The Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is becoming increasingly popular, and many organizations are adopting it as their cloud provider of choice. This means that there is a growing demand for professionals who are skilled in using the GCP to design, develop, and manage cloud solutions. The Google Associate Cloud Engineer certification is a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in using GCP. Nonetheless, getting ready for the exam can be quite challenging due to its extensive coverage of various GCP-related topics. This is where a cheat sheet can prove invaluable. A cheat sheet is a concise and user-friendly reference document that assists you in swiftly reviewing and recalling essential information.
In this blog, we will provide you with a cheat sheet that covers the most important topics and concepts that you need to know to pass the Google Associate Cloud Engineer certification exam. We will also provide you with some tips and tricks to help you use the cheat sheet effectively. So, let’s get started!
Google Associate Cloud Engineer: Exam Overview
The Google Associate Cloud Engineer role involves the deployment of applications, monitoring of operations across multiple projects, and the upkeep of enterprise solutions to ensure they meet specified performance standards. These professionals have hands-on experience with both public cloud and on-premises solutions. Additionally, they possess the capability to utilize the Google Cloud Console and command-line interface for executing routine platform-related tasks associated with the maintenance of one or more deployed solutions that utilize Google-managed or self-managed services on Google Cloud.
Glossary for Google Associate Cloud Engineer Terminology
- Cloud Computing – Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet. It involves the provision of computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, software, and other resources over the internet.
- Cloud Service Provider (CSP) – A cloud service provider (CSP) is an organization that delivers cloud computing services to both businesses and individuals. Notable examples of CSPs encompass Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Virtual Machine (VM) – A virtual machine (VM) is a software emulation of a physical computer. It allows several operating systems to run on a single physical machine.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider hosts computing infrastructure such as servers, storage, and networking hardware. Customers rent this infrastructure and use it to host their applications and data.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Platform as a service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider offers a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications. PaaS providers typically offer a preconfigured environment with programming languages, libraries, and tools for application development.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a cloud computing paradigm where software applications are hosted by a third-party provider and accessible to customers via the internet.
- Load Balancing – Load balancing involves the distribution of incoming network traffic among multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed, ultimately enhancing the performance and availability of applications.
- Auto Scaling – Auto scaling is a feature that allows a cloud service to automatically adjust its computing resources based on changes in demand. This helps to ensure that there is always enough capacity to handle incoming traffic.
- Cloud Storage – Cloud storage pertains to the storage of data on distant servers accessible via the internet. Providers of cloud storage deliver flexible and scalable storage solutions that are accessible from any location.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) – A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a virtual network that is isolated from other networks and is used by a single organization. It provides a secure environment for running applications and storing data.
- Cloud Security – Cloud security refers to the measures taken to protect cloud computing environments from cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches. It involves a combination of physical security, network security, and data security measures.
Exam preparation resources for Google Associate Cloud Engineer Exam
There are several resources available for preparing for the Google Associate Cloud Engineer exam. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Google Cloud Certification Exam Guide: This guide provides an overview of the certification exam, including the topics covered, the format of the exam, and tips for preparing for the exam. You can access the guide here: https://cloud.google.com/certification/guides/cloud-engineer
- Google Cloud’s Online Training: Google Cloud offers several online training courses that cover the topics included in the Associate Cloud Engineer certification exam. These courses are self-paced and include interactive demos and quizzes. You can access the training here: https://cloud.google.com/training/cloud-infrastructure
- Practice Exams: Taking practice exams is a highly effective method for getting ready for the certification exam. Google Cloud provides a practice exam tailored for the Associate Cloud Engineer certification, replicating the real exam experience. You can access the practice exam here: https://cloud.google.com/certification/practice-exam/cloud-engineer
- Official Study Guide: Google Cloud offers an official study guide that covers all the topics included in the Associate Cloud Engineer certification exam. The study guide includes detailed explanations and examples, as well as practice questions and quizzes. You can access the study guide here: https://services.google.com/fh/files/misc/cloud-engineer-study-guide.pdf
- Google Cloud Community: The Google Cloud Community is an online forum where you can connect with other professionals who are preparing for the certification exam. The community is an excellent resource for asking questions, sharing study tips, and learning from others’ experiences. You can access the community here: https://cloud.google.com/community
Expert tips to pass the Google Associate Cloud Engineer Exam
Here are some expert tips to help you pass the Google Associate Cloud Engineer Exam:
- Study the exam guide thoroughly: Make sure you understand the exam guide and its contents, which includes the skills tested, the exam format, and the scoring process.
