The Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam is a certification exam that validates an individual’s ability to build custom business applications using the Microsoft Power Platform. With the growing demand for custom application development in organizations, this certification has become a popular choice for professionals seeking to advance their careers in the field of app development.
Many individuals may wonder just how hard the Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam is. The exam covers a wide range of topics, including creating and managing data models, designing user interfaces, automating business processes, and more. As such, it requires a comprehensive understanding of the Microsoft Power Platform and a mastery of the skills needed to develop custom business applications.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam, exploring its format, content, and difficulty level. We will also provide tips and resources to help you prepare for the exam and increase your chances of success. Whether you are a seasoned app developer or new to the field, this blog post will give you a clear understanding of what to expect from the Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam.
Glossary for Microsoft Power Platform App Maker Terminology
- Power Platform: A collection of Microsoft products and services that allows users to analyze data, automate workflows, and create custom business applications.
- Power Apps: A service that allows users to create custom business applications without writing code.
- Power Apps Studio: The visual interface used to create, customize and publish Power Apps.
- Canvas App: A type of Power App that allows users to design and customize the layout and user interface.
- Model-Driven App: A type of Power App that provides a standardized data model and UI for users to work with.
- Power Automate: A service that allows users to automate workflows and tasks across multiple applications and services.
- Connectors: Pre-built interfaces that allow Power Apps and Power Automate to integrate with other applications and services.
- Common Data Service (CDS): A cloud-based data storage service that provides a standard data schema for Power Apps and other Microsoft services.
- Environment: A container for a set of resources used to build and deploy Power Apps and other Microsoft services.
- Solution: A packaged set of components that can be deployed to multiple environments.
- Power BI: A data analysis and visualization service that allows users to connect to various data sources, and create interactive reports and dashboards.
- Power Virtual Agents: A chatbot service that allows users to create and deploy intelligent chatbots without writing code.
- Microsoft Dataverse: A low-code data platform that allows users to create and manage data entities, fields, relationships, and business logic.
- Dataverse for Teams: A simplified version of Microsoft Dataverse that comes built-in with Microsoft Teams.
Exam preparation resources for Microsoft Power Platform App Maker (PL-100) exam
Here are some official exam preparation resources for the Microsoft Power Platform App Maker (PL-100) exam:
- Microsoft’s official PL-100 Exam page: This page provides an overview of the exam, including its objectives, format, and requirements. It also offers links to official Microsoft training courses and certification paths.
Link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/exams/pl-100
- Microsoft’s official exam skills outline: This document outlines the skills that are measured on the PL-100 exam, broken down by objective. It can help you understand what topics you need to focus on as you prepare for the exam.
Link: https://query.prod.cms.rt.microsoft.com/cms/api/am/binary/RWtfcJ
- Microsoft’s official learning paths: These paths provide structured learning journeys that cover the skills and knowledge needed to pass the PL-100 exam. They include a mix of interactive online modules, videos, and hands-on labs.
Link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/pl-100
- Microsoft’s official exam practice test: This practice test is designed to give you a sense of what to expect on the PL-100 exam. It includes sample questions that are similar to the ones you’ll see on the actual exam, along with detailed explanations of the correct answers.
Link: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/learning/pl-100-exam.aspx
- Microsoft’s official community forums: These forums provide a space for PL-100 exam candidates to ask questions, share resources, and connect with other professionals who are also preparing for the exam.
Link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/topics/power-platform-app-maker-pl-100.html
About Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam
For the Microsoft PL-100 exam, you must design solutions for simplifying and automating tasks and processes for yourself and your team. It is necessary for you to understand the data you have to deal with, the difficulties you must tackle, and the procedures and app experiences that are required. Also, working knowledge of how to solve business difficulties. Further, you must also be self-motivated and solution-oriented for connecting to and using features of programs such as Microsoft Teams, Microsoft 365 apps and services, and third-party solutions. You must be motivated to learn about the capabilities and limits of various tools, as well as how to use them. Passing this exam can help you get job roles like:
- Business Analyst
- Data Analyst
- Business Owner
- Business User
- Developer
- DevOps Engineer
- App Maker
- Technology Manager
Exam Format
There are 40-60 questions in the Microsoft PL-100 Exam. Questions on the exam might be scenario-based single-answer questions, multiple-choice questions, arrange in the right sequence type questions, drag & drop questions, and mark review, drag, and drop type questions. You must, however, get a score of 700 or better in order to pass the exam. In addition, the Microsoft PL-100 Exam costs $165 USD and is offered in both English and Japanese.
