We are well familiar with the AWS certification exams and the level it takes you to after earning the certification. With the combination of the latest technologies and expert research work, AWS always stays up to date with its exam. In 2020, there were a lot of ups and downs for certifications and the methods for taking exams. Keeping all that in mind, AWS has done modifications in its exam in the year 2021. One of the major changes was bringing up the new updated exam – AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02).
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) is the new version that will replace the previous AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C01) Exam. Coming on to the point, in this article, we will be talking about this latest exam and all the new details that will come with this. So, without wasting any time let’s start with a basic overview of the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) Exam.
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator Associate: Exam Overview
The AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam is suitable for candidates who are system administrators in cloud operations. Moreover, they should be working in this role with at least 1 year of experience with deployment, management, networking, and security on AWS.
Further, this exam validates candidates ability in various areas. This include:
- Firstly, deploying, managing, and operating workloads on AWS
- Secondly, supporting and maintaining AWS workloads according to the AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Thirdly, performing operations by using the AWS Management Console and the AWS CLI
- Implementing security controls for meeting compliance requirements
- Then, monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting systems
- Next, apply networking concepts and implementing architectural requirements
- After that, performing business continuity and disaster recovery procedures
- Lastly, identifying, classifying, and remediating incidents
You must know that before starting preparing for any exam, it is important to understand the knowledge required for the exam. This will also work as revision that you have that experience and understanding in that particular area or not. For AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam, there is recommended knowledge that AWS provides. Let’s check this out.
Recommended AWS Knowledge
- Firstly, a minimum of one year of experience with AWS technology and in deploying, managing, and operating workloads on AWS
- Secondly, understanding and knowledge of the AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Thirdly, experience with the AWS Management Console and the AWS CLI
- Next, knowledge and understanding of AWS networking and security services
- Lastly, experience in implementing security controls and compliance requirements
Moving on, in the next section, we will understand about the updated exam details for the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam.
AWS SysOps Administrator – Associate: Exam Details
The AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate is a beta exam that is available at a discounted rate of 75 USD. To complete the exam, there will be a time duration of 220 minutes. Candidates successfully passing the exam will earn the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate certification with all the associated benefits. And, the exam can be taken in the English Language.
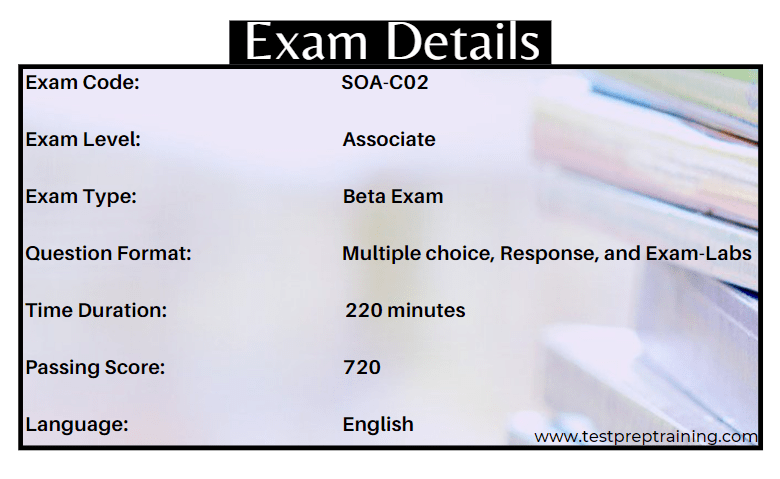
Talking about the exam score, this is a pass or fail exam in which the result for the exam score ranges from 100–1,000 and a minimum passing score is 720.
Coming onto the exam scheduling. There have been many modifications in this beta exam related to scheduling. Let’s understand that.
Exam Scheduling
For the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) beta exam, the appointments are limited, so it is necessary to register early to participate. However, there is no need to worry, as the updated exam (SOA-C02) will be generally available in Q3 2021.
