The AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam is for experts who want to show they are skilled in safeguarding AWS systems. This exam covers various subjects like controlling access, securing networks, safeguarding data, and handling security incidents.
Preparing for the AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam can be a challenging task, as the exam requires a deep understanding of AWS security services and best practices. That’s why I have created this cheat sheet to help you prepare for the exam in a more efficient and effective way. This cheat sheet includes key concepts, important tips, and sample questions that will help you master the exam material and pass the exam with confidence.
Whether you are a security professional looking to advance your career or an IT professional seeking to enhance your AWS skills, this cheat sheet will provide you with the knowledge and skills you need to pass the AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam. So, let’s dive in and start preparing for the exam!
AWS Certified Security-Specialty: Overview
The AWS Certified Security Specialty certification encompasses topics in which security professionals and staff need to be skilled in. not to mention, they must have an understanding of security fundamentals, follow best practices, and build expertise in key services that are unique to the AWS platform.

Moreover, this certification is designed to certify the candidate’s AWS knowledge across security topics that include data protection and encryption, infrastructure security, incident response, identity, and access management, monitoring, and logging.
AWS Certified Security-Specialty Glossary
- Access Key – An access key is an alphanumeric code that AWS provides to a user to authenticate their access to AWS services.
- Authentication – Authentication means confirming who you are before using AWS resources.
- Authorization – Authorization is deciding if you’re allowed to use AWS stuff based on who you are and what you’re allowed to do.
- CloudTrail – CloudTrail is an AWS service that provides visibility into user activity by recording AWS API calls and delivering the resulting log files to an S3 bucket.
- Compliance – Compliance refers to adhering to security standards and regulations, such as the GDPR or HIPAA, to ensure the security and privacy of data.
- Data Encryption – Data encryption means turning regular information into secret code so bad guys can’t read it without permission.
- IAM – IAM, short for Identity and Access Management, is like a security guard for AWS. It controls who can do what with AWS stuff.
- KMS – KMS, or Key Management Service, is an AWS service that allows users to create, manage, and use encryption keys to protect their data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – MFA is a security feature that requires users to provide more than one form of authentication, such as a password and a security token, to access AWS resources.
- Network Security – Network security is like locking the doors and windows of a house to keep intruders out. It’s about protecting a company’s computer network and data from unauthorized access or attacks.
- PCI DSS – PCI DSS, which stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, are rules to make sure that credit card information is handled safely and securely. It’s like having strict guidelines for how to protect sensitive financial data.
- Security Group – A security group is a virtual firewall that controls inbound and outbound traffic to an AWS resource, such as an EC2 instance.
- Security Token Service (STS) – STS is an AWS service that provides temporary security credentials to allow users to access AWS resources.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE) – SSE is a feature that allows users to encrypt data at rest within AWS services, such as S3 or RDS.
- SSL/TLS – SSL/TLS, known as Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security, is like a special code that makes sure that when you send information over the internet, it stays private and safe from others who might want to see it. It’s like having a secret language for your online conversations.
Exam preparation resources for AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam
Here are some official resources for preparing for the AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam:
- AWS Certification website: The AWS Certification website has a dedicated page for the Security-Specialty Exam, which provides an overview of the exam, its objectives, and recommended preparation resources.
Link: https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-security-specialty/
- Exam guide: The AWS Certified Security-Specialty Exam Guide is like a user manual that tells you everything you need to know about the exam. It explains how the exam is set up, what kind of questions you’ll face, and even some helpful hints for doing well on the test.
- Exam readiness training: AWS offers a range of exam readiness training courses, including instructor-led courses, self-paced digital courses, and virtual classroom training. These courses cover the key concepts and skills required for the exam.
Link: https://aws.amazon.com/training/course-descriptions/aws-certified-security-specialty-exam-readiness/
- Whitepapers: AWS offers a range of whitepapers that cover various security-related topics, such as securing data in transit and at rest, securing AWS environments, and incident response. These whitepapers can help you prepare for the exam by providing a deeper understanding of the security concepts covered in the exam.
- Sample questions: AWS offers practice questions that you can try to check what you know and get ready for the exam. These questions are meant to show you the kind of questions you’ll see on the real test.
Course Outline
Course Outline refers to the blueprint of the exam guide which defines the course aims and learning outcomes. The main objective of the course outline is to provide candidates with an overall plan for the course, enabling them to plan their own schedules and learn effectively.
The AWS Certified Security Specialty course outline includes weightings, test domains, and objectives only. Let’s take a look at the table below.
Domain 1: Threat Detection and Incident Response (14%)
Task Statement 1.1: Design and implement an incident response plan.