Is the Microsoft PL-100 exam difficult?
Talking about the Microsoft PL-100 exam, this exam is for you if you’re a business professional with a deep understanding of your solution area and wants to put your passion for putting Microsoft Power Platform solutions to work for your team to simplify, automate, and transform tasks and processes. However, you’ll need to know how to do things like data modelling, basic UX design, requirements analysis, and process analysis as a technical business analyst. No, the exam is not difficult if you have the right preparation resources and learning guide. Focus your preparation on key learning areas
Covering the knowledge area:
- This exam requires you to be self-directed and solution-focused with skills to work with the maker tools of Microsoft Power Platform for solving business problems.
- Secondly, it is necessary to have experience with Visual Basic for Applications, Excel PivotTables, Teams, and other tools. And, you must be comfortable working with IT administrators and Microsoft Power Platform developers using technology.
- Lastly, the role of app maker comes with responsibilities such as:
- Creating and designing apps, as well as automating operations.
- Using an app or an automated procedure to analyze and visualize data.
- Applying and managing apps and automated workflows.
In order to help you cover the above knowledge area and in getting advanced with the concepts below, we will talk about the exam study guide by learning the various study methods and ways!
Study Guide for Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam
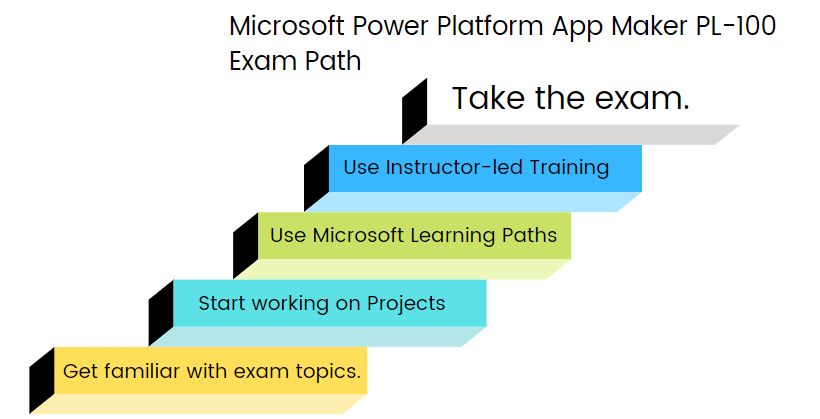
1. Exploring the exam topics
The Microsoft PL-100 test assesses your knowledge and skills in the areas listed below
– Design business solutions (35–40%)
Identify Microsoft Power Platform components
- Determine the required Microsoft Power Apps app type for a business scenario (Microsoft Documentation: Solutions overview)
- Determine which Microsoft Power Platform components meet a given business scenario
- Describe business logic in Microsoft Dataverse
- Describe connectors (Microsoft Documentation: Connectors overview)
- Describing use cases for cloud flows and desktop flows (Microsoft Documentation: Overview of the different types of flows)
- Describe use cases for AI and Microsoft Copilot in Microsoft Power Platform
- Describe Microsoft Power Platform environments
- Describe use cases for Power Automate Process Mining
- Determine reporting options for given business scenarios including views, Microsoft Power BI visualizations, and dashboards
Configure and manage Microsoft Dataverse
- Create tables and table columns based on a data model
- Link tables by using lookups
- Configure Dataverse business rules
- Describe how Dataverse uses role-based access control (RBAC)
- Add table permissions to existing Dataverse security roles
- Create tables and table columns by using Copilot in Dataverse
- Import and export data by using Microsoft Excel
- Determine when to use Microsoft Dataverse for Teams or Microsoft Dataverse
Manage Microsoft Power Platform components during development
- Create a Dataverse solution
- Export and import a Dataverse solution
- Export and import a non-solution canvas app or a non-solution cloud flow
- Add existing components to a Dataverse solution
– Analyze and visualize data (10–15%)
Create and consume Microsoft Power BI dashboards
- Create a simple report from an existing dataset by using Power BI Service (Microsoft Documentation: Create quick reports in the Power BI service)
- Creating Power BI dashboards from existing reports (Microsoft Documentation: Create a Power BI dashboard from a report)
- Embed Power BI dashboards and tiles in canvas apps and model-driven apps (Microsoft Documentation: Embed a Power BI report in a model-driven app main form)
- Share Power BI dashboards (Microsoft Documentation: Share Power BI reports and dashboards with coworkers and others)
Describe AI Builder models
- Describe use cases for AI Builder (Microsoft Documentation: AI models and business scenarios)
- Describing the differences between prebuilt models and custom models (Microsoft Documentation: Overview of prebuilt AI models)
- Describe the process for training custom models
- Use a model from within Microsoft Power Automate or Microsoft Power Apps (Microsoft Documentation: AI Builder in Power Apps overview)
– Create business solutions (50–55%)
Create and manage model-driven apps
- Create and configure model-driven apps (Microsoft Documentation: What are model-driven apps in Power Apps?)
