The Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam is a special test that checks what professionals know and can do with Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This test is for architects, designers, and other experts who make plans and take care of cloud solutions on GCP.
Still, getting through this test isn’t simple. It needs lots of getting ready and hard work. Because more and more businesses want to move their computer stuff to the cloud, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is really liked. This means there are a lot more jobs for people who are certified in Google Cloud.
This blog is all about how tough the Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam is, what stuff it tests you on, and tricks to get ready for and pass it. Whether you know a lot about clouds or you’re just beginning to learn, this blog will give you useful advice and tips to help you do well on your certification test.
Glossary for Google Professional Cloud Architect Terminology
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – a suite of cloud computing services provided by Google that runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products, such as Google Search and YouTube.
- Cloud Computing – Getting computer things whenever you want them from the internet, like servers, storage, apps, and services.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) – a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider offers virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) – In this type of cloud computer resource, the company that runs the cloud gives a setup where makers can create and launch apps. They don’t need to worry about the basic computer stuff underneath.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) – a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider offers software applications over the internet, which are typically accessed through a web browser or a mobile app.
- Virtual Machine (VM) – A pretend computer that works just like a real one, living inside a regular computer and doing the same jobs.
- Compute Engine – Google Cloud Platform has a feature that lets people use virtual computers on Google’s setup.
- App Engine – Google Cloud Platform gives a tool where developers can create and put out web apps and mobile backends. They can use languages like Java, Python, and Go that a lot of people like.
- Kubernetes – A free tool for making sure lots of small software packages work together well. It sets them up, makes them bigger or smaller as needed, and looks after how they run.
- Load Balancer – a tool or software that spreads out internet traffic across many computers to make sure none of them get too busy. This helps applications work well and be available.
- Cloud Storage – a feature from Google Cloud Platform where you can keep your data on the internet and get it back when you need it.
- BigQuery – a computer system in the cloud from Google Cloud Platform that holds a lot of information and lets you ask it questions using special words.
- Cloud SQL – a service from Google Cloud Platform where you can make and handle databases on the internet.
- Cloud Spanner – a special kind of database from Google Cloud Platform that can grow really big and is available all around the world. It’s good at keeping data consistent and safe.
- Cloud Dataflow – a tool from Google Cloud Platform that helps you make and run paths for data in the cloud, using something called Apache Beam.
- Cloud Pub/Sub – a feature from Google Cloud Platform that helps different apps talk to each other in real-time by sending and getting messages.
- Cloud IAM – a tool from Google Cloud Platform that lets you control who can use what in the Google Cloud.
- Cloud Security – a bunch of tools from Google Cloud Platform that keep things safe from cyber problems and people who shouldn’t have access.
Exam preparation resources for the Google Professional Cloud Architect exam
Google Cloud offers various resources for preparing for the Professional Cloud Architect certification exam, including study guides, documentation, videos, and practice exams. Here are some of the official resources:
- Professional Cloud Architect Certification Exam Guide: This exam guide provides an overview of the exam format, recommended experience, and the topics that will be covered. You can find it here: https://cloud.google.com/certification/cloud-architect
- Google Cloud documentation: The documentation provides in-depth information on all Google Cloud products and services. You can find it here: https://cloud.google.com/docs
- Coursera courses: Google Cloud has partnered with Coursera to provide online courses that cover topics related to the certification exam. You can find them here: https://www.coursera.org/googlecloud
- Practice Exam: Google offers a practice exam that simulates the actual exam environment. You can find it here: https://cloud.google.com/certification/practice-exam/cloud-architect
- Exam Readiness: This is a self-paced online course that covers key exam concepts and includes sample questions. You can find it here: https://cloud.google.com/training/courses/Cloud-Architect-Exam-Prep
- Google Cloud YouTube channel: The Google Cloud YouTube channel features videos on various topics related to Google Cloud services. You can find it here: https://www.youtube.com/user/googlecloudplatform
Google Certified Professional – Cloud Architect: Overview
Before we move on to exam structure and format, it becomes important to understand what the exam actually is. Therefore, here is an overview of the Google Cloud Architect certification
A Professional Cloud Architect exam enables organizations to leverage Google Cloud technologies. With an in-depth understanding of cloud architecture and Google Cloud Platform, a professional can design, develop and manage robust, secure, scalable, highly available, and dynamic solutions to drive business objectives.