Knowledge of:
- AWS best practices for incident response (AWS Documentation: AWS Security Incident Response Guide)
- Cloud incidents
- Roles and responsibilities in the incident response plan (AWS Documentation: Define roles and responsibilities)
- AWS Security Finding Format (ASFF) (AWS Documentation: AWS Security Finding Format (ASFF))
Skills in:
- Implementing credential invalidation and rotation strategies in response to compromises (for example, by using AWS Identity and Access Management [IAM] and AWS Secrets Manager) (AWS Documentation: Automatically rotate IAM user access keys at scale with AWS Organizations and AWS Secrets Manager)
- Isolating AWS resources (AWS Documentation: Design isolated resource environments)
- Designing and implementing playbooks and runbooks for responses to security incidents (AWS Documentation: Develop and test security incident response playbooks)
- Deploying security services (for example, AWS Security Hub, Amazon Macie, Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Inspector, AWS Config, Amazon Detective, AWS Identity and Access Management Access Analyzer) (AWS Documentation: Security, identity, and compliance)
- Configuring integrations with native AWS services and third-party services (for example, by using Amazon EventBridge and the ASFF)
Task Statement 1.2: Detect security threats and anomalies by using AWS services.
Knowledge of:
- AWS managed security services that detect threats (AWS Documentation: Monitoring data security with managed AWS security services)
- Anomaly and correlation techniques to join data across services (AWS Documentation: Concepts for anomaly or outlier detection)
- Visualizations to identify anomalies
- Strategies to centralize security findings (AWS Documentation: Centralized Security Management)
Skills in:
- Evaluating findings from security services (for example, GuardDuty, Security Hub, Macie, AWS Config, IAM Access Analyzer) (AWS Documentation: AWS service integrations with AWS Security Hub)
- Searching and correlating security threats across AWS services (for example, by using Detective)
- Performing queries to validate security events (for example, by using Amazon Athena) (AWS Documentation: Querying AWS CloudTrail logs)
- Creating metric filters and dashboards to detect anomalous activity (for example, by using Amazon CloudWatch) (AWS Documentation: Using CloudWatch anomaly detection)
Task Statement 1.3: Respond to compromised resources and workloads.
Knowledge of:
- AWS Security Incident Response Guide (AWS Documentation: AWS Security Incident Response Guide)
- Resource isolation mechanisms (AWS Documentation: Design isolated resource environments)
- Techniques for root cause analysis (AWS Documentation: What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?)
- Data capture mechanisms (AWS Documentation: Capture data)
- Log analysis for event validation (AWS Documentation: Analyzing log data with CloudWatch Logs Insights)
Skills in:
- Automating remediation by using AWS services (for example, AWS Lambda, AWS Step Functions, EventBridge, AWS Systems Manager runbooks, Security Hub, AWS Config) (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Automation)
- Responding to compromised resources (for example, by isolating Amazon EC2 instances) (AWS Documentation: Remediating a potentially compromised Amazon EC2 instance)
- Investigating and analyzing to conduct root cause analysis (for example, by using Detective) (AWS Documentation: What is Amazon Detective?)
- Capturing relevant forensics data from a compromised resource (for example, Amazon Elastic Block Store [Amazon EBS] volume snapshots, memory dump) (AWS Documentation: Amazon EBS snapshots)
- Querying logs in Amazon S3 for contextual information related to security events (for example, by using Athena) (AWS Documentation: Querying AWS CloudTrail logs)
- Protecting and preserving forensic artifacts (for example, by using S3 Object Lock, isolated forensic accounts, S3 Lifecycle, and S3 replication) (AWS Documentation: Using S3 Object Lock)
- Preparing services for incidents and recovering services after incidents (AWS Documentation: Recovery)
Domain 2: Security Logging and Monitoring (18%)
Task Statement 2.1: Design and implement monitoring and alerting to address security events.
Knowledge of:
- AWS services that monitor events and provide alarms (for example, CloudWatch, EventBridge) (AWS Documentation: Alarm events and EventBridge)
- AWS services that automate alerting (for example, Lambda, Amazon Simple Notification Service [Amazon SNS], Security Hub) (AWS Documentation: Automated response and remediation)
- Tools that monitor metrics and baselines (for example, GuardDuty, Systems Manager)
Skills in:
- Analyzing architectures to identify monitoring requirements and sources of data for security monitoring (AWS Documentation: Designing and implementing logging and monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch)
- Analyzing environments and workloads to determine monitoring requirements (AWS Documentation: Perform an analysis on the workload demand)
- Designing environment monitoring and workload monitoring based on business and security requirements
- Setting up automated tools and scripts to perform regular audits (for example, by creating custom insights in Security Hub) (AWS Documentation: Custom insights)
- Defining the metrics and thresholds that generate alerts (AWS Documentation: Using Amazon CloudWatch alarms)
Task Statement 2.2: Troubleshoot security monitoring and alerting.