- Familiarize yourself with the exam format: The examination includes multiple-choice and multiple-select questions. No penalties are imposed for incorrect answers, so it is advisable to respond to all the questions.
- Get hands-on experience: It’s important to have hands-on experience working with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) products and services. Practice using GCP and its tools to familiarize yourself with them.
- Understand GCP’s core services: Understand GCP’s core services, such as Compute Engine, Kubernetes Engine, and App Engine. Understand the difference between these services and know how to use them.
- Review GCP’s pricing: Familiarize yourself with GCP’s pricing structure, and learn how to estimate costs based on usage.
- Use official documentation: Google provides a wealth of official documentation on its products and services. Use these resources to gain a deeper understanding of GCP and to prepare for the exam.
- Take practice exams: Engage in practice exams to evaluate your understanding and pinpoint areas requiring enhancement. Google provides a practice exam that replicates the real exam experience.
- Join study groups: Join study groups and forums where you can ask questions, share your knowledge, and learn from others who are also preparing for the exam.
- Manage your time effectively: The exam is timed, so manage your time effectively. Don’t spend too much time on any one question. If you get stuck on a question, skip it and come back to it later.
- Stay calm and focused: The examination may create stress, but it’s crucial to maintain composure and concentration. If necessary, take short breaks, and maintain a positive mindset throughout the exam.
Keep in mind that achieving success in the Google Associate Cloud Engineer Exam demands diligence, commitment, and a comprehensive grasp of GCP. By following these recommendations, you can enhance your chances of success.
Skills Assessed
The Google Associate Cloud Engineer Certification exam assesses your ability to –
- Firstly, set up a cloud solution environment
- Secondly, plan and configure a cloud solution
- Then, deploy and implement a cloud solution
- Also, ensure successful operation of a cloud solution
- Moreover, configure access and security
Google Associate Cloud Engineer Cheat Sheet
Obtaining industry-recognized certification from Google provides you with a competitive advantage over other candidates. Furthermore, earning a professional certification enhances your job prospects and showcases your skills. To succeed in this exam, thorough studying and preparation are essential. This cheat sheet offers the appropriate resources and strategies, serving as your path to acing the exam with flying colors.
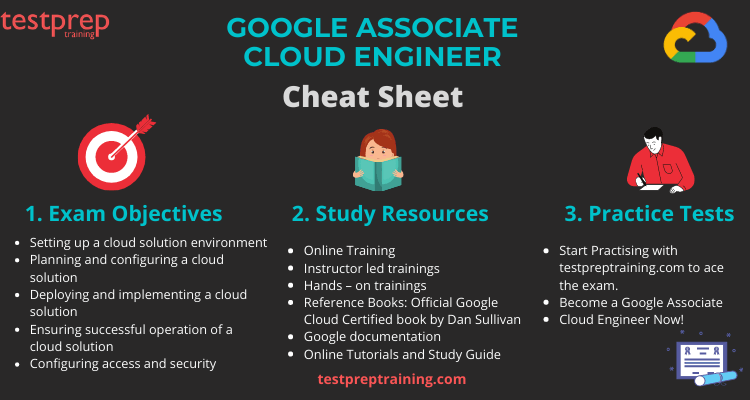
Understand the Exam Objectives
Familiarising yourself with the exam course is very essential to grasp the exam concepts. Given the wide syllabus this exam covers, it is suggested that you refer the Official Exam Guide by Google and learn more about the exam course. It provides descriptive details about the exam domains. Deeply understand these domains and tailor your study plan around these concepts.The exam domains covered in the Google Associate Cloud Engineer Course exam are:
1. Setting up a cloud solution environment (17.5%)
1.1 Setting up cloud projects and accounts. Activities include:
- Creating a resource hierarchy
- Applying organizational policies to the resource hierarchy
- Granting members IAM roles within a project
- Managing users in Cloud Identity (manually and automated) (GCP Documentation: Cloud Identity)
- Enabling APIs within projects (GCP Documentation: Enabling an API in your Google Cloud project)
- Provisioning and setting up products in Google Cloud’s operations suite
1.2 Managing billing configuration. Activities include:
- Creating one or more billing accounts (GCP Documentation: Create, modify, or close your Cloud Billing account)
- Linking projects to a billing account (GCP Documentation: Modify a project’s billing settings)
- Establishing billing budgets and alerts (GCP Documentation: Set budgets and budget alerts)
- Setting up billing exports
1.3 Installing and configuring the command line interface (CLI), specifically the Cloud SDK (e.g., setting the default project).
