HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) Cheat Sheet is designed to provide you with a sequential way to have a strong revision. We all know that HCISPP certifications most suitable certification for getting the core understanding and experience required to implement, maintain the relevant security and privacy controls of a healthcare establishment. And, HCISPP presents confirmation of a practitioner’s experience of best practices and methods to guard organizations and sensitive data against emerging warnings and breaches. With keeping all these things together, this cheat sheet will help you throughout your HCISPP Exam Preparation.
So, first, let’s start with the basics of the exam and cover the overview part.
HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP): Overview
The HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) exam, offered by the International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium, signifies expertise in critical areas of healthcare information privacy and security. This certification places a strong emphasis on healthcare regulatory complexities, data governance, and risk management, catering to a specific target audience.
Intended Audience:
The HCISPP is excellent for information security professionals entrusted with guarding protected health information (PHI) with including those in the following positions:
- Firstly, Compliance Officer
- Secondly, Information Security Manager
- Thirdly, Privacy Officer
- Fourthly, Compliance Auditor
- Then, Risk Analyst
- Medical Records Supervisor
- After that, Information Technology Manager
- Privacy and Security Consultant
- Health Information Manager
- Lastly, Practice Manager
HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP): Exam Prerequisites
For HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) Exam:
- Firstly, you must have a minimum of two years of work experience in knowledge areas of the HCISPP.
- Secondly, if you don’t have the required experience then also you may become an Associate of (ISC)² bypassing the HCISPP examination. But, after that, the Associate of (ISC)² will have three years to earn the two years of the required experience.
- Finally, candidates are required to have at least two years of cumulative paid work experience in one or more domains of the HCISPP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK), which encompasses security, compliance, and privacy. It’s important to note that legal practice can be substituted for compliance expertise, and an information management background can replace privacy knowledge. Of these two years of experience, at least one year must be specifically within the healthcare sector.
Quick Cheat Sheet for HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP)
The HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) exam is internationally recognized and will add significant value to your CV by certifying your abilities and knowledge. As a result, a significant deal of attention, passion, work, and time is required for this exam. With the right materials and training, you can effectively prepare for and pass the HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) exam. Let’s now explore the essential materials for a successful and efficient revision.
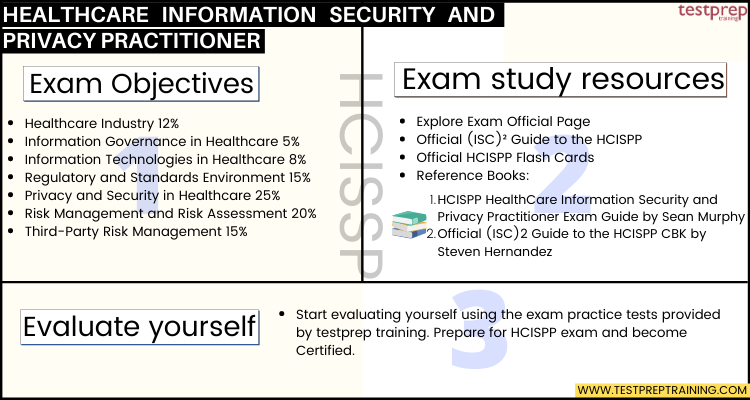
1. Understanding Exam Topics
The HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) test objectives give you more information about the methodologies, components, resources, and exam description. Furthermore, a comprehensive examination of the HCISPP Exam Guide will enable you to better align yourself with the exam’s primary goals. As a consequence, you’ll be able to go over the portions and topics that you find challenging and mark them for subsequent study. However, the following are the subjects covered in this HCISPP Exam Outline:
Domain 1: Healthcare Industry
- Understanding the Healthcare Environment Components
- Types of Organizations in the Healthcare Sector
- Health Insurance
- Coding International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 10)
- Revenue Cycle
- Workflow Management
- Regulatory Environment
- Public Health Reporting
- Clinical Research
- Healthcare Records Management
- Understanding Third-Party Relationships
- Vendors
- Business Partners
- Regulators
- Other Third-Party Relationships
- Understanding Foundational Health Data Management Concepts
- Information Flow and Life Cycle in the Healthcare Environments
- Health Data Characterization
