ISO 9001 Lead Implementer

The “ISO 9001 Lead Implementer” certification is for individuals who want to show their ability to demonstrate their competence in implementing a quality management system and leading an implementation team. The aim of the “PECB ISO 9001 Lead Implementer” exam is to verify that the candidate possesses the required skills to assist an organization in setting up, executing, overseeing, and sustaining a Quality Management System (QMS).
ISO 9001 outlines the rules for creating, running, sustaining, and consistently bettering a quality management system (QMS). A QMS following ISO 9001 helps companies consistently deliver products and services that meet customer needs. It also supports an organization’s processes, resources, assets, and values to boost customer satisfaction and enhance overall efficiency.
A QMS based on ISO 9001 consists of connected processes and procedures that help an organization reach its quality goals. Additionally, it requires strong leadership and commitment from top management to instill a culture of quality and integrate it into daily operations.
Prerequisite:
Requirements for enrolling in this exam include a foundational understanding of ISO management system standards, a general grasp of ISO 9001, and familiarity with MS implementation principles. Additionally, having knowledge of ISO’s quality management principles can enhance the learning experience. Further, candidates must have a total of five years of experience with two years of work experience in Quality Management and project activities of a total of 300 hours.
Target Audience:
The ISO 9001 Lead Implementer certification is designed for:
- Managers or consultants actively engaged in and responsible for implementing a quality management system within an organization.
- Project managers, consultants, or expert advisers aspiring to excel in the implementation of a quality management system.
- Individuals tasked with ensuring compliance with ISO 9001 requirements in an organization.
- Members of a QMS implementation team.
What you will learn?
Upon completion of this certification, participants will possess the capability to:
- Clearly articulate the fundamental concepts and principles of a Quality Management System (QMS) grounded in ISO 9001.
- Understand and interpret ISO 9001 requirements for a QMS through the lens of an implementer.
- Commence and strategize the implementation of a QMS based on ISO 9001, employing PECB’s IMS2 Methodology and other recognized best practices.
- Provide assistance to an organization in effectively managing, sustaining, and continually enhancing a QMS based on ISO 9001.
- Prepare an organization to successfully undergo a third-party certification audit.
Exam Details

The ISO 9001 Lead Implementer exam consists of 80 questions. This multiple-choice test assesses candidates’ understanding of both simple and complex concepts. It includes stand-alone questions, which are independent of any context, and scenario-based questions, which are context-dependent. In scenario-based questions, candidates read a situation and answer five related questions.
To answer both types of questions, candidates must apply concepts and principles learned in the training course, analyze problems, identify and evaluate alternatives, and combine various concepts or ideas. Achieving a minimum score of 70% is required to pass the exam. The exam is open-book, and candidates can use reference materials such as a hard copy of the ISO 9001 standard, training course materials (accessible through the PECB Exams app and/or printed), personal notes from the training course, and a hard copy dictionary.
Candidates can take the exam without attending the training course, with different prices applicable for each type:
- Lead Exam: $1000
- Manager Exam: $700
- Foundation Exam: $500
- Transition Exam: $500
The certification application fee is $500.