2. Planning and configuring a cloud solution (17.5%)
2.1 Planning and estimating Google Cloud product use using the Pricing Calculator
2.2 Planning and configuring compute resources. Considerations include:
- Selecting appropriate compute choices for a given workload (e.g., Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, Cloud Run, Cloud Functions) (GCP Documentation: Choosing the right compute option in GCP: a decision tree)
- Using preemptible VMs and custom machine types as appropriate (GCP Documentation: Custom Machine Types)
2.3 Planning and configuring data storage options. Considerations include:
- Product choice (e.g., Cloud SQL, BigQuery, Firestore, Spanner, Bigtable) (GCP Documentation: Google Cloud products)
- Choosing storage options (e.g., Zonal persistent disk, Regional balanced persistent disk, Standard, Nearline, Coldline, Archive)
2.4 Planning and configuring network resources. Tasks include:
- Differentiating load balancing options (GCP Documentation: Cloud Load Balancing overview)
- Identifying resource locations in a network for availability (GCP Documentation: Geography and regions)
- Configuring Cloud DNS (GCP Documentation: Cloud DNS )
3. Deploying and implementing a cloud solution (25%)
3.1 Deploying and implementing Compute Engine resources. Tasks include:
- Launching a compute instance using the Google Cloud console and Cloud SDK (gcloud) (e.g., assign disks, availability policy, SSH keys)
- Creating an autoscaled managed instance group using an instance template (GCP Documentation: Creating managed instance groups)
- Generating/uploading a custom SSH key for instances (GCP Documentation: Managing SSH keys in metadata)
- Installing and configuring the Cloud Monitoring and Logging Agent
- Assessing compute quotas and requesting increases (GCP Documentation: Requesting an increase in quota)
3.2 Deploying and implementing Google Kubernetes Engine resources. Tasks include:
- Installing and configuring the command line interface (CLI) for Kubernetes (kubectl)
- Deploying a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster with different configurations including AutoPilot, regional clusters, private clusters, etc.
- Deploying a containerized application to Google Kubernetes Engine (GCP Documentation: Deploying a containerized web application)
- Configuring Google Kubernetes Engine application monitoring and logging (GCP Documentation: Overview of Google Cloud’s operations suite for GKE)
3.3 Deploying and implementing App Engine, Cloud Run, and Cloud Functions resources. Tasks include, where applicable:
- Deploying an application and updating scaling configuration, versions, and traffic splitting (GCP Documentation: Splitting Traffic)
- Deploying an application that receives Google Cloud events (e.g., Pub/Sub events, Cloud Storage object change notification events)
3.4 Deploying and implementing data solutions. Tasks include:
- Initializing data systems with products (e.g., Cloud SQL, Firestore, BigQuery, Spanner, Pub/Sub, Bigtable, Dataproc, Dataflow, Cloud Storage) (GCP Documentation: Initialization actions)
- Loading data (e.g., command line upload, API transfer, import/export, load data from Cloud Storage, streaming data to Cloud Pub/Sub) (GCP Documentation: Introduction to loading data)
3.5 Deploying and implementing networking resources. Tasks include:
- Creating a VPC with subnets (e.g., custom-mode VPC, shared VPC) (GCP Documentation: Using VPC networks)
- Launching a Compute Engine instance with custom network configuration (e.g., internal-only IP address, Google private access, static external and private IP address, network tags) (GCP Documentation: Creating instances with multiple network interfaces)
- Creating ingress and egress firewall rules for a VPC (e.g., IP subnets, network tags, service accounts) (GCP Documentation: VPC firewall rules overview)
- Creating a VPN between a Google VPC and an external network using Cloud VPN (GCP Documentation: Cloud VPN overview)
- Creating a load balancer to distribute application network traffic to an application (e.g., Global HTTP(S) load balancer, Global SSL Proxy load balancer, Global TCP Proxy load balancer, regional network load balancer, regional internal load balancer) (GCP Documentation: External TCP/UDP Network Load Balancing overview)
3.6 Deploying a solution using Cloud Marketplace. Tasks include:
- Browsing Cloud Marketplace catalogue and viewing solution details (GCP Documentation: GOOGLE CLOUD MARKETPLACE)
- Deploying a Cloud Marketplace solution (GCP Documentation: Creating Deployments with Google Cloud Platform Marketplace)