Online Proctoring Rules
Those who will take the exam via online proctoring must know that external monitors are allowed for the SOA-C02 exam. Firstly, run the system test first for ensuring that the network meets the system requirements. Further, for accessing a list of testing centers offering the beta exam, sign in to your AWS Certification Account and select “Schedule New Exam.” After selecting the scheduling with Pearson VUE, you can have access to the list of specific testing centers that offer this exam.
Further, the registration for the new AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate beta exam is open. So, you can take the beta exam from February 16, 2021, to March 26, 2021. Talking about the current version of the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate exam (SOA-C01), this will continue to be available throughout the beta phase of the new exam.
As we got all the exam details and the overview of the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam. But, the questions arise is why an update was necessary and what is new in this exam?. So, for this, in the next section, we will discuss the important changes.
AWS SysOps Administrator Associate SOA-C02 Exam: What’s new?
AWS has made updates to the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate exam for accounting for the rapid pace of innovation on the AWS platform and the latest best practices for the SysOps administrator role. The new AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam comes with a combination of multiple-choice, multiple responses, and exam lab items. After completing the exam labs, you will be demonstrating skills relevant to a SysOps administrator role by building solutions with the AWS Management Console and AWS CLI. Let’s understand more about this!
In this exam there may be three types of questions on the examination. This includes:
- Firstly, Multiple choice. In which there are one correct response and three incorrect responses.
- Secondly, Multiple responses. This can have two correct responses out of five options.
- Lastly, Exam lab. This consists of a scenario that has a set of tasks to be performed in the AWS Management Console or AWS CLI.
Further, when you begin your exam, you will be notified of the number of questions in the multiple-choice and multiple response section as well as the number of exam labs in the exam lab section. So, before moving to the next one, first, finish all work on an exam lab before. As you will not be able to return to a prior exam lab.
Now coming onto the important modification that has been made in this new exam. The course outline. In the below section we will check out the topics for the exam as well as the percentage weightage for the topics.
AWS SOA-C02 exam: Content Outline
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam guide provides the weightings, domains, and objectives. The topics given in this course outline will help you a lot during the exam preparation. The domains include:
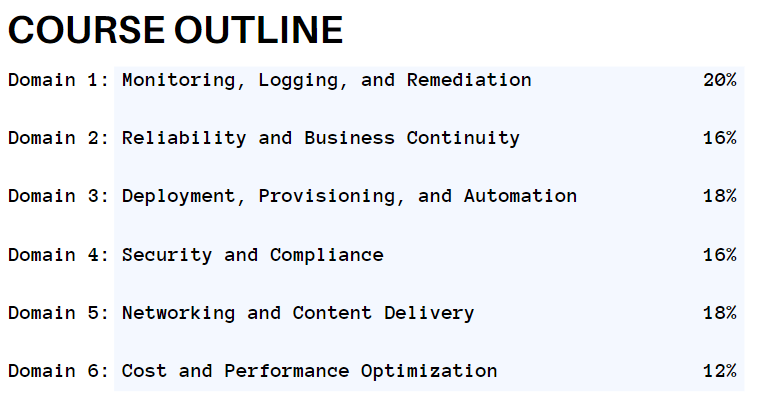
Domain 1: Monitoring, Logging, and Remediation
1.1 Implementing metrics, alarms, and filters by using AWS monitoring and logging services
- Identify, collect, analyze, and export logs (for example, Amazon CloudWatch Logs, CloudWatch Logs Insights, AWS CloudTrail logs) (AWS Documentation: Analyzing Log Data with CloudWatch Logs Insights, Define Amazon CloudWatch Logs, CloudWatch Logs Insights Sample Queries)
- Collect metrics and logs using the CloudWatch agent (AWS Documentation: Collecting Metrics and Logs from Amazon EC2 Instances and On-Premises Servers)
- Creating CloudWatch alarms (AWS Documentation: Create a CloudWatch Alarm Based on a Static Threshold, Create a CloudWatch alarm for an instance, Using Amazon CloudWatch Alarms)
- Develop metric filters (AWS Documentation: Creating Metrics From Log Events Using Filters, Creating Metric Filters)
- Creating CloudWatch dashboards (AWS Documentation: Creating a CloudWatch Dashboard, Using Amazon CloudWatch Dashboards)
- Configuring notifications (for example, Amazon Simple Notification Service [Amazon SNS], Service Quotas, CloudWatch alarms, AWS Health events) (AWS Documentation: Setting Up Amazon SNS Notifications, Configuring Amazon SNS notifications for Amazon SES, Configuring Notifications for CloudWatch Logs Alarms, Monitoring AWS Health events with Amazon CloudWatch Events, Service Quotas, and Amazon CloudWatch alarms)