- Create and configure Dataverse table forms (Microsoft Documentation: Create and design model-driven app forms)
- Create and configure Dataverse table views
- Share model-driven apps with other users and groups (Microsoft Documentation: Share a model-driven app using Power Apps)
- Create and configure model-driven dashboards
- Create and configure model-driven app charts
Create and manage canvas apps
- Connect to data sources in canvas apps (Microsoft Documentation: Understand data sources for canvas apps)
- Interpret App Checker results (Microsoft Documentation: Use solution checker to validate your model-driven apps in Power Apps)
- Manage versions of canvas apps (Microsoft Documentation: Restore a canvas app to a previous version)
- Publish canvas apps (Microsoft Documentation: Save and publish canvas apps)
- Share canvas apps with other users and groups (Microsoft Documentation: Share a canvas app with your organization, Share a canvas app with guest users)
- Add canvas app assets and components to screens (Microsoft Documentation: Canvas component overview)
- Describe modern controls and themes
Create and manage screens for canvas apps
- Determine when to use screens, forms, containers, galleries, buttons, labels, input controls, images, charts, and custom controls (Microsoft Documentation: Gallery control in Power Apps, Controls and properties in canvas apps)
- Configure UI elements (Microsoft Documentation: Automate using UI elements)
- Implement Power Fx formulas (Microsoft Documentation: Microsoft Power Fx overview, Power Fx formula reference for Power Apps)
- Implement collections and variables
- Run a Microsoft Power Automate cloud flow from a canvas app
Create Power Automate cloud flows
- Describe types of triggers (Microsoft Documentation: Get started with triggers)
- Configure triggers (Microsoft Documentation: Trigger a cloud flow based on email properties)
- Configure flow steps
- Test and troubleshoot a cloud flow
- Implement conditional logic
- Create approvals and monitor the approval process by using Power Automate and Microsoft Teams (Microsoft Documentation: Approvals in Microsoft Teams)
- Share cloud flows (Microsoft Documentation: Share a cloud flow)
2. Start working on projects
For Microsoft Power Platform App Maker PL-100 Exam, you have to be motivated enough to learn about the capabilities and limits of various tools, as well as how to use them. And, to obtain this, start volunteering on a project for getting real-life experience with data modeling, basic UX design, requirements analysis, or process analysis. This will not only help you enhance your knowledge level but also help you get practical experience for how things actually work.
3. Start using the Microsoft Learning Paths
Microsoft’s learning path offers you access to exam-related knowledge using various modules. The official exam website has these study resources for the Microsoft PL-100 exam. The learning paths for this exam include:
• Creating a canvas app in Power Apps
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/create-powerapps/
This path gives a basic overview of Power Apps, then guides the process of creating and customizing an app, as well as managing and distributing it.
Prerequisites:
- Knowledge of OneDrive, SharePoint, and Excel.
• Creating a model-driven application in Power Apps
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/create-app-models-business-processes/
This learning path will show you how to utilize Dataverse to create a model-driven app in Power Apps.
Prerequisites:
- Familiarity with Power Apps, Excel, and Power Automate.
• Automating a business process using Power Automate
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/automate-process-power-automate/
This course introduces you to Power Automate and shows you how to create processes and manage flows.
Prerequisites:
- Familiarity with SharePoint, OneDrive, and Excel.
• Managing permissions and administration for Dataverse
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/manage-permissions-administration-common-data-service/
You will learn how to handle permissions associated with environments and entities in this learning path. Moreover, you’ll also learn how to use various administrative portals and how to get to them.
• Get started using Dataverse
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/get-started-cds/
This learning path will teach the fundamentals underlying Dataverse as well as its benefits. Further, in this, there’s also a discussion on setting up an environment, entities, fields, and options sets.
• Master advanced formula techniques and custom updates
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/understand-advanced-topics/
This course will teach you how to use complex formulas and make custom changes.