3.7 Implementing resources via infrastructure as code. Tasks include:
- Building infrastructure via Cloud Foundation Toolkit templates and implementing best practices
- Installing and configuring Config Connector in Google Kubernetes Engine to create, update, delete, and secure resources
4. Ensuring successful operation of a cloud solution (20%)
4.1 Managing Compute Engine resources. Tasks include:
- Managing a single VM instance (e.g., start, stop, edit configuration, or delete an instance) (GCP Documentation: Virtual machine instances)
- Remotely connecting to the instance
- Attaching a GPU to a new instance and installing CUDA libraries (GCP Documentation: Adding or removing GPUs)
- Viewing current running VM inventory (instance IDs, details) (GCP Documentation: Instance life cycle)
- Working with snapshots (e.g., create a snapshot from a VM, view snapshots, delete a snapshot) (GCP Documentation: Creating persistent disk snapshots)
- Working with images (e.g., create an image from a VM or a snapshot, view images, delete an image) (GCP Documentation: Images)
- Working with instance groups (e.g., set autoscaling parameters, assign instance template, create an instance template, remove instance group) (GCP Documentation: Instance groups)
- Working with management interfaces (e.g., Google Cloud console, Cloud Shell, Cloud SDK) (GCP Documentation: Cloud management tools)
4.2 Managing Google Kubernetes Engine resources. Tasks include:
- Viewing current running cluster inventory (nodes, pods, services) (GCP Documentation: GKE Dashboards)
- Browsing the container image repository and viewing container image details (GCP Documentation: gcloud container images list)
- Working with node pools (e.g., add, edit, or remove a node pool) (GCP Documentation: Node pools)
- Working with pods (e.g., add, edit, or remove pods) (GCP Documentation: Pod)
- Working with services (e.g., add, edit, or remove a service) (GCP Documentation: About Google Cloud services)
- Working with stateful applications (e.g. persistent volumes, stateful sets) (GCP Documentation: Deploying a stateful application)
- Managing Horizontal and Vertical autoscaling configurations
- Working with management interfaces (e.g., Google Cloud Console, Cloud Shell, Cloud SDK, kubectl) (GCP Documentation: Cloud management tools)
4.3 Managing Cloud Run resources. Tasks include:
- Adjusting application traffic splitting parameters (GCP Documentation: Splitting Traffic)
- Setting scaling parameters for autoscaling instances (GCP Documentation: Autoscaling groups of instances)
- Determining whether to run Cloud Run (fully managed) or Cloud Run for Anthos
4.4 Managing storage and database solutions. Tasks include:
- Managing and securing objects in and between Cloud Storage buckets (GCP Documentation: Moving and renaming buckets)
- Setting object life cycle management policies for Cloud Storage buckets (GCP Documentation: Object Lifecycle Management)
- Executing queries to retrieve data from data instances (e.g., Cloud SQL, BigQuery, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Datastore, Cloud Bigtable) (GCP Documentation: Querying Cloud Storage data)
- Estimating costs of a BigQuery query (GCP Documentation: Estimating storage and query costs)
- Backing up and restoring data instances (e.g., Cloud SQL, Cloud Datastore) (GCP Documentation: Restoring an instance)
- Reviewing job status in Cloud Dataproc, Cloud Dataflow, or BigQuery (GCP Documentation: Life of a Dataproc Job)
4.5 Managing networking resources. Tasks include:
- Adding a subnet to an existing VPC (GCP Documentation: Using VPC networks)
- Expanding a subnet to have more IP addresses (GCP Documentation: gcloud compute networks subnets expand-ip-range)
- Reserving static external or internal IP addresses (GCP Documentation: Reserving a new static external IP address)
- Working with CloudDNS, CloudNAT, Load Balancers and firewall rules
4.6 Monitoring and logging. Tasks include:
- Creating Cloud Monitoring alerts based on resource metrics
- Creating and ingesting Cloud Monitoring custom metrics (e.g., from applications or logs)
- Configuring log sinks to export logs to external systems (e.g., on-premises or BigQuery) (GCP Documentation: Exporting with the Logs Viewer)
- Configuring log routers
- Viewing and filtering logs in Stackdriver (GCP Documentation: Advanced logs queries)
- Viewing specific log message details in Stackdriver (GCP Documentation: Viewing logs (Classic))
- Using cloud diagnostics to research an application issue (e.g., viewing Cloud Trace data, using Cloud Debug to view an application point-in-time) (GCP Documentation: Error Reporting)