1.2 Remediating issues based on monitoring and availability metrics
- Troubleshooting or taking corrective actions based on notifications and alarms (AWS Documentation: Amazon CloudWatch Features, Troubleshooting CloudWatch Events)
- Configuring Amazon EventBridge rules to trigger actions (AWS Documentation: Creating a rule for an AWS service, Creating an EventBridge Rule That Triggers on an AWS API Call Using AWS CloudTrail)
- Using AWS Systems Manager Automation documents to take action based on AWS Config rules (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Automation, Systems Manager Automation actions reference, Working with runbooks, AWS Config)
Domain 2: Reliability and Business Continuity
2.1 Implementing scalability and elasticity
- Creating and maintaining AWS Auto Scaling plans (AWS Documentation: AWS Auto Scaling, How scaling plans work)
- Implementing caching (AWS Documentation: Caching Overview, Caching strategies)
- Applying Amazon RDS replicas and Amazon Aurora Replicas (AWS Documentation: Using Amazon Aurora Auto Scaling with Aurora replicas, Replication with Amazon Aurora)
- Implementing loosely coupled architectures (AWS Documentation: Building Loosely Coupled, Scalable, C# Applications with Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS, Loosely Coupled Scenarios)
- Differentiating between horizontal scaling and vertical scaling
2.2 Implement high availability and resilient environments
- Configuring Elastic Load Balancer and Amazon Route 53 health checks (AWS Documentation: Configuring Amazon Route 53 to route traffic to an ELB load balancer, Creating Amazon Route 53 health checks, and configuring DNS failover)
- Differentiating between the use of a single Availability Zone and Multi-AZ deployments. For example, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling groups, Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon FSx, Amazon RDS (AWS Documentation: Regions and Zones, High availability (Multi-AZ) for Amazon RDS, Amazon RDS Multi-AZ Deployments, Elastic Load Balancing, and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling)
- Implementing fault-tolerant workloads. For example, Amazon Elastic File System [Amazon EFS], Elastic IP addresses (AWS Documentation: Mounting with an IP address, Amazon EFS: How it works)
- Applying Route 53 routing policies (for example, failover, weighted, latency based) (AWS Documentation: Choosing a routing policy)
2.3 Implementing backup and restore strategies
- Automating snapshots and backups based on use cases (for example, RDS snapshots, AWS Backup, RTO and RPO, Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, retention policy) (AWS Documentation: Working with backups, Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager)
- Restoring databases (for example, point-in-time restore, promote read replica) (AWS Documentation: Working with read replicas)
- Implementing versioning and lifecycle rules (AWS Documentation: Lifecycle configuration elements, Managing your storage lifecycle)
- Configuring Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication (AWS Documentation: Amazon S3 Replication, Configuring replication, Replicating objects)
- Executing disaster recovery procedures (AWS Documentation: Plan for Disaster Recovery (DR))
Domain 3: Deployment, Provisioning, and Automation
3.1 Provisioning and maintaining cloud resources
- Creating and managing AMIs (for example, EC2 Image Builder) (AWS Documentation: EC2 Image Builder, How EC2 Image Builder works)
- Creating, managing, and troubleshooting AWS CloudFormation (AWS Documentation: Troubleshooting AWS CloudFormation)
- Provisioning resources across multiple AWS Regions and accounts. For example, AWS Resource Access Manager, CloudFormation StackSets, IAM cross-account roles (AWS Documentation: Use CloudFormation StackSets to Provision Resources, Multiple-account, multiple-Region AWS CloudFormation, Use AWS CloudFormation StackSets for Multiple Accounts in an AWS Organization)