Course Outline
The exam covers the following domains:
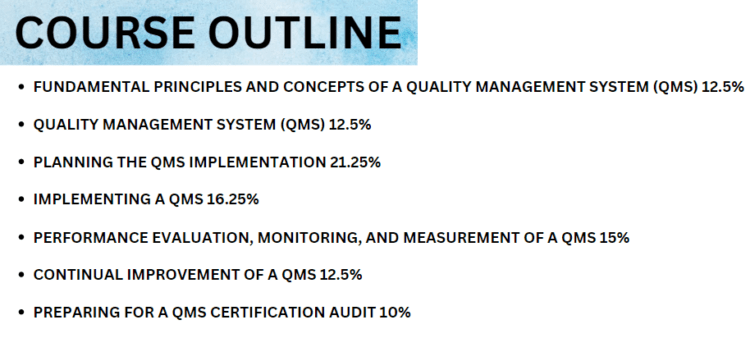
Domain 1: Understanding basic principles and concepts of a quality management system (QMS)
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Explain what a management system is
- Explain the main concepts of the quality management system
- Explain the connection between management, quality management, and QMS
- Differentiate the main standards in the ISO 9000 series
- Communicate the benefits of implementing a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Explain the common misconceptions about ISO 9001
- Explain other quality management methods and techniques
- Explain the evolution of quality paradigms
- Provide a coherent definition of quality
- Describe the importance of quality
- Explain the quality management principles presented in ISO 9001
- Describe the role and usage of process approach in a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Explain the role of the Plan-Do-CheckAct (PDCA) cycle in a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Explain risk-based thinking
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- ISO’s definition for a management system
- ISO 9000’s definition of a quality management system
- Main concepts related to management, quality management, and QMS
- Main standards in the ISO 9000 series, their applicability, and relationship between the standards
- Benefits of implementing a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Common misconceptions about ISO 9001
- Other quality management methods and techniques
- Evolution of the quality paradigms
- ISO 9000’s definition of quality
- Importance of quality
- Seven quality management principles set out by ISO 9001
- Role of the process approach in a QMS based on ISO 9001
- PDCA cycle and its role in ISO 9001
- Concept of risk-based thinking and its usage in ISO 9001
Domain 2: Undersand Quality management system (QMS) and ISO 9001 requirements
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Explain the difference between the QMS implementation project and daily QMS operations
- Explain the main approaches for a QMS implementation project
- Initiate the QMS implementation project
- Describe the competencies of a QMS project manager
- Explain the importance of a business case on the implementation of a QMS
- Utilize PECB’s IMS2 methodology for the QMS implementation project
- Utilize best practices for the implementation project
- Communicate the ultimate objectives of a QMS implementation project
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Differences between the QMS implementation project and day-to-day management of the QMS
- Implementation approaches for a QMS
- Competencies of a QMS project manager, beside the knowledge of the ISO 9001 requirements
- Advantages and disadvantages of a QMS project manager being an employee or an external consultant
- Business case on the QMS implementation, and its components
- PECB IMS2 methodology for the QMS implementation project
- Best practices for a QMS implementation project
- Objectives of a QMS implementation project, regardless of the approach used
Domain 3: Learn about planning the QMS implementation
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Explain the role of top management with respect to the quality management system
- Interpret the information required to establish a quality policy
- Identify the roles and responsibilities of key interested parties during the implementation and operation of a QMS
- Determine the internal and external context of an organization
- Perform a gap analysis
- Define and justify a QMS scope specific to the organization’s quality objectives
- Perform the different processes of the risk assessment
- Set relevant quality objectives
- Plan, initiate, and carry out change with regard to the QMS
- Determine the optimal resources needed for an effective QMS implementation and operation
- Determine the competencies needed for the QMS operation
- Raise awareness among the persons doing work under the organization’s control with regard to the QMS
- Communicate relevant information to support the QMS and the achievement of quality objectives
- Ensure that the organization properly controls for maintaining QMS documented information
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Main activities required by top management with respect to the quality management system
- Importance of leadership and commitment to ensure QMS effectiveness
- Main attributes of a quality policy
- Process for drafting a quality policy
- Methods of communicating a quality policy
- Main organizational structures applicable for an organization to manage a QMS
- What typically constitutes an organization’s internal and external context
- Approaches used to understand the context of an organization
- Techniques used to gather information about an organization and to perform a gap analysis of a management system
- Characteristics of a QMS scope in terms of organizational, technological, and physical boundaries
- Different approaches and methodologies used to perform the risk assessment process
- Typical quality and QMS objectives and how to achieve specific results
- Tools that facilitate the change management process
- Typical resources required for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of a quality management system
- Competence analysis approaches and training programs
Domain 4: Learn how to implement an QMS
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Plan, implement, and control the processes needed for the provision of products and services
- Establish mechanisms through which the organization engages in communication activities
- Plan and implement a complaintshandling process
- Establish the necessary processes for determining the requirements for products and services
- Implement and maintain a design and development process
