Now that you have made your decision to take the GMAT exam. Congratulations! Let’s get ready to showcase your most relevant skills, and show that you are serious about business school.
You must know beforehand that studying for the GMAT is a serious time commitment. In general, it requires two to three months or more for thorough preparation. So before you begin to prepare let us understand in depth about the exam and the strategies to prepare for the exam.
What is GMAT Exam?
The GMAT exam, also called the Graduate Management Admission Test, is a standardized test used by over 7,000 graduate management programs around the world, including about 2,300 business schools. This test is designed to help you assess and showcase your academic potential for succeeding in graduate-level management studies.
Brief Overview:
The exam has four-part used to measure your analytical writing, integrated reasoning, verbal, and quantitative reasoning. These are high order reasoning skills that management faculty worldwide have identified as important for candidates. Moreover these higher-order reasoning skills involving complex judgments, critical thinking, analysis, and problem-solving.
Specifically, GMAT scores offer a consistent, trusted, and dependable way to measure how well you perform academically in the fundamental subjects of a graduate management program. The GMAT exam’s credibility, impartiality, and significance in the admissions process have been firmly established through various academic research studies.
Why take the GMAT Exam?
It is very important to understand why taking the GMAT exam is important. Your score in GMAT exam helps you stand out in the admissions process to showcase your readiness to pursue graduate management education. Moreover, business schools use GMAT scores to select the most qualified applicants. Also, the candidates taking the GMAT should be serious about earning a graduate business degree. Also, it’s a proven predictor of a student’s ability to succeed in the program.
Overall, most business schools that use the GMAT exam usually provide score ranges or average scores for their student profiles. This information helps you understand how competitive your academic performance is for a specific program and how it matches up with other students’ scores. It’s crucial to reach out to the schools you’re interested in, regardless of your GMAT performance, and inquire about how they consider GMAT scores and other factors in their admissions process.
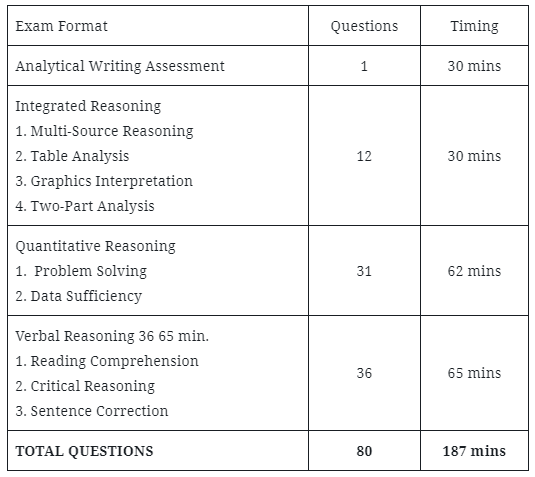
GMAT Exam Format
The test is divided into four parts, each with its own time limit.
- Firstly, there’s the Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA) section, where you’ll write one essay.
- Next, the Integrated Reasoning section has questions involving graphs and data, and you need to answer in various ways.
- Then, the Quantitative Reasoning part has multiple-choice questions related to math.
- Lastly, the Verbal Reasoning section has multiple-choice questions focusing on language skills.
The GMAT exam’s Verbal and Quantitative sections are computer adaptive. This means the test is created from a big pool of questions and adjusts to your skill level. When you answer a question, the computer scores it and uses your answers to choose the next question. You can’t skip or change past answers. If you’re unsure, try to eliminate wrong choices and pick the best one. Even though questions change, the types stay the same for all exams. Your score depends on question difficulty, correct answers, and the total questions you answer. This adaptable test measures skills well across different levels, from low to high ability.
What is the course outline?
The GMAT exam is designed to measure advanced analytical skills in various ways.
- In the first part, called Analytical Writing Assessment, you’ll need to analyze and write about the logic behind an argument.