Knowledge of:
- Configuration of monitoring services (for example, Security Hub) (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Security Hub?)
- Relevant data that indicates security events (AWS Documentation: Logging and events)
Skills in:
- Analyzing the service functionality, permissions, and configuration of resources after an event that did not provide visibility or alerting (AWS Documentation: Refining permissions in AWS using last accessed information)
- Analyzing and remediating the configuration of a custom application that is not reporting its statistics (AWS Documentation: What Is AWS Config?)
- Evaluating logging and monitoring services for alignment with security requirements (AWS Documentation: Monitoring and Logging)
Task Statement 2.3: Design and implement a logging solution.
Knowledge of:
- AWS services and features that provide logging capabilities (for example, VPC Flow Logs, DNS logs, AWS CloudTrail, Amazon CloudWatch Logs) (AWS Documentation: Logging IP traffic using VPC Flow Logs)
- Attributes of logging capabilities (for example, log levels, type, verbosity) (AWS Documentation: AWS Lambda function logging in Python)
- Log destinations and lifecycle management (for example, retention period) (AWS Documentation: Managing your storage lifecycle)
Skills in:
- Configuring logging for services and applications (AWS Documentation: Configure service and application logging)
- Identifying logging requirements and sources for log ingestion
- Implementing log storage and lifecycle management according to AWS best practices and organizational requirements (AWS Documentation: Managing your storage lifecycle)
Task Statement 2.4: Troubleshoot logging solutions.
Knowledge of:
- Capabilities and use cases of AWS services that provide data sources (for example, log level, type, verbosity, cadence, timeliness, immutability) (AWS Documentation: AWS services for logging and monitoring)
- AWS services and features that provide logging capabilities (for example, VPC Flow Logs, DNS logs, CloudTrail, CloudWatch Logs) (AWS Documentation: Logging IP traffic using VPC Flow Logs)
- Access permissions that are necessary for logging (AWS Documentation: CloudWatch Logs permissions reference)
Skills in:
- Identifying misconfiguration and determining remediation steps for absent access permissions that are necessary for logging (for example, by managing read/write permissions, S3 bucket permissions, public access, and integrity) (AWS Documentation: Enabling Amazon S3 server access logging)
- Determining the cause of missing logs and performing remediation steps (AWS Documentation: Remediating security issues discovered by GuardDuty)
Task Statement 2.5: Design a log analysis solution.
Knowledge of:
- Services and tools to analyze captured logs (for example, Athena, CloudWatch Logs filter) (AWS Documentation: Logging and monitoring in Athena)
- Log analysis features of AWS services (for example, CloudWatch Logs Insights, CloudTrail Insights, Security Hub insights) (AWS Documentation: Analyzing log data with CloudWatch Logs Insights)
- Log format and components (for example, CloudTrail logs) (AWS Documentation: CloudTrail log file examples)
Skills in:
- Identifying patterns in logs to indicate anomalies and known threats (AWS Documentation: Log anomaly detection)
- Normalizing, parsing, and correlating logs (AWS Documentation: Parsing logs and structured logging)
Domain 3: Infrastructure Security (20%)
Task Statement 3.1: Design and implement security controls for edge services.
Knowledge of:
- Security features on edge services (for example, AWS WAF, load balancers, Amazon Route 53, Amazon CloudFront, AWS Shield) (AWS Documentation: How AWS WAF works with Amazon CloudFront features)
- Common attacks, threats, and exploits (for example, Open Web Application Security Project [OWASP] Top 10, DDoS)
- Layered web application architecture (AWS Documentation: Three-tier architecture overview)
Skills in:
- Defining edge security strategies for common use cases (for example, public website, serverless app, mobile app backend) (AWS Documentation: Identity and access management)
- Selecting appropriate edge services based on anticipated threats and attacks (for example, OWASP Top 10, DDoS)
- Selecting appropriate protections based on anticipated vulnerabilities and risks (for example, vulnerable software, applications, libraries) (AWS Documentation: Vulnerability Reporting)
- Defining layers of defense by combining edge security services (for example, CloudFront with AWS WAF and load balancers)
- Applying restrictions at the edge based on various criteria (for example, geography, geolocation, rate limit) (AWS Documentation: Restricting the geographic distribution of your content)
- Activating logs, metrics, and monitoring around edge services to indicate attacks (AWS Documentation: Metrics and alarms)
Task Statement 3.2: Design and implement network security controls.