Prerequisites:
It is suggested to have knowledge of the learning path such as:
- Working with data in a Power Apps canvas app
- Using the UI and controls in a canvas app in Power Apps
• Using best practices for securing and governing Microsoft Power Platform environments
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/best-practices-environments/
Discover best practices for securing and controlling Microsoft Power Platform settings by following this learning path. However, in this, you will learn how to utilize tools and templates to stay productive while securing and managing the Microsoft Power Platform.
Prerequisites:
- Firstly, a basic understanding of Microsoft Power Automate and Power Apps including their purpose and the process of using these tools within an organization.
- Secondly, a Microsoft Power Platform license with administrative rights.
• Building and using analytics reports with Power BI
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/create-use-analytics-reports-power-bi/
This learning path will show you how to utilize and create business intelligence reports using Power BI.
Prerequisites:
- Firstly, familiarity with Excel
- Secondly, access to the Power BI service
- Lastly, Power BI Desktop
• Bringing AI to your business with AI Builder
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/bring-ai/
This learning path takes you through AI Builder, teaches you how to create models, and shows you how to utilize them in Power Apps and Power Automate.
Prerequisites:
- Firstly, you must be signed up for Power Apps or Power Automate
- Secondly, you must have access to Microsoft Dataverse
• Using the UI and controls in a canvas app in Power Apps
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/ui-controls-canvas-app-powerapps/
This learning path will concentrate on how to deliver the greatest app navigation and create the best user interface utilizing themes, icons, graphics, personalization, multiple form factors, and controls.
Prerequisites:
- Firstly, a basic understanding of creating a Power Apps canvas app
- Secondly, recommended having experience of working with controls in Power Apps
• Building a business process flow in Power Automate
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/create-business-process-flow/
This learning path will show you how to use Power Automate to create business process flows.
Prerequisites:
- A basic understanding of Microsoft Power Automate.
4. Get yourself prepared with the Instructor-led Training Course
Microsoft Power Platform App Maker
This course will show you how to use Microsoft Power Platform to create apps utilizing low-code strategies to simplify, automate, and change corporate operations and processes.
Skills of an App Maker for this course:
- The App Maker has the skills for creating solutions for simplifying, automating, and converting tasks and processes for themselves and their team with advanced knowledge in the solution business domain.
- Secondly, they know how to model data, develop user experiences, analyze requirements, and analyze processes.
- Thirdly, the App Maker builds and enforces business procedures, organizes digital data collecting, enhances repetitive job efficiency, and automates business operations.
- Then, to solve business difficulties, the App Maker employs Power Platform’s Maker tools. They may use Microsoft programs’ advanced features as well as third-party productivity solutions.
- The App Maker is knowledgeable about the capabilities and limits of various tools, as well as how to use them. Moreover, they are self-directed, solution-oriented professionals.
- Lastly, they are knowledgeable of the operational requirement and have a clear picture of the intended output. They use phased and iterative methodologies to solve challenges.
5. Using Practice Tests
It’s important to remember that the test will cover a wide range of topics. As a result, you should get as much experience as possible before taking the test. The most efficient way to do so is to use exam practice tests. By taking the Microsoft PL-100 Exam, you will be able to better understand your study plan and prepare for the real thing. You may also identify your weak points and attempt to strengthen them. You’ll also be able to comprehend the question pattern and enhance your answering abilities, allowing you to manage your time throughout the test.
Things to know about the exam:
➼ Exam retake policy
- Candidates who fail the test for the first time must wait 24 hours before retaking it, according to this guideline. They can reschedule the exam on the certification dashboard during this period. However, if this happens a second time, they have to wait at least 14 days before taking the exam again. Between the third and fourth try, as well as the fourth and fifth attempts, a 14-day waiting period is necessary. Candidates, on the other hand, can take the exam five times each year. Furthermore, the 12-month term begins when the first attempt is made.
➼ Exam reschedule and the cancellation policy
- If applicants cancel their examinations within 24 hours of the planned appointment, Microsoft will temporarily waive the rescheduling and cancellation fees. If you postpone or cancel an appointment at least 6 working days in advance, there will be no charge. However, a fee will charge if a candidate cancels or reschedules a test within 5 business days of the scheduled exam time. Lastly, if a candidate fails to show up for an exam session or fails to reschedule within 24 hours, the exam money forfeit on its whole.
Final Words
The Microsoft PL-100 Exam is a great way to demonstrate your abilities. This exam will put your collaboration skills, knowledge, and abilities to the test. As a result, in order to improve your preparation, you must concentrate on all of the essential areas. Give it your all and work your hardest to pass the exams. To study step-by-step, create a study plan, understand test patterns, and pass the exam utilizing the information supplied above.