- For the second part, called Integrated Reasoning, you’ll have to interpret and combine information from different sources to come up with logical conclusions.
- The third section, Quantitative Reasoning, involves using math skills like arithmetic, algebra, and geometry to solve problems.
- Lastly, in the Verbal section, you’ll read and understand written content. You’ll also need to evaluate arguments and make logical judgments.
GMAT Test-Taking Strategies
We will now discuss in length about each section covered in the GMAT Exam.

1. Analytical Writing Assessment
This is the first section related to Analytical Writing Assessment consists of one 30-minute writing task. The Analysis of an Argument measures your ability to think critically, communicate your ideas, and formulate an appropriate and constructive critique. You will be required to type your essay on a computer keyboard.
Test Strategies
- Firstly, read the question carefully and make sure you have taken all parts of a question into account before you start answering.
- Secondly, do not start immediately. You should take a few minutes to think about the question and then plan begin writing.
- Thirdly, take care to organize your ideas and make revisions to improve it.
- Next, you should focus on the task of analyzing and asking yourself questions.
- Also you should illustrate fully, if using any examples. Avoid using simply list your examples rather, explain how they illustrate your point.
- Lastly, you must make sure your response reads like a narrative.
Remember, your response should not read like an outline. It should use full sentences, together with logical transitions between points, together with appropriate examples and instances.
Scoring Process
- No Score 0 – When not written in English, is merely attempting t o copy the topic, or consists only of keystroke characters.
- Fundamentally Deficient 1 – When paper demonstrates fundamental deficiencies in analytical writing skills.
- Seriously Flawed 2 – When the essay shows significant problems with analytical writing abilities.
- Limited 3 – When the essay shows some level of skill in analytical writing and control over writing elements, but it has noticeable flaws.
- Adequate 4 – When the essay provides a capable evaluation of the argument and shows sufficient command over writing elements.
- Strong 5 – When paper presents a well-developed critique of the argument and demonstrates good control of the elements of effective writing.
- Outstanding 6 – When the paper offers a clear and skillfully expressed analysis of the argument, showcasing a thorough understanding of effective writing techniques.
2. Integrated Reasoning
We will now be discussing the test taking strategies for integrated reasoning under various section –
Multi-Source Reasoning Questions Test-Taking Strategies
- At first, you will not be expected to be completely familiar with the material presented in Multi-Source Reasoning sets. Therefore, answer all questions on the basis of given information by various sources.
- Secondly, analyze every source of information carefully, because the questions require a detailed understanding of the information presented.
- Thirdly, the text passages often build ideas sequentially, so as you read how each statement adds to the main idea of the passage as a whole.
- Fourthly, read the questions very carefully, and make sure you understand what is being asked.
- Lastly, select the answer choices that have the most support based on the information provided.
Table Analysis Questions Test-Taking Strategies
- Firstly, you should examine the given table and accompanying text to determine the type of information provided.
- Secondly, there will be question containing condition that each phrase, statement, numerical value, or algebraic expression does or does not meet given information. Therefore, understanding the condition will help you to clarify the choice to be made in each case.
- Thirdly, you should read each phrase, statement, numerical value, or algebraic expression carefully to determine the data analysis required. Therefore, careful reading can help you work more efficiently by using table sorts strategically to identify data of interest.
- Next, you must judge each phrase, or statement, numerical value, or algebraic expression carefully, based on the condition specified.
Two-Part Analysis Questions Test-Taking Strategies
- Firstly, read all the information given carefully. Moreover, do not let your knowledge influence your answer choices.
- Secondly, you should determine exactly what the question is asking.
- In particular, pay close attention to how the question describes the tasks.
3. Quantitative Reasoning
Problem Solving Test-Taking Strategies
- Make sure to check the on-screen timer from time to time. Work diligently, but don’t use too much time reviewing answers or thinking too much about challenging problems.
- When solving problems, take the time to work through them to avoid mistakes. If there are no diagrams or figures, you can draw your own to help.