- Viewing Google Cloud status (GCP Documentation: Google Cloud Status Dashboard)
5. Configuring access and security (20%)
5.1 Managing identity and access management (IAM). Tasks include:
- Viewing IAM policies
- Creating IAM policies
- Managing the various role types and defining custom IAM roles (e.g., primitive, predefined and custom) (GCP Documentation: Basic concepts)
5.2 Managing service accounts. Tasks include:
- Creating service accounts
- Using service accounts in IAM policies with minimum permissions (GCP Documentation: Service accounts)
- Assigning service accounts to resources (GCP Documentation: Creating and enabling service accounts for instances)
- Managing IAM of a service account
- Managing service account impersonation
- Creating and managing short-lived service account credentials
5.3 Viewing audit logs
Quick links for Resources to enhance your learning
The demand for Google Cloud Certified Associate Cloud Engineer exam has accelerated and so there are abundant resources in the marketplace for your preparations. It is necessary to choose the ones that best suit you and are authentic. Here are some Google Associate Cloud Engineer Study Material for you to explore-
Google Associate Cloud Engineer Online Training
Online Training is the best way to prepare for the exam while developing strong understanding of the concepts. The online classes also provide you with good reading material like notes or recommends books that might be beneficial for you. Google offers its own training courses that might help you in scoring well:
Instructor led trainings
Instructor led trainings are also one of the best options to prepare for the exam. Instructors who are well versed and have excelled in this field are on board for teaching in the best possible way. Google has officially launched its training sessions which can be found on official site. These Google Associate Cloud Engineer Training are:
Hands – on trainings
Practicing and learning to apply the concepts in real life is very important. This exam tests your competency for a job so all your concepts should be crystal clear and you should know their application too. Google recommends trainings through the following labs:
- GCP Essentials
- Baseline: Infrastructure
- Cloud Engineering
- Networking in the Google Cloud
- Kubernetes in the Google Cloud
- Hands-on lab: Cloud Run – Hello Cloud Run
- Hands-on lab: Deploying an Application to App Engine Flexible
Books – Your best friends
Books have been an age old tradition and essential ingredient when it comes to preparing for any exam. They provide deep understanding of the exam concepts. Also books offer real life scenarios that help you prepare for a practical exam. We recommend you to refer the following Google Associate Cloud Engineer Books:
- Official Google Cloud Certified book by Dan Sullivan
- Google Cloud Certified Associate Cloud Engineer All-in-One Exam Guide by Jack Hyman
Learn with Google documentation
Google documentation is the most authentic resource for preparation and that too free of cost. You can explore these documentations and can find absolutely reliable and quality content for your preparation.. Google has divided its documentations in the following four major sections:
Online Tutorials and Study Guide
Always remember that all incredible things need time. Therefore preparing for a certification is not easy. So, mastering the exam concepts through Google Associate Cloud Engineer Tutorial is a must to clear this exam. Further, you should also follow a Study Guide to stay on the right track. It helps you diversify your study strategy and ensure the best possible results.
Evaluate yourself with Practice Tests
Mistakes are bound to happen, but they can certainly be minimized. In the context of exams, practicing with sample papers is highly effective in reducing errors. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in training the brain for the task at hand. Practice papers create a simulated environment that helps the brain adapt to the actual exam conditions. Therefore, engaging in practice tests serves multiple purposes: it helps identify strengths and weaknesses, highlights areas requiring improvement, and ensures comprehensive coverage of the syllabus. It’s essential to incorporate practice tests into your study routine after you’ve covered the entire syllabus. Furthermore, tackling multiple practice tests will boost your confidence, motivating you to outperform your previous attempts. Get Ready to Self Evaluate your preparations with Google Associate Cloud Engineer Practice Tests!