Knowledge of:
- VPC security mechanisms (for example, security groups, network ACLs, AWS Network Firewall) (AWS Documentation: Security best practices for your VPC)
- Inter-VPC connectivity (for example, AWS Transit Gateway, VPC endpoints) (AWS Documentation: Amazon VPC-to-Amazon VPC connectivity options)
- Security telemetry sources (for example, Traffic Mirroring, VPC Flow Logs) (AWS Documentation: Logging IP traffic using VPC Flow Logs)
- VPN technology, terminology, and usage (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Site-to-Site VPN?)
- On-premises connectivity options (for example, AWS VPN, AWS Direct Connect) (AWS Documentation: AWS Direct Connect)
Skills in:
- Implementing network segmentation based on security requirements (for example, public subnets, private subnets, sensitive VPCs, on-premises connectivity)
- Designing network controls to permit or prevent network traffic as required (for example, by using security groups, network ACLs, and Network Firewall) (AWS Documentation: Control traffic to subnets using network ACLs)
- Designing network flows to keep data off the public internet (for example, by using Transit Gateway, VPC endpoints, and Lambda in VPCs) (AWS Documentation: What is a transit gateway?)
- Determining which telemetry sources to monitor based on network design, threats, and attacks (for example, load balancer logs, VPC Flow Logs, Traffic Mirroring) (AWS Documentation: Monitor your Network Load Balancers)
- Determining redundancy and security workload requirements for communication between on-premises environments and the AWS Cloud (for example, by using AWS VPN, AWS VPN over Direct Connect, and MACsec) (AWS Documentation: AWS Direct Connect)
- Identifying and removing unnecessary network access (AWS Documentation: Security best practices in IAM)
- Managing network configurations as requirements change (for example, by using AWS Firewall Manager) (AWS Documentation: Working with AWS Firewall Manager policies)
Task Statement 3.3: Design and implement security controls for compute workloads.
Knowledge of:
- Provisioning and maintenance of EC2 instances (for example, patching, inspecting, creation of snapshots and AMIs, use of EC2 Image Builder) (AWS Documentation: What is EC2 Image Builder?)
- IAM instance roles and IAM service roles (AWS Documentation: IAM roles)
- Services that scan for vulnerabilities in compute workloads (for example, Amazon Inspector, Amazon Elastic Container Registry [Amazon ECR]) (AWS Documentation: Scanning Amazon ECR container images with Amazon Inspector)
- Host-based security (for example, firewalls, hardening)
Skills in:
- Creating hardened EC2 AMIs (AWS Documentation: Create a custom Windows AMI)
- Applying instance roles and service roles as appropriate to authorize compute workloads (AWS Documentation: IAM roles for Amazon EC2)
- Scanning EC2 instances and container images for known vulnerabilities (AWS Documentation: Scanning Amazon EC2 instances with Amazon Inspector)
- Applying patches across a fleet of EC2 instances or container images (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager)
- Activating host-based security mechanisms (for example, host-based firewalls)
- Analyzing Amazon Inspector findings and determining appropriate mitigation techniques (AWS Documentation: Understanding findings in Amazon Inspector)
- Passing secrets and credentials securely to compute workloads (AWS Documentation: AWS security credentials)
Task Statement 3.4: Troubleshoot network security.
Knowledge of:
- How to analyze reachability (for example, by using VPC Reachability Analyzer and Amazon Inspector) (AWS Documentation: Getting started with Reachability Analyzer)
- Fundamental TCP/IP networking concepts (for example, UDP compared with TCP, ports, Open Systems Interconnection [OSI] model, network operating system utilities)
- How to read relevant log sources (for example, Route 53 logs, AWS WAF logs, VPC Flow Logs) (AWS Documentation: Logging IP traffic using VPC Flow Logs)
Skills in:
- Identifying, interpreting, and prioritizing problems in network connectivity (for example, by using Amazon Inspector Network Reachability) (AWS Documentation: Network Reachability)
- Determining solutions to produce desired network behavior (AWS Documentation: AWS Config Managed Rules)
- Analyzing log sources to identify problems (AWS Documentation: Analyzing log data with CloudWatch Logs Insights)
- Capturing traffic samples for problem analysis (for example, by using Traffic Mirroring) (AWS Documentation: What is Traffic Mirroring?)
Domain 4: Identity and Access Management (16%)
Task Statement 4.1: Design, implement, and troubleshoot authentication for AWS resources.