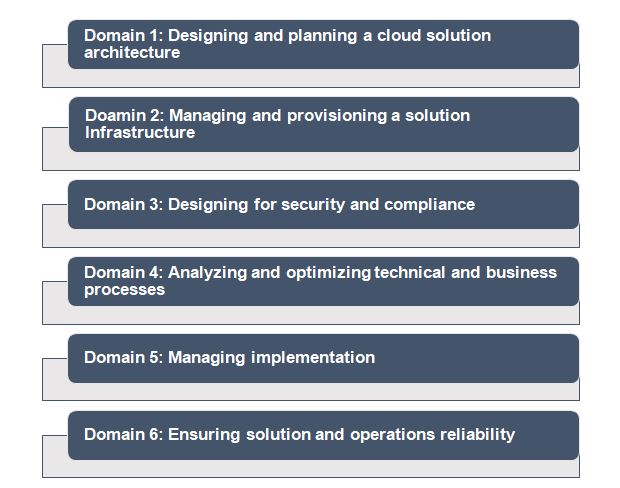
The Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect exam assesses your ability to the following areas:
- Design and plan a cloud solution architecture
- Manage and provision the cloud solution infrastructure
- Design for security and compliance
- Analyze and optimize technical and business processes
- Manage implementations of cloud architecture
- Ensure solution and operations reliability
Basic Details
Once you get a quick overview of the exam, it‘s time to give attention to the exam details. Details play a crucial role, be it exam details or any other details. Even if you know the details, make sure you give them a look as they may change with change in time.
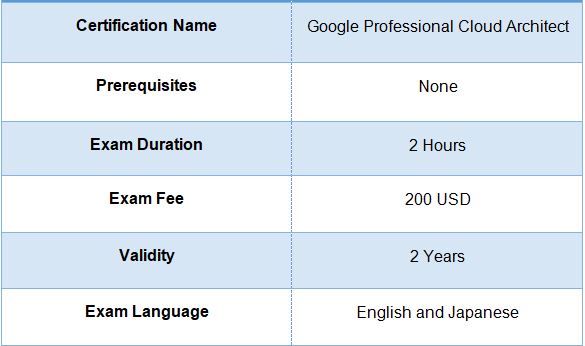
The test to become a Professional Cloud Architect has 40 questions you pick from multiple answers. You have 2 hours to finish. If you pass, the certificate is good for 2 years. There’s no exact score needed to pass. You can take the test in English or Japanese. It costs $200 USD to become a Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect.
Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect Requirements
Google Cloud Architect certification exam is not restricted to any particular role, yet it is considered that it is mainly intended for –
- Firstly, Solutions/ Enterprise Architects
- Secondly, Members of the Operations Team
- After that, System Administrators
- Moreover, Fresh Graduates who want to build a career in Cloud Architect
Course Outline
To start the exam preparation, it is highly important to make yourself familiar with the exam objectives. Google has divided the course outline into various sections and then subtopics. Let’s understand the topics covered in the Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect Certification Course so you focus your time upon them to pass the exam.