- Data Interoperability and Exchange, International Health Exchange (IHE), Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM))
- Legal Medical Records
(ISC)2 Reference: Healthcare Security and Privacy
Domain 2: Information Governance in Healthcare
- Understanding Information Governance Frameworks
- Security Governance
- Privacy Governance
- Identifying Information Governance Roles and Responsibilities
- Aligning Information Security and Privacy Policies, Standards and Procedures
- Policies
- Standards
- Processes and Procedures
- Understanding and Comply with the Code of Conduct/Ethics in a Healthcare Information Environment
- Organizational Code of Ethics
- (ISC)² Code of Ethics
(ISC)2 Reference: HCISPP Experience Requirements
Domain 3: Information Technologies in Healthcare
- Understanding the Impact of Healthcare Information Technologies on Privacy and Security
- Increased Exposure Affecting Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability (e.g., threat landscape)
- Oversight and Regulatory Challenges
- Interoperability
- Information Technologies
- Understanding Data Life Cycle Management (e.g., create, store, use, share, archive, destroy)
- Understanding Third-Party Connectivity
- Trust Models for Third-Party Interconnections
- Technical Standards (e.g., physical, logical, network connectivity)
- Connection Agreements (e.g., Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), Interconnection Security Agreements (ISAs))
(ISC)2 Reference: CYBER THREATS TO HEALTHCARE
Domain 4: Regulatory and Standards Environment
- Identifying Regulatory Requirements
- Legal Issues that Pertain to Information Security and Privacy for Healthcare Organizations
- Data Breach Regulations
- Protected Personal and Health Information (e.g., Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Personal Health Information (PHI))
- Jurisdiction Implications
- Data Subjects
- Research
- Recognizing Regulations and Controls of Various Countries
- Treaties
- Laws and Regulations (e.g., European Union (EU) Data Protection Directive, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act /Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HIPAA/HITECH), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA))
- Understanding Compliance Frameworks
- Privacy Frameworks (e.g., Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Privacy principles, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP)) »
- Security Frameworks (e.g., International Organization for Standardization (ISO), National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Common Criteria (CC))
(ISC)2 Reference: RESEARCH REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS
Domain 5: Privacy and Security in Healthcare
- Understanding Security Objectives/Attributes
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- Understanding General Security Definitions and Concepts
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Data Encryption
- Training and Awareness
- Logging, Monitoring and Auditing
- Vulnerability Management
- Segregation of Duties
- Least Privilege (Need to Know)
- Business Continuity (BC)
- Disaster Recovery (DR)
- System Backup and Recovery
- Understanding General Privacy Definitions and Concepts
- Consent/Choice
- Limited Collection/Legitimate Purpose/Purpose Specification
- Disclosure Limitation/Transfer to Third-Parties/ Trans-border Concerns
- Access Limitation
- Accuracy, Completeness and Quality
- Management, Designation of Privacy Officer, Supervisor Re-authority, Processing Authorization and Accountability
- Training and Awareness
- Transparency and Openness
- Proportionality, Use and Disclosure, and Use Limitation
- Access and Individual Participation
- Notice and Purpose Specification
- Events, Incidents and Breaches
- Understanding the Relationship Between Privacy and Security
- Dependency
- Integration
- Understanding Sensitive Data and Handling
- Sensitivity Mitigation
- Categories of Sensitive Data
(ISC)2 Reference: Privacy
Domain 6: Risk Management and Risk Assessment
- Understanding Enterprise Risk Management
- Information Asset Identification
- Asset Valuation
- Exposure
- Likelihood
- Impact
- Threats
- Vulnerability
- Risk
- Controls
- Residual Risk
- Acceptance
- Understanding Information Risk Management Framework (RMF)
- Understanding the Risk Management Process
- Definition
- Approach (e.g., qualitative, quantitative)
- Intent
- Life Cycle/Continuous Monitoring
- Tools/Resources/Techniques
- Desired Outcomes
- Role of Internal and External Audit/Assessment
- Identifying Control Assessment Procedures Utilizing Organization Risk Frameworks