Knowledge of:
- Methods and services for creating and managing identities (for example, federation, identity providers, AWS IAM Identity Center [AWS Single Sign-On], Amazon Cognito) (AWS Documentation: Identity providers and federation)
- Long-term and temporary credentialing mechanisms (AWS Documentation: Use temporary credentials)
- How to troubleshoot authentication issues (for example, by using CloudTrail, IAM Access Advisor, and IAM policy simulator) (AWS Documentation: Troubleshooting AWS CloudTrail identity and access)
Skills in:
- Establishing identity through an authentication system, based on requirements (AWS Documentation: How IAM works)
- Setting up multi-factor authentication (MFA) (AWS Documentation: General steps for enabling MFA devices)
- Determining when to use AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) to issue temporary credentials (AWS Documentation: Requesting temporary security credentials)
Task Statement 4.2: Design, implement, and troubleshoot authorization for AWS resources.
Knowledge of:
- Different IAM policies (for example, managed policies, inline policies, identity-based policies, resource-based policies, session control policies) (AWS Documentation: Policies and permissions in IAM)
- Components and impact of a policy (for example, Principal, Action, Resource, Condition) (AWS Documentation: IAM JSON policy elements reference)
- How to troubleshoot authorization issues (for example, by using CloudTrail, IAM Access Advisor, and IAM policy simulator) (AWS Documentation: Troubleshooting AWS CloudTrail identity and access)
Skills in:
- Constructing attribute-based access control (ABAC) and role-based access control (RBAC) strategies (AWS Documentation: What is ABAC for AWS?)
- Evaluating IAM policy types for given requirements and workloads (AWS Documentation: Policy evaluation logic)
- Interpreting an IAM policy’s effect on environments and workloads (AWS Documentation: IAM policy elements: Variables and tags)
- Applying the principle of least privilege across an environment
- Enforcing proper separation of duties
- Analyzing access or authorization errors to determine cause or effect (AWS Documentation: Using AWS Identity and Access Management Access Analyzer)
- Investigating unintended permissions, authorization, or privileges granted to a resource, service, or entity (AWS Documentation: Managing access permissions for your AWS organization)
Domain 5: Data Protection (18%)
Task Statement 5.1: Design and implement controls that provide confidentiality and integrity for data in transit.
Knowledge of:
- TLS concepts (AWS Documentation: Transport Layer Security (TLS))
- VPN concepts (for example, IPsec) (AWS Documentation: What is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?)
- Secure remote access methods (for example, SSH, RDP over Systems Manager Session Manager) (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Session Manager)
- Systems Manager Session Manager concepts
- How TLS certificates work with various network services and resources (for example, CloudFront, load balancers) (AWS Documentation: TLS listeners for your Network Load Balancer)
Skills in:
- Designing secure connectivity between AWS and on-premises networks (for example, by using Direct Connect and VPN gateways) (AWS Documentation: AWS Direct Connect )
- Designing mechanisms to require encryption when connecting to resources (for example, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, CloudFront, Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, load balancers, Amazon Elastic File System [Amazon EFS], Amazon API Gateway) (AWS Documentation: Encrypting Amazon RDS resources)
- Requiring TLS for AWS API calls (for example, with Amazon S3) (AWS Documentation: Infrastructure security in Amazon S3)
- Designing mechanisms to forward traffic over secure connections (for example, by using Systems Manager and EC2 Instance Connect) (AWS Documentation: Connect using EC2 Instance Connect)
- Designing cross-Region networking by using private VIFs and public VIFs
Task Statement 5.2: Design and implement controls that provide confidentiality and integrity for data at rest.
Knowledge of:
- Encryption technique selection (for example, client-side, server-side, symmetric, asymmetric) (AWS Documentation: AWS KMS concepts)
- Integrity-checking techniques (for example, hashing algorithms, digital signatures) (AWS Documentation: Checking object integrity)
- Resource policies (for example, for DynamoDB, Amazon S3, and AWS Key Management Service [AWS KMS]) (AWS Documentation: Key policies in AWS KMS)
- IAM roles and policies (AWS Documentation: Policies and permissions in IAM)
Skills in:
- Designing resource policies to restrict access to authorized users (for example, S3 bucket policies, DynamoDB policies) (AWS Documentation: Examples of Amazon S3 bucket policies)
- Designing mechanisms to prevent unauthorized public access (for example, S3 Block Public Access, prevention of public snapshots and public AMIs) (AWS Documentation: Blocking public access to your Amazon S3 storage)
- Configuring services to activate encryption of data at rest (for example, Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, Amazon Simple Queue Service [Amazon SQS], Amazon EBS, Amazon EFS) (AWS Documentation: Encryption at rest in Amazon SQS)
- Designing mechanisms to protect data integrity by preventing modifications (for example, by using S3 Object Lock, KMS key policies, S3 Glacier Vault Lock, and AWS Backup Vault Lock) (AWS Documentation: Using S3 Object Lock)
- Designing encryption at rest by using AWS CloudHSM for relationaldatabases (for example, Amazon RDS, RDS Custom, databases on EC2 instances)
- Choosing encryption techniques based on business requirements (AWS Documentation: Creating an enterprise encryption strategy for data at rest)
Task Statement 5.3: Design and implement controls to manage the lifecycle of data at rest.