Domain 1: Designing and planning a cloud solution architecture
1.1 Designing a solution infrastructure that meets business requirements. Considerations include:
- Business use cases and product strategy (Google Documentation: Best practices for enterprise organizations, Implementing policies for customer use cases)
- Cost optimization (Google Documentation: Performance and cost optimization)
- Supporting the application design (Google Documentation: Google Cloud system design considerations)
- Integration with external systems (Google Documentation: Using APIs from an External Network, Security, privacy, and compliance)
- Movement of data (Google Documentation: Data lifecycle)
- Design decision trade-offs (Google Documentation: Google Cloud system design considerations)
- Build, buy, or modify
- Success measurements (e.g., key performance indicators [KPI], return on investment [ROI], metrics) (Google Documentation: KPIs for APIs: How Metrics Change Over Time)
- Compliance and observability (Google Documentation: Security, privacy, and compliance)
1.2 Designing a solution infrastructure that meets technical requirements. Considerations include:
- High availability and failover design (Google Documentation: Overview of the high availability configuration)
- The elasticity of cloud resources (Google Documentation: Google Cloud overview)
- Scalability to meet growth requirements (Google Documentation: Reliability, Security, privacy, and compliance)
- Performance and latency (Google Documentation: Performance and cost optimization)
1.3 Designing network, storage, and compute resources. Considerations include:
- Integration with on-premises/multi-cloud environments (Google Documentation: Hybrid and multi-cloud architecture patterns)
- Cloud-native networking (VPC, peering, firewalls, container networking) (Google Documentation: VPC network overview)
- Choosing data processing technologies (Google Documentation: Data processing, Dataflow, Dataproc)
- Choosing appropriate storage types (e.g., object, file, RDBMS, NoSQL, NewSQL) (Google Documentation: Google Cloud Databases)
- Choosing to compute resources (e.g., preemptible, custom machine type, specialized workload) (Google Documentation: Compute, Creating a VM Instance with a custom machine type)
- Mapping compute needs to platform products (Google Documentation: Google Cloud products)
1.4 Creating a migration plan (i.e., documents and architectural diagrams). Considerations include:
- Integrating solution with existing systems (Google Documentation: Migration to Google Cloud: Getting started)
- Migrating systems and data to support the solution
- Licensing mapping (Google Documentation: Bringing your own licenses)
- Network planning (Google Documentation: Best practices and reference architectures for VPC design, VPC network overview))
- Testing and proof of concept (Google Documentation: Running a hybrid render farm proof of concept)
- Dependency management planning (Google Documentation: Specifying Dependencies)
1.5 Envisioning future solution improvements. Considerations include:
- Cloud and technology improvements (Google Documentation: Google Cloud Improvements)
- Business needs evolution (Google Documentation: Best practices for enterprise organizations, Google Cloud Improvements)
- Evangelism and advocacy (Google Documentation: API Team Best Practices: Developers, Evangelists, and Champions)
Domain 2: Managing and provisioning a solution Infrastructure
2.1 Configuring network topologies. Considerations include:
- Extending to on-premises (hybrid networking) (Google Documentation: Extending On-Premises Network-Attached Storage to Cloud Storage with Komprise, Google Cloud Hybrid Connectivity)
- Extending to a multicloud environment that may include Google Cloud to Google Cloud communication (Google Documentation: Hybrid and multi-cloud architecture patterns)
- Security protection (e.g. intrusion protection, access control, firewalls)
2.2 Configuring individual storage systems. Considerations include:
- Data storage allocation (Google Documentation: Best practices for Cloud Storage)
- Data processing/compute provisioning (Google Documentation: Provisioning VMs on sole-tenant nodes, Data processing, Dataflow, Dataproc)
- Security and access management (Google Documentation: Identity and Access Management)
- Network configuration for data transfer and latency (Google Documentation: GCP network performance, Performance, and cost optimization)
- Data retention and data life cycle management (Google Documentation: Data lifecycle, Retention policies and retention policy locks)
- Data growth management (Google Documentation: Data lifecycle, Cloud storage growth)
2.3 Configuring compute systems. Considerations include:
- Compute system provisioning (Google Documentation: Provisioning VMs on sole-tenant nodes, Compute Engine)
- Compute volatility configuration (preemptible vs. standard) (Google Documentation: Preemptible VM instances, Creating and starting a preemptible VM instance)
- Network configuration for compute resources (Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, serverless networking)
- Infrastructure orchestration, resource configuration, and patch management
- Container orchestration
Domain 3: Designing for security and compliance
3.1 Designing for security. Considerations include:
- Identity and access management (IAM) (Google Documentation: Identity and Access Management)