- Selecting deployment scenarios and services (for example, blue/green, rolling, canary) (AWS Documentation: Blue/Green deployment with CodeDeploy, Working with deployment configurations in CodeDeploy, Set up an API Gateway canary release deployment)
- Identifying and remediating deployment issues (for example, service quotas, subnet sizing, CloudFormation, and AWS OpsWorks errors, permissions) (AWS Documentation: AWS service quotas, AWS OpsWorks, AWS::EC2::Subnet)
3.2 Automating manual or repeatable processes
- Using AWS services (for example, OpsWorks, Systems Manager, CloudFormation) to automate deployment processes (AWS Documentation: AWS OpsWorks, Use AWS CloudFormation to configure a service role for Automation, AWS CodeDeploy)
- Implementing automated patch management (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager, Patch management overview)
- Scheduling automated tasks by using AWS services (for example, EventBridge, AWS Config) (AWS Documentation: EventBridge Event Examples from Supported AWS Services, Build a scheduler as a service, AWS Config)
Domain 4: Security and Compliance
4.1 Implementing and managing security and compliance policies
- Implementing IAM features (for example, password policies, MFA, roles, SAML, federated identity, resource policies, policy conditions) (AWS Documentation: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Creating a Role for SAML 2.0 federation (console), Policies and permissions in IAM, Identity providers and federation, IAM Identities (users, groups, and roles))
- Troubleshooting and auditing access issues by using AWS services (for example, CloudTrail, IAM Access Analyzer, IAM policy simulator) (AWS Documentation: Logging IAM and AWS STS API calls with AWS CloudTrail, Using AWS IAM Access Analyzer, AWS security audit guidelines, Logging Access Analyzer API calls with AWS CloudTrail)
- Validating service control policies and permission boundaries (AWS Documentation: Service control policies, Permissions boundaries for IAM entities)
- Reviewing AWS Trusted Advisor security checks (AWS Documentation: AWS Trusted Advisor)
- Validating AWS Region and service selections based on compliance requirements (AWS Documentation: Compliance validation for Amazon EC2, Compliance validation for AWS Identity and Access Management, Regions and Zones)
- Implementing secure multi-account strategies (for example, AWS Control Tower, AWS Organizations) (AWS Documentation: AWS multi-account strategy for your AWS Control Tower landing zone, AWS Control Tower)
4.2 Implementing data and infrastructure protection strategies
- Enforcing a data classification scheme (AWS Documentation: Leveraging AWS Cloud to Support Data Classification, Data Classification)
- Creating, managing, and protecting encryption keys (AWS Documentation: Creating keys)
- Implementing encryption at rest (for example, AWS Key Management Service [AWS KMS]) (AWS Documentation: AWS Key Management Service, AWS Key Management Service concepts)
- Implementing encryption in transit (for example, AWS Certificate Manager, VPN) (AWS Documentation: AWS Certificate Manager, Protecting data using encryption)
- Securely store secrets by using AWS services (for example, AWS Secrets Manager, Systems Manager Parameter Store) (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store, Referencing AWS Secrets Manager secrets from Parameter Store parameters)
- Reviewing reports or findings (for example, AWS Security Hub, Amazon GuardDuty, AWS Config, Amazon Inspector) (AWS Documentation: Amazon Inspector, Assessment reports, Amazon GuardDuty)
Domain 5: Networking and Content Delivery
5.1 Implementing networking features and connectivity
- Configuring a VPC (for example, subnets, route tables, network ACLs, security groups, NAT gateway, internet gateway ) (AWS Documentation: VPC with public and private subnets (NAT), NAT gateways, Internet gateways, Network ACLs)
- Configuring private connectivity (for example, Systems Manager Session Manager, VPC endpoints, VPC peering, VPN) (AWS Documentation: Create a Virtual Private Cloud endpoint, AWS Systems Manager Session Manager, AWS PrivateLink and VPC endpoints, VPC peering)
- Checking AWS network protection services (for example, AWS WAF, AWS Shield) (AWS Documentation: How AWS Shield works, What are AWS WAF, AWS Shield, and AWS Firewall Manager?)