Knowledge of:
- Lifecycle policies
- Data retention standards
Skills in:
- Designing S3 Lifecycle mechanisms to retain data for required retention periods (for example, S3 Object Lock, S3 Glacier Vault Lock, S3 Lifecycle policy) (AWS Documentation: Managing your storage lifecycle)
- Designing automatic lifecycle management for AWS services and resources (for example, Amazon S3, EBS volume snapshots, RDS volume snapshots, AMIs, container images, CloudWatch log groups, Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager) (AWS Documentation: Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager)
- Establishing schedules and retention for AWS Backup across AWS services (AWS Documentation: Creating a backup plan)
Task Statement 5.4: Design and implement controls to protect credentials, secrets, and cryptographic key materials.
Knowledge of:
- Secrets Manager (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Secrets Manager?)
- Systems Manager Parameter Store (AWS Documentation: AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store)
- Usage and management of symmetric keys and asymmetric keys (for example, AWS KMS)
Skills in:
- Designing management and rotation of secrets for workloads (for example, database access credentials, API keys, IAM access keys, AWS KMS customer managed keys)
- Designing KMS key policies to limit key usage to authorized users (AWS Documentation: Key policies in AWS KMS)
- Establishing mechanisms to import and remove customer-provided key material (AWS Documentation: Importing key material for AWS KMS keys)
Domain 6: Management and Security Governance (14%)
Task Statement 6.1: Develop a strategy to centrally deploy and manage AWS accounts.
Knowledge of:
- Multi-account strategies (AWS Documentation: Organizing Your AWS Environment Using Multiple Accounts)
- Managed services that allow delegated administration (AWS Documentation: AWS services that you can use with AWS Organizations)
- Policy-defined guardrails
- Root account best practices (AWS Documentation: Root user best practices for your AWS account)
- Cross-account roles (AWS Documentation: Delegate access across AWS accounts using IAM roles)
Skills in:
- Deploying and configuring AWS Organizations (AWS Documentation: Creating and configuring an organization)
- Determining when and how to deploy AWS Control Tower (for example, which services must be deactivated for successful deployment) (AWS Documentation: Deploying AWS Control Tower in an AWS Landing Zone organization)
- Implementing SCPs as a technical solution to enforce a policy (for example, limitations on the use of a root account, implementation of controls in AWS Control Tower)
- Centrally managing security services and aggregating findings (for example, by using delegated administration and AWS Config aggregators) (AWS Documentation: How central configuration works)
- Securing AWS account root user credentials (AWS Documentation: AWS security credentials)
Task Statement 6.2: Implement a secure and consistent deployment strategy for cloud resources.
Knowledge of:
- Deployment best practices with infrastructure as code (IaC) (for example, AWS CloudFormation template hardening and drift detection) (AWS Documentation: AWS CloudFormation best practices)
- Best practices for tagging (AWS Documentation: Best Practices for Tagging AWS Resources)
- Centralized management, deployment, and versioning of AWS services
- Visibility and control over AWS infrastructure
Skills in:
- Using CloudFormation to deploy cloud resources consistently and securely (AWS Documentation: AWS CloudFormation best practices)
- Implementing and enforcing multi-account tagging strategies (AWS Documentation: Implementing and enforcing tagging)
- Configuring and deploying portfolios of approved AWS services (for example, by using AWS Service Catalog) (AWS Documentation: Automate AWS Service Catalog portfolio and product deployment by using AWS CDK)
- Organizing AWS resources into different groups for management (AWS Documentation: What are resource groups?)
- Deploying Firewall Manager to enforce policies (AWS Documentation: Working with AWS Firewall Manager policies)
- Securely sharing resources across AWS accounts (for example, by using AWS Resource Access Manager [AWS RAM]) (AWS Documentation: Shareable AWS resources)
Task Statement 6.3: Evaluate the compliance of AWS resources.