- Resource hierarchy (organizations, folders, projects) (Google Documentation: Resource hierarchy, Using resource hierarchy for access control)
- Data security (key management, encryption) (Google Documentation: Encryption at rest in Google Cloud)
- Separation of duties (SoD) (Google Documentation: Separation of duties)
- Security controls (e.g., auditing, VPC Service Controls, organization policy) (Google Documentation: Overview of VPC Service Controls)
- Managing customer-managed encryption keys with Cloud KMS (Google Documentation: Customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK))
- Remote access
3.2 Designing for compliance. Considerations include:
- Legislation (e.g., health record privacy, children’s privacy, data privacy, and ownership) (Google Documentation: Compliance resource center)
- Commercial (e.g., sensitive data such as credit card information handling, personally identifiable information [PII]) (Google Documentation: Scan for sensitive data in just a few clicks, Take charge of your sensitive data with the Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) API)
- Industry certifications (e.g., SOC 2) (Google Documentation: SOC 2)
- Audits (including logs) (Google Documentation: Cloud Audit Logs)
Domain 4: Analyzing and optimizing technology and business processes
4.1 Analyzing and defining technical processes. Considerations include:
- Software development life cycle plan (SDLC)
- Continuous integration / continuous deployment (Google Documentation: Setting up a CI/CD pipeline)
- Troubleshooting / root cause analysis best practices
- Testing and validation of software and infrastructure (Google Documentation: Validate Your Data, Testing Overview)
- Service catalogue and provisioning (Google Documentation: Provisioning Overview)
- Business continuity and disaster recovery (Google Documentation: Disaster recovery planning guide, Solving for business continuity)
4.2 Analyzing and defining business processes. Considerations include:
- Stakeholder management (e.g. influencing and facilitation)
- Change management (Google Documentation: Opening doors, embracing change with cloud data warehouses)
- Team assessment/skills readiness (Google Documentation: Migration to Google Cloud: Assessing and discovering your workloads)
- Decision-making process
- Customer success management
- Cost optimization / resource optimization (Capex / Opex) (Google Documentation: Cloud cost optimization, Cost Management)
4.3 Developing procedures to ensure reliability of solutions in production (e.g., chaos engineering, penetration testing) (Google Documentation: Patterns for scalable and resilient apps)
Domain 5: Managing implementation
5.1 Advising development/operation team(s) to ensure successful deployment of the solution. Considerations include:
- Application development (Google Documentation: Application modernization, Application Development)
- API best practices (Google Documentation: API Key Best Practices)
- Testing frameworks (load/unit/integration) (Google Documentation: Testing Overview, test – Run gsutil unit/integration tests (for developers))
- Data and system migration tooling (Google Documentation: Data center migration)
5.2 Interacting with Google Cloud programmatically. Considerations include:
- Google Cloud Shell
- Google Cloud SDK (gcloud, gsutil and bq)
- Cloud Emulators (e.g. Cloud Bigtable, Datastore, Spanner, Pub/Sub, Firestore)
Domain 6: Ensuring solution and operations reliability
6.1 Monitoring/logging/profiling/alerting solution (Google Documentation: Introduction to alerting, Alerting behavior)
6.2 Deployment and release management (Google Documentation: Google Cloud Deployment Manager)
6.3 Assisting with the support of solutions in operation (Google Documentation: Cloud Monitoring, Operations)
6.4 Evaluating quality control measures (Google Documentation: Google security whitepaper)
What makes Google Professional Cloud Architect difficult?
The Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam is widely considered to be a challenging exam, with a difficulty level that is on par with other top cloud certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert, and the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) exam.
Several factors contribute to the difficulty level of the exam, including:
- Broad range of topics: The exam covers a wide range of topics related to GCP, including infrastructure, data storage and processing, networking, security, and more. This requires candidates to have a strong understanding of all these areas, making the exam more challenging.
- Scenario-based questions: In the test, there are questions about situations where you have to use what you know in real life. This can be hard because you need to really understand the ideas and use them in a real way.
- High passing score: The passing score for the exam is 70%, which is relatively high compared to other cloud certifications.
Despite the difficulty level, the exam is highly respected and recognized in the industry, and obtaining the certification can be a valuable asset for professionals in the cloud architecture field.
When compared to other cloud certifications, the Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam is generally considered to be on par with other top cloud certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect and Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert.