5.2 Configuring domains, DNS services, and content delivery
- Configuring Route 53 hosted zones and records (AWS Documentation: Creating a public hosted zone, Creating records by using the Amazon Route 53 console)
- Implementing Route 53 routing policies (for example, geolocation, geoproximity) (AWS Documentation: Choosing a routing policy, Creating and managing traffic policies)
- Customizing DNS (for example, Route 53 Resolver) (AWS Documentation: Getting started with Route 53 Resolver, Resolving DNS queries between VPCs and your network, Configuring Amazon Route 53 as your DNS service)
- Configuring Amazon CloudFront and S3 origin access identity (OAI) (AWS Documentation: Restricting Access to Amazon S3 Content by Using an Origin Access Identity)
- Configuring S3 static website hosting (AWS Documentation: Hosting a static website using Amazon S3, Configuring a static website on Amazon S3)
5.3 Troubleshooting network connectivity issues
- Interpreting VPC configurations (for example, subnets, route tables, network ACLs, security groups) (AWS Documentation: Route tables for your VPC, Internetwork traffic privacy in Amazon VPC, Network ACLs, VPC Flow Logs)
- Collecting and interpreting logs (for example, VPC Flow Logs, Elastic Load Balancer access logs, AWS WAF web ACL logs, CloudFront logs) (AWS Documentation: Logging web ACL traffic information, Configuring and using standard logs (access logs), VPC Flow Logs, Access logs for your Network Load Balancer)
- Identifying and remediating CloudFront caching issues (AWS Documentation: Amazon CloudFront)
- Troubleshoot hybrid and private connectivity issues (AWS Documentation: troubleshoot network performance issues between Amazon EC2 Linux instances in a VPC, Troubleshoot connecting to your instance, Hybrid Connectivity)
Domain 6: Cost and Performance Optimization
6.1 Implement cost optimization strategies
- Implementing cost allocation tags (AWS Documentation: Using Cost Allocation Tags)
- Identify and remediate underutilized or unused resources by using AWS services and tools (for example, Trusted Advisor, AWS Compute Optimizer, Cost Explorer) (AWS Documentation: AWS Trusted Advisor, AWS Tools for Reporting and Cost Optimization, optimize costs using AWS Trusted Advisor)
- Configure AWS Budgets and billing alarms (AWS Documentation: Creating a Billing Alarm to Monitor Your Estimated AWS Charges, Managing your costs with AWS Budgets)
- Assessing resource usage patterns to qualify workloads for EC2 Spot Instances (AWS Documentation: Spot Instances)
- Identify opportunities to use managed services (for example, Amazon RDS, AWS Fargate, EFS) (AWS Documentation: Using Amazon EFS file systems with Amazon ECS, Amazon Elastic Container Service, Amazon ECS on AWS Fargate, Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS))
6.2 Implement performance optimization strategies
- Recommend compute resources based on performance metrics (AWS Documentation: List the available CloudWatch metrics for your instances, Metrics analyzed by AWS Compute Optimizer)
- Monitor Amazon EBS metrics and modify the configuration to increase performance efficiency (AWS Documentation: I/O characteristics and monitoring, Amazon CloudWatch metrics for Amazon EBS)
- Implementing S3 performance features (for example, S3 Transfer Acceleration, multipart uploads) (AWS Documentation: Configuring fast, secure file transfers using Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration, Multipart upload overview)
- Monitor RDS metrics and modify the configuration to increase performance efficiency (for example, performance insights, RDS Proxy) (AWS Documentation: Managing connections with Amazon RDS Proxy, Using Performance Insights on Amazon RDS)
- Enabling enhanced EC2 capabilities (for example, enhanced network adapter, instance store, placement groups) (AWS Documentation: Enhanced networking on Linux, Enable enhanced networking with the Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) on Windows instances, Placement groups)
Now, we have almost covered all the major changes and the modifications that have been made in the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam. It’s time for preparation. Candidates preparing for the SOA-C02 exam must need the training ways and methods. So, in the below section we will talk about the AWS importance and the training resources to crack this beta exam.