- Participating in Risk Assessment Consistent with the Role in Organization
- Information Gathering
- Risk Assessment Estimated Timeline
- Gap Analysis
- Mitigating Actions
- Avoidance
- TransferAcceptance
- Communications and Reporting
- Understanding Risk Response
- Utilizing Controls to Remediate Risk
- Administrative
- Physical
- Technical
- Participating in Continuous Monitoring
(ISC)2 Reference: Risk Assessment Clarification
Domain 7: Third-Party Risk Management
- Understanding the Definition of Third-Parties in the Healthcare Context
- Maintaining a List of Third-Party Organizations
- Third-Party Role/Relationship with the Organization
- Health Information Use
- Applying Management Standards and Practices for Engaging Third-Parties
- Relationship Management
- Determining When a Third-Party Assessment Is Required
- Organizational Standards
- Triggers of a Third-Party Assessment
- Supporting Third-Party Assessments and Audits
- Information Asset Protection Controls
- Compliance with Information Asset Protection Controls
- Communication of Results
- Participating in Third-Party Remediation Efforts
- Risk Management Activities
- Risk Treatment Identification
- Corrective Action Plans
- Compliance Activities Documentation
- Responding to Notifications of Security/Privacy Events
- Internal Processes for Incident Response
- Relationship Between Organization and Third-Party Incident Response
- Breach Recognition, Notification and Initial Response
- Responding to Third-Party Requests Regarding Privacy/Security Events
- Organizational Breach Notification Rules
- Organizational Information Dissemination Policies and Standards
- Risk Assessment Activities
- Chain of Custody Principles
- Promoting Awareness of Third-Party Requirements
- Information Flow Mapping and Scope
- Data Sensitivity and Classification
- Privacy and Security Requirements
- Risks Associated with Third-Parties
(ISC)2 Reference: Third-Party Risk Management in Healthcare
2. Use Exam Page for Staying Up to Date
During your review period, keep an eye on the HCISPP exam website to see if there has been any modification or update to the exam. Furthermore, the official site for the Healthcare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) exam gives details on the test’s technical features. It is the most reliable source for learning about exam policies, receiving exam updates, and learning about test course structure.
3. Official (ISC)² Guide to the HCISPP
The Official (ISC)² Guide to the HCISPP provides a comprehensive overview of the HCISPP’s major principles and standards. This handbook covers all of the knowledge requirements for demonstrating expertise in the area of healthcare security and privacy. In addition, it covers all seven areas, beginning with the healthcare industry and ending with third-party risk management.
4. Official HCISPP Flash Cards
You may study for their test whenever and wherever you choose using Official Flash Cards. Similarly, HCISPPI Flash Cards allow applicants to study whenever and wherever they choose. While conducting the HCISPP Flash Cards, you will receive quick feedback on whether or not your response is right. It also includes the option to mark particular cards for further investigation. Remember that these cards are divided into sections for each topic to make studying more convenient.
5. Using Reference Books
When it comes to studying for any type of exam, books are unquestionably the first resource that springs to mind. They are widely available, and we select books based on our preferences. Depending on your level of knowledge, you can consult a variety of books accessible online, in bookstores, or in libraries. Some of the books recommended for the Healthcare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) test are:
- Firstly, HCISPP HealthCare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner All-in-One Exam Guide by Sean Murphy
- Secondly, Official (ISC)2 Guide to the HCISPP CBK by Steven Hernandez.
6. Evaluate yourself with HCISPP Practice Tests
During the exam preparation period, practice exams are essential. You will learn about your weak and strong areas by assessing yourself with these HCISPP Practice Exams. Time management, on the other hand, is critical during the exam. As a consequence of your practice, you will be able to enhance your response abilities, which will save you a lot of time. Furthermore, the optimum time to begin conducting practice exams is after you have completed one topic since this will serve as a revision tool for you.