However, it is important to note that the difficulty level of any exam can vary depending on individual factors such as experience, study habits, and learning style. Ultimately, the difficulty level of an exam should not deter individuals from pursuing a certification that is relevant to their career goals and aspirations.
Learning Resources
Knowing the dynamic nature of the Google Cloud Architect Certification Exam, it is important to have an equally dynamic strategy for Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect Preparation. That is to say, combining various online and offline learning techniques to get a proper grasp of the subject matters equally. Consider yourself lucky as Google understands your need and has prepared various avenues that you can use for your exam preparation. Some of them are listed here in our Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect Study Guide
Learning Resource 1: Google Exam Guide
The Google exam guide is where you should start. We really recommend it. It’s not just about explaining the course but also has stories about pretend businesses and solutions. These stories give more info to help you pick the right answers. This will really help you get ready for the Google Cloud Architect test. So, before you look at anything else, be sure to read this guide.
Learning Resource 2: Google Cloud Platform Documentation
This is the second most important thing that you must study, right after the exam guide. It will help you understand all the aspects of the Google Cloud Platform from a developer’s perspective. It refers to comprehensive yet precise documentation, guides, and resources for Google Cloud Platform products and services. Moreover, it can act as a tool which helps you decide which real-world application you would want to work with based on GCP, once your certification is done.
Learning Resource 3: Google Cloud Solutions Reference Guide
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is like a collection of computer services in the cloud. It helps you fix hard problems in your business and try out new things with Google Cloud. The guide is like a simple book that tells you everything you can do with Google Cloud Platform. What’s interesting is that it also tells you about different companies that work with Google Cloud. When you’re done reading, you’ll know about all the important and not-so-important companies in the field.
Learning Resource 4: Google Cloud Platform Blog
Change in cloud results to change in policies that govern it. With the advent of new technologies and ever-changing political policies, it is quite difficult to keep up with the latest developments in the field. However, this hurdle can be crossed if you have a dedicated source of information that can be trusted. The Cloud Platform blog by Google is the right place for you. In addition, by going through this blog on a regular basis, you will keep on getting the latest information whenever you decide to attempt the exam.
Learning Resource 5: Practice Tests or Mock Tests
Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect Practice Tests Practice Tests or Mock tests are somewhat similar to final exams where the paper pattern is similar and so is the marking scheme, used to gauge actual potential and iron out your weaknesses. In other words, the main aim of the practice tests or mock tests is to identify your strong and weak areas. Solving these tests give you an idea about the final exam. It helps you to analyze yourself and identify where you stand. Moreover, it gives you a score at the end to know your results. Get unlimited access to official practice tests here!
Best practices for studying for the exam:
Here are some best practices to follow when studying for the Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam:
- Make a plan: Make a plan that covers all the things you need to learn and sets time for reading, practicing, and looking back at what you learned.
- Gain practical experience: Get experience by using GCP and making solutions for real problems.
- Use flashcards: Make flashcards to remember important ideas, words, and short forms.
- Study with others: Join groups or online places to talk about what you’re studying, share tips, and work together with other people.
- Rest a bit: Take breaks so you don’t get too tired, and you can stay focused and excited when you study.
- Manage time: Learn how to use your time during the test. Do the easy questions first, so you can get more points.
Expert’s Corner
In conclusion, the Google Professional Cloud Architect Exam is widely recognized as a challenging certification exam for professionals working with Google Cloud Platform. The broad range of topics covered, scenario-based questions, and high passing score all contribute to the exam’s difficulty level.
Even though it might be hard, getting the certification is like a special thing for people who work with cloud buildings. It shows you really know about GCP and can make plans and take care of cloud stuff in real situations.
With adequate preparation, including studying the recommended resources and best practices for exam preparation, professionals can increase their chances of passing the exam and obtaining the certification. Ultimately, the difficulty level of the exam should not deter individuals from pursuing this certification if it aligns with their career goals and aspirations.
Wishing you luck with your Google certification!
Stand out from the crowd with advanced learning skills and expert tutorials on Google Professional Cloud Architect. Prepare and become Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Architect Now!



