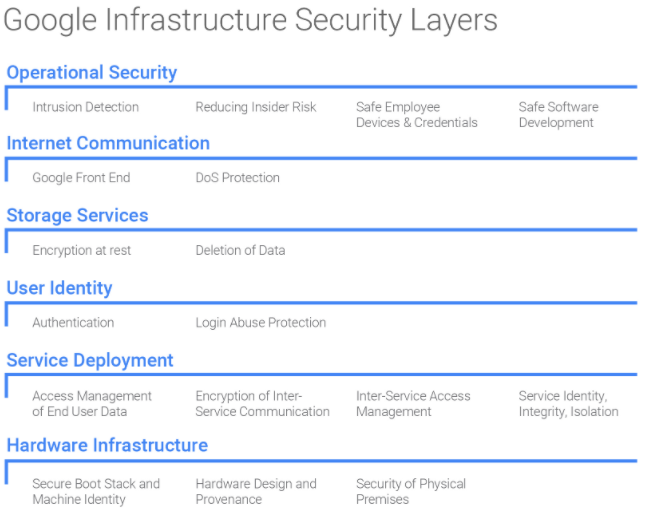
1. Datacenter physical security
Only a little fraction of Google operators ever get to tour a GCP data center. Those data marts, the zones that we have been speaking so much about, apparently would seem out of a Security film to those that did—biometric detectors, security lasers, cameras, alarms, and all of the cloak-and-dagger stuff.
2. Custom hardware and trusted booting
A special form of security attack designated privileged path attacks is on the rise. These include hateful code running from the smallest likely spots that you’d assume, hypervisor, the OS image, or boot loader. There is a unique way to actually defend against these, which is to create and develop every single element in-house. Also, Google has achieved that, including a firmware stack, curated OS images, hardware, and a concentrated hypervisor. Further, Google data hubs are populated with hundreds of servers attach to a local network. Google chooses and approves building elements from vendors and forms custom secure server cabinets and networking devices for the server machines. Google has cryptographic marks on all low-level elements, such as bootloader, BIOS, base OS, kernel, and to verify the exact software stack is booting up.
3. Data encryption
By default, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) always encrypts all consumer data at ease as well as in motion. This encryption is intuitive, and it needs no action on the user’s role. Steadfast disks, for example, are previously encrypt utilizing AES-256, and the passkey themselves are encrypted with master keys. Further, All certain key management and rotation are controlled by Google. In extension to this default encryption, a few other encryption possibilities survive as well.
4. Google Front End
Whenever we require to reveal a service utilizing GCP, service enrollment, the TLS certificate administrators, and DNS are achieve by Google itself. This convenience is called the (GFE) Google Front End service. For instance, a simplistic file of Python code can be operate as an application on App Engine that (application) will have its personal DNS name, IP, and so on.
5. Secure Service Deployment
Google’s security documentation will usually apply to guard service deployment, and it is necessary to recognize that in this context, the word service has a special meaning in the setting of security: service is the application binary that an expert writes and operates on the infrastructure. This secure setting deployment is based on 3 attributes:
- Identity: Each service operating on Google foundation has an associated service account identification. A service has to present cryptographic credentials presented to it to determine its identity while presenting or receiving (RPC) remote procedure calls to additional services. Customers use these connections to make certain that they are correlating to an expected server and the server will use them to limit access to information and processes to particular clients.
- Integrity: Google practices a cryptographic authentication and permission method at an application tier to give powerful access control at the distraction level for interservice connection. Google has access and egress filtering tools at several periods in their network to evade IP spoofing. With this path, Google is capable to maximize its network’s production and its availability.
- Isolation: Google has an active sandbox method to separate services operating on an equal machine. This incorporates language and kernel-based sandboxes, Linux user division, and hardware virtualization. Also, Google defends the operation of delicate services like cluster orchestration in GKE on completely devoted machines.
6. Secure interservice communication
The word inter-service communication leads to GCP’s sources and assistance speaking to each other. For preparing so, the partners of the services have unique whitelists of services that can obtain them. Utilizing them, the keeper of the service can also provide some IAM characters to relate with the services administered by them. Apart from that, GCP engineers on the backend who would be capable to maintain the soft and downtime-free running of the services are also presented with unique identities to reach the services (to maintain them, not to change their user-input data).
Google encrypts interservice connections by encapsulating application layer orders in RPS mechanisms to separate the application layer and to remove any sort of dependence on network security.
7. Data disposal
The wastes of the determine disks and additional storage devices that we utilize are also cleanse completely by Google. This data removal process includes certain steps: an approved individual will blow the disk clean utilizing a logical wipe. Then, a diverse authorized individual will examine the cleaned disk. The consequences of the erasure are save and logged too. Then, the erase driver is delivered into inventory for reuse. If the disk was corrupt and could not be washed clean, it is save securely and not be reuse, and such devices are systematically destroy. Each dexterity where data disposal takes section is inspect once a week.