Knowledge of:
- Data classification by using AWS services (AWS Documentation: Data classification overview)
- How to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of AWS resources (for example, by using AWS Config) (AWS Documentation: Evaluating Resources with AWS Config Rules)
Skills in:
- Identifying sensitive data by using Macie (AWS Documentation: Discovering sensitive data with Amazon Macie)
- Creating AWS Config rules for detection of noncompliant AWS resources (AWS Documentation: Remediating Noncompliant Resources with AWS Config Rules)
- Collecting and organizing evidence by using Security Hub and AWS Audit Manager (AWS Documentation: Reviewing the evidence in an assessment)
Task Statement 6.4: Identify security gaps through architectural reviews and cost analysis.
Knowledge of:
- AWS cost and usage for anomaly identification (AWS Documentation: Getting started with AWS Cost Anomaly Detection)
- Strategies to reduce attack surfaces (AWS Documentation: Attack surface reduction)
- AWS Well-Architected Framework (AWS Documentation: AWS Well-Architected Framework)
Skills in:
- Identifying anomalies based on resource utilization and trends (AWS Documentation: Using CloudWatch anomaly detection)
- Identifying unused resources by using AWS services and tools (for example, AWS Trusted Advisor, AWS Cost Explorer) (AWS Documentation: Analyzing your costs with AWS Cost Explorer)
- Using the AWS Well-Architected Tool to identify security gaps (AWS Documentation: Security in AWS Well-Architected Tool)
AWS Cheat Sheet
The AWS cheat sheet incorporates the list of basic terms in the AWS landscape. The basic terms include AWS services and information about AWS and cloud computing. Any AWS terminology cheat sheet would include details about AWS (Amazon Web Services) and cloud computing.
Cloud Computing and Services
The AWS cheat sheet provides details about cloud computing and its different forms. Cloud computing is like using the internet for computing, with many remote servers. It’s helpful for storing data centrally and accessing computer services. Cloud computing mainly comes in three types: public, private, and hybrid cloud.
- First things first, the public cloud comprises a third-party service distributor giving resources and services to customers through the internet.
- After this, the private cloud involves the provision and management of resources and services specifically for a particular company.
- Subsequently, a hybrid cloud is an amalgamation of both public and private cloud traits.
AWS Influence
AWS influence plays an essential role in the formation of the AWS Cloud Practitioner cheat sheet. This helps to achieve a clear and better insight into the upshot of AWS and its potential trends in the near future. Nowadays, almost every association with a computer could have a use case relevant to AWS services. This is a clear indication that AWS is a trustworthy alternative for conventional solutions such as with S3 Glacier.