- Determine the requirements for products and services
- Explain the typical reasons for outsourcing and main risks associated with it
- Establish measures to control externally provided processes, products, and services
- Establish measures and controls through which an organization can provide its products and services under controlled conditions
- Implement controls for the protection of property belonging to customers or external providers
- Establish processes and controls through which the organization ensures the preservation of outputs during production and service provision
- Control the nonconforming outputsDetermine the requirements for postdelivery activities
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Requirements for the provision of products and services
- Details to be included when communicating with customers
- Methods and tools for an effective communication with customers
- Principles upon which the complaints-handling process must be established
- Approaches used for determining the requirements for products and services
- Design and development approaches and methods, including planning, inputs/outputs, controls, and changes
- Typical reasons for outsourcing and risks associated with it
- Type and extent of controls for externally provided processes, products, and services
- Controlled conditions for production and service provision
- Controls used for the protection of property belonging to customers or external providers
- Typical processes and controls used for the preservation of outputs during production and service provision
- Requirements for dealing with nonconforming outputs
- Typical requirements for post-delivery activities and approaches to meet those requirements
Domain 5: Understand monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of a QMS
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of a QMS
- Explain the main terms related to QMS performance
- Determine measurement objectives
- Establish performance measures that are related to the organization’s quality objectives
- Determine the methods for monitoring customer satisfaction
- Verify to what extent the identified QMS objectives have been met
- Establish key performance indicators
- Define and implement a QMS internal audit program
- Establish mechanisms through which top management performs regular and methodical reviews to ensure the suitability, adequacy, effectiveness, and efficiency of a QMS
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Best practices and techniques used to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of a QMS
- Main terms related to QMS performance: monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation
- Measurement objectives in the context of a QMS
- Methodologies for determining effective performance measures
- Methods used for monitoring customer perceptions
- Appropriate data gathering methods
- Attributes of key performance indicators and steps for using them
- Main concepts and components related to the implementation and operation of a QMS internal audit program
- Best practices used to perform management reviews
Domain 6: Learn about the continual improvement of a QMS
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Determine the processes through which an organization treats nonconformities
- Identify and analyze the root causes of nonconformities, and propose action plans to treat them
- Continually improve the effectiveness and efficiency of a QMS
- Implement continual improvement processes in an organization
- Determine the appropriate tools to support the continual improvement of processes of an organization
- Implement necessary measures for documenting improvements in a QMS
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Requirements for treating nonconformities
- Approaches, tools, and techniques used to identify the root causes of nonconformities
- Process for treating nonconformities
- Approaches used to develop corrective action plans
- Processes related to the continual monitoring of change factors
- Maintenance and improvement of a QMS
- Typical approaches used for documenting improvements in a QMS
Domain 7: Learn how to prepare for a QMS certification audit
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Describe the main steps, processes, and activities related to the QMS certification audit
- Explain a QMS certification audit based on the evidence-based approach
- Assist organizations in identifying and selecting the most suitable certification body that meets their needs and expectations
- Determine whether an organization is ready and prepared for the QMS certification audit
- Train and prepare an organization’s personnel for the QMS certification audit
- Discuss and challenge the audit findings and conclusions with external auditors
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Evidence-based approach audit
- Types of audit and their differences
- Differences between Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits
- Stage 1 audit requirements, steps, and activities
- Documented information review criteria
- Stage 2 audit requirements, steps, and activities
- Audit follow-up requirements, steps, and activities
- Surveillance audits and recertification audit requirements, steps, and activities Requirements, guidelines, and best practices for developing action plans following a QMS certification audit
ISO 9001 Lead Implementer Exam FAQs
Exam Policies
PECB has specific policies regarding its exams, including the following:
Exam Taking Rules:
Candidates must be present at least 30 minutes before the exam commences. Late arrivals will not receive extra time and may be denied entry to the exam. Candidates must bring a valid ID card (national ID, driver’s license, or passport) and show it to the invigilator. The exam lasts for one hour. For Foundation exams taken in a non-native language (paper-based), an additional 10 minutes can be granted upon request on the exam day.