AWS Certification: Benefits & Training Resources
AWS Certification is better known for validating cloud skills to help professionals highlight in-demand abilities and organizations to build effective, innovative teams for cloud initiatives using AWS. Moreover, the AWS offers certification starting from role-based certifications for those in Cloud Practitioner, Architect, Developer, and Operations roles and at last the Specialty certifications in specific technical areas. These certifications can benefit from a wide range of expert insights, resources, and programs as you move toward achieving AWS Certification.
Coming onto the training, AWS provides the best study resources that will help you pass the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam. So, let’s explore those methods.
AWS Exam guide
For every certification, AWS provides an exam guide that contains the content outline, exam overview, and the target audience for the certification exam. Before starting preparing for the exam, it is important to go through this guide to understand the knowledge requirement and other major derails for the exam.
AWS Training
For build technical skills for the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam, AWS recommended courses to help you throughout the exam preparation. This include:
Using this you will be able to learn the fundamentals of identifying AWS services for making informed decisions about IT solutions as per the business requirements. Moreover, in this course, you will:
- Firstly, learn and understand the terminology and concepts related to the AWS platform
- Secondly, understand the process of navigating the AWS Management Console
- Lastly, learn about the key concepts of AWS security measures and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
In this course, you will learn about systems operators and the process of managing and operating automatable and repeatable deployments of networks and systems on AWS. Moreover, you will learn and understand the systems operations functions like installing, configuring, automating, monitoring, securing, maintaining, and troubleshooting.
AWS Exam Readiness
Exam Readiness training helps to learn how to interpret exam questions and allocate your study time. This includes classroom training for learning and engaging in a physical or virtual classroom with an AWS-accredited instructor. For AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam it includes:
Exam Readiness: AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate
For this exam, exam readiness offers an intermediate-level course that will help candidates to learn how to prepare for the exam by exploring the exam’s topic areas and how they plan to SysOps on AWS and to specific areas to study. This course checks the sample exam questions in each topic area and teaches you the process of interpreting the concepts being tested so that you can more easily eliminate incorrect responses. The objective of this course include:
- Firstly, navigate the logistics of the examination process.
- Secondly, understanding the exam structure and question types.
- Thirdly, identifying how questions relate to AWS SysOps concepts.
- Lastly, allocate your time studying for the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate exam.
Evaluate yourself with Practice Tests
Taking a practice test is a great way to understand study strategy and to learn about your weak areas. Moreover, practice tests help you to ensure the best possible learning and use the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) practice exam, you will learn and understand the pattern of the questions so that you don’t face any problem during the exam.
Final Words
For those preparing for the beta exam, the AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate (SOA-C02) exam can be your key to achieve your goal. By becoming an AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate, you will earn digital badges that you can use to display your abilities and even share your real-time achievement with employers and on social media. So, this new exam can provide you a source of benefits that can end up in having a good career. Further, you can start preparing for the exam using the list of training methods provided in this article.