- Always read each question carefully to understand what it’s asking for. For word problems, break down the information step by step and turn it into math equations or other helpful forms.
- Before answering a question, quickly look over the answer choices. This can prevent you from choosing an answer that’s not provided.
- If a problem seems too hard, don’t spend too much time on it. Make an educated guess and move on to the next question.
Data Sufficiency Test-Taking Strategies
- Do not waste valuable time solving a problem.
- Consider each statement separately.
- Judge the statements in tandem if neither statement is sufficient by itself.
- Answer the question asked.
- Be very careful not to make unwarranted assumptions based on the images represented.
4. Quantitative Reasoning
Reading Comprehension Test-Taking Strategies
- Don’t expect to know everything in the reading comprehension passages.
- Study each passage closely, as the questions need a specific and detailed understanding of the content.
- Pay attention to important words and phrases to stay on track with the passage’s main points.
- Be sure to read the questions thoroughly to understand what’s being asked.
- Carefully go through all the options for each question.
- Don’t assume you’ve found the best answer without checking all the choices.
- Pick the answer that best matches the information in the passage.
- Keep in mind that understanding, not speed, is the most important factor for reading comprehension questions.
Critical Reasoning Test-Taking Strategies
- Read very carefully the set of statements on which a question is based.
- Identify the conclusion.
- Determine exactly what each question asks.
- Read all the answer choices carefully.
- Do not assume that a given answer is the best without first reading all the choices.
Sentence Correction Test-Taking Strategies
- Carefully read the whole sentence and grasp the intended meaning.
- Check the part that’s underlined for mistakes and possible fixes before checking the options.
- Examine each answer choice with care.
- Figure out how to improve the part of the sentence you think is wrong.
- Thoroughly review both the sentence and the answer choices.
- Focus on clarity, grammar, word usage, and how well the words fit.
- Read the entire sentence again, replacing the underlined part with the choice you like.
Expert Corner
In reality, there isn’t a definite ‘pass’ or ‘fail’ for the GMAT exam, meaning there’s no set score to meet for success. However, a low GMAT score might make it challenging to get into your desired MBA program. To simplify, a GMAT passing score is one that boosts your chances of getting into an MBA program, while a failing score might limit your options. Keep in mind that different programs accept a range of GMAT scores based on how competitive they are. For instance, Stanford’s average accepted score is around 730, while Wake Forest School of Business accepts an average of 580. So, before focusing on how to pass the GMAT, it’s crucial to decide on a target score based on where you’re applying.
Tips to Pass GMAT Exam
- Learn the GMAT Format thoroughly: First and foremost, you should by heart learn every detail about the GMAT format. One way to do this is, is by taking computerized adaptive GMAT practice tests.
- Practice Real GMAT Questions: One of the best way to measure your progress as you prepare for the GMAT is to practice with real time GMAT Exam Questions.
- Work on your basic Skills: The primary aim of GMAT exam is to examine your fundamental skills in quantitative reasoning and logical reasoning , as well as reading comprehension. Focus on addressing any gaps in your knowledge of the basics that will help you succeed on the exam.
- Focus on your weaknesses: Focus on identifying your error patterns, as it will give you the biggest improvement in terms of your score. Therefore, if you avoid repeating the same mistakes, you can break easily breakthrough and make it to the list.
- Improve your Timing: Keep a track of how long each question should take you in each section of the GMAT. You should improve your timing through drills. It is also very important to customize practice questions designed to improve your accuracy.
- Prevent from making silly mistakes: Often careless mistakes occur due to missing important details or failing to read the complete question . It has been seen that students try to glide over the question and directly skip to the answer choices leading to making mistakes.
“Don’t practice until you get it right. Practice until you can’t get it wrong.”
Enhance your preparation with real time practice tests and official guides. Pass GMAT Exam Now!
Try thousands of GMAT Free Practice Test with detailed explanation Today!