8. In-built DDoS protections
Dispensed Denial-of-Service attacks are thoroughly studied, and anticipations against attacks are previously built into various GCP services, prominently in networking and capacity balancing. Load balancers can really be considered as hardened, bastion hosts that work like lightning rods to draw attacks, and so are pleasantly fixed by Google to guarantee that they can resist those interventions. HTTP and SSL proxy load balancers can preserve your backend examples from various threats, involving port exhaustion, SYN floods, and IP fragment floods.
9. Insider risk and intrusion detection
Google continually observes activities of all possible devices in Google infrastructure for unusual activities. To guard employees’ accounts, Google has reinstated perishable OTP second portions with U2F, cooperative security keys.
Also, Google observes its customer tools that employees use to manage their infrastructure. Google also administers a periodical check on the status of OS models with security applications on consumer devices. Google has a particular mechanism to give way privileges called application-level access administration control, which reveals interior applications to only particular users from perfectly managed devices and conventional network and geographic places. Further, Google has stern and secure access to maintain its managing access rights. They have a precise monitoring method of employee actions and also a predefined goal for administrative access for employees.
Secure Service Deployment
Google uses several means to secure its infrastructure. Here are essential security controls performed to guard service deployment:
- Cryptographic authorization and authentication— It is administered at the application level for every inter-service connection. This characteristic gives granular access control.
- Segmentation and firewalls—Google cloud infrastructure is guarded by firewalls and practices ingress and egress filtering at significant network junctions, to check IP spoofing.
- Service account identity— It is correlated with any service that operates on the (GCP) Google cloud infrastructure. The setting must utilize its cryptographic credentials to get or perform (RPCs) remote procedure calls to other services or identify itself to clients.
GCP Security Tools
Google proposes various tools that can assist us to perform security measures for the workloads.
1. Google Cloud KMS
Google Cloud Key Management (KMS) Service lets us maintain cryptographic keys. We can utilize Google’s KMS to rotate, create, and stop several sorts of cryptographic solutions, incorporating RSA 3072, AES256, RSA 2048, EC P384, RSA 4096, and EC P256. We can either manually switch keys or choose to automate the method.
2. Google Cloud IAM
Google presents an (IAM) identity and access management service that gives us granular access authority. We can practice IAM to define which groups or users can obtain access to cloud sources. We can allocate roles, involving predefined, primitive, and custom. Google’s IAM generates audit trails of permit authorizations and deletions automatically.
3. Google Cloud Identity
Google Cloud Identity lets us maintain the security of the cloud applications and projects. We can obtain assistance through the Google Admin Console. Also, we can utilize Cloud Identity to facilitate multi-factor authentication and individual sign-on authentication.
4. Stackdriver Logging
Google Stackdriver is an observing service created for hybrid clouds. It gives many capabilities, involving Stackdriver Logging, which is a contrived service that lets us maintain and investigate log data. Stackdriver Logging begins with its personal API and can ingest data from system logs. Further, we can practice Stackdriver logs for security observing and management purposes.
5. Google Access Transparency
Google Access Transparency lets us observe near-real-time log data, which designates why and when Google’s private IT staff obtained their circumstances. Typically, the IT staff obtains the environment when acknowledging to support applications or when attempting to heal from an outage. We can desegregate this assistance with Stackdriver Logging.
6. Google Cloud Security Scanner
Google Cloud Security Scanner assistance can identify vulnerabilities in (GKE) Google Kubernetes Engine, (GCE) Google Compute Engine, and (GAE) Google App Engine. Further, Cloud Security Scanner lets us design, schedule, operate and maintain scans by the GCP console. The scanner can identify many vulnerabilities, like cross-site scripting (XSS), Flash injection, and incorporated content, also outdated or vulnerable JavaScript (JS) libraries.
7. Google Cloud Resource Manager
The Google Resource Manager lets us maintain and organize the Google cloud sources. Furthermore, we can utilize the service to maintain access controls and IAM policies beyond various combinations of resources, which are classified as folders, organizations, or projects.
Let’s wrap it up!
Final Words
W
In conclusion, Google Cloud Platform provides a robust set of security features to help protect your applications and data. From identity and access management to network security and data encryption, GCP offers a comprehensive security approach that can help you protect against cyber threats. Additionally, GCP’s threat detection features can help you identify and respond to security incidents in real time, further enhancing your security posture. By understanding and leveraging these security features, you can better protect your GCP environment and ensure the safety and security of your data and applications. Remember that security is an ongoing process and requires constant vigilance, so it’s important to stay up-to-date on the latest security trends and best practices to ensure the continued safety of your GCP environment.
Understand the Google Professional Cloud Security Engineer (GCP) exam with Testpreptraing! Stay safe and keep practicing!