PECB Exam Format and Types:
PECB offers two types of exam formats:
- Paper-based: Exams are provided on paper; candidates can only use the exam paper and a pen. Electronic devices like laptops, tablets, or phones are not allowed. The exam is supervised by a PECB-approved Invigilator at the training course location organized by the Partner.
- Online: Exams are electronically delivered through the PECB Exams application. The use of electronic devices, such as tablets and cell phones, is prohibited. The exam session is remotely supervised by a PECB Invigilator via the PECB Exams application and an external/integrated camera.
Exam Results:
Candidates will receive their exam results through email. The timeframe for result communication varies; it takes three to eight weeks for essay-type exams and two to four weeks for multiple-choice paper-based exams, while online multiple-choice exam results are provided instantly. Successfully passing the exam allows candidates to apply for one of the credentials within the respective certificate program.
Exam Retake Policy:
Candidates have the opportunity to retake the exam multiple times, but there are certain restrictions regarding the time intervals between retakes. If a candidate does not pass the exam on the first attempt, they must wait for 15 days after the initial exam date for the next attempt (1st retake).
ISO 9001 Lead Implementer Exam Study Guide

1. PECB Training Course
The PECB ISO 9001 Lead Implementer is a five-day training course designed to help participants acquire the skills needed to establish, implement, operate, maintain, and continually improve a Quality Management System (QMS). This course aims to provide an in-depth understanding of ISO 9001 requirements, along with best practices and approaches for QMS implementation and maintenance.
Attending this course enables individuals to assist organizations in adopting a structured, evidence-based approach to manage the quality of their products and services. Additionally, participants will gain insights into the significance of customer focus and the benefits of establishing an organizational culture that promotes and supports quality.
The ISO 9001 Lead Implementer training course is suitable for:
- Personnel responsible for maintaining and improving the quality of the organization’s products and services.
- Personnel responsible for meeting customer requirements.
- Consultants, advisors, and professionals seeking in-depth knowledge of ISO 9001 requirements for a QMS.
- Professionals looking to familiarize themselves with PECB’s IMS2 Methodology for QMS implementation.
- Individuals responsible for ensuring QMS conformity to ISO 9001 requirements.
- Members of QMS implementation and operation teams.
- Individuals aspiring to pursue a career in quality management.
2. PECB Elearning
PECB’s eLearning training courses are tailored to individual needs, addressing spatial and temporal constraints. This ensures an exceptional learning experience with engaging and high-quality courses across various fields. As we pave the way for a future without physical barriers, you can begin on a learning journey. Here are compelling reasons to consider PECB eLearning Training Courses:
- Learn at your own pace, at a time that suits you.
- Choose courses based on your specific needs and preferences.
- Access online resources, training courses, and pertinent information.
- Benefit from premium and interactive content presented by various experts.
- Save on expenses by taking courses from the comfort of your chosen environment.
3. Utilize the Exam Handbook
Obtain all essential details about the ISO 9001 Lead Implementer exam from the candidate handbook. This guide serves as your primary reference, offering information on the exam’s structure, format, topics, rules, and more. It consolidates all necessary information for your exam preparation in one convenient place, making it a valuable resource. Thoroughly review the handbook to familiarize yourself with the exam, enhancing your chances of success.
4. Engage in Practice Tests
Taking practice tests for the ISO 9001 Lead Implementer exam is a strategic and efficient approach to readiness. These practice exams closely resemble the actual test, allowing you to acclimate to the format, question types, and time constraints. They help you identify strengths and areas needing improvement, enabling targeted study efforts. Leverage this valuable resource to boost exam preparedness, increase familiarity with the material, and enhance your likelihood of success.