Initially started as a cloud-based solution for storage and computing services, AWS is now applicable to almost every area such as databases, business productivity, virtual desktops, IoT development, machine learning, and analytics. Furthermore, AWS offers better adaptability for the growth of startups with limited resources for funding traditional datacenter deployments.
AWS Region, AZs, Edge locations
One of the essential phrases in the AWS glossary is the AWS regions. These entries in the AWS cheat sheet notify about all crucial aspects of the AWS landscape.
- First thing first, every region is a separate geographic area, completely independent, isolated from the other regions. Also, helps in achieving the greatest possible fault tolerance and stability.
- Secondly, the interaction between regions is across the public Internet.
- Subsequently, all-regions have multiple Availability Zones.
- After this, each and every AZ is actually isolated, geographically separated from each other and outlined as an independent failure zone
- Moreover, AZs are united with low-latency private links (not public internet)
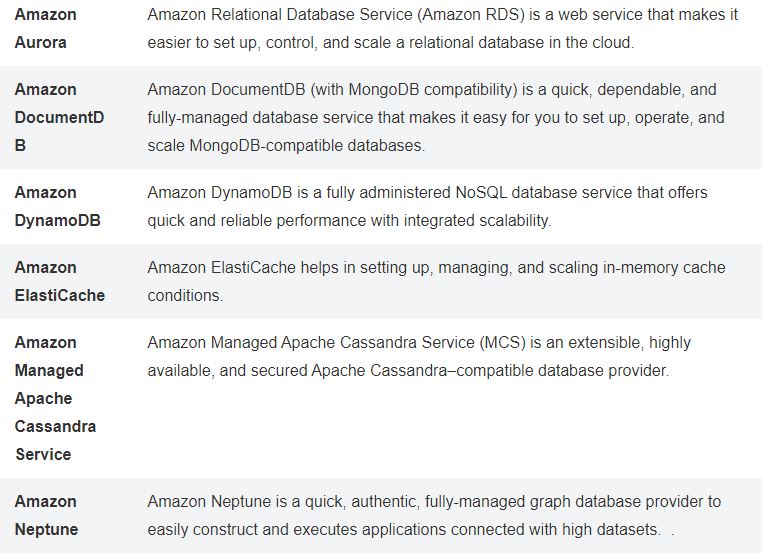
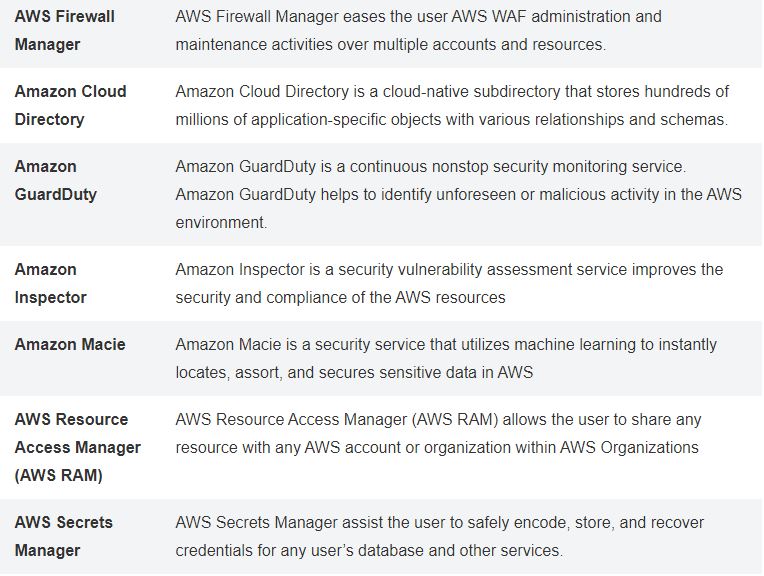
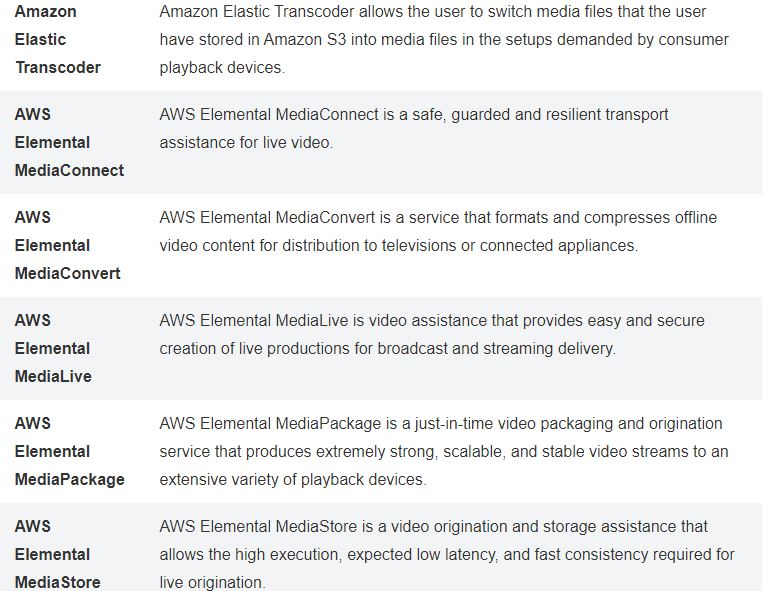
AWS Services
- Compute
- Storage
- Database
- Developer Tools
- Security, Identity, & Compliance
- Cryptography & PKI
- Machine Learning
- Management & Governance
- Migration & Transfer
- Mobile
- Networking & Content Delivery
- Media Services
- End-User Computing
- Analytics
- Application Integration
- Business Applications
- Satellite
- Robotics
- Blockchain
- Game Development
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Customer Enablement Services
- Customer Engagement
- AR & VR
- SDKs & Toolkits
- General Reference
- AWS Management Console
- Additional Resources









Expert’s Corner
To conclude, AWS is a strong pillar that can help you produce a stable career in the field of Information Technology. There is nothing wrong to say that AWS certification is a great opportunity to enhance your skills and experience. It not only provides you a reputed position in your company but also offers you higher pay in comparison to your other peers.
The above article featuring AWS Certified Security-Specialty is an initiative taken in consideration of the increasing demand for the exam. The article addresses every important detail which is of supreme importance. Although, the exam is not tough as it mainly covers features and services which you would have used in your day to day working on AWS or services which have a clear demarcation of their purpose. All you need is a focussed mindset and proper preparation to sweep through the exam easily.
Still got questions? Feel free to ask. We would love to hear from you.
Build your knowledge and technical expertise with advanced learning skills and expert tutorials on AWS Certified Security-Specialty. Prepare and become a Certified Now!


