ISO 9001 Lead Auditor

The “ISO 9001 Lead Auditor” certification is for those who want to prove they have the skills to audit a quality management system and lead an audit team. Key market skills include the ability to efficiently plan and conduct audits following the certification process, apply audit techniques and practices, and manage or contribute to audit teams and programs.
Target Audience:
The ISO 9001 Lead Auditor certification is designed for:
- Auditors who want to conduct and lead QMS audits on behalf of certification bodies.
- Professionals interested in adopting PECB’s AMS2 Methodology for audit conduct.
- Individuals accountable for ensuring conformity to ISO 9001 requirements.
- Technical experts aiming to get ready for a QMS audit.
- Professionals aspiring to build a career in conformity assessment.
Prerequisite:
- For this certification, you need a basic grasp of ISO 9001 requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and a thorough understanding of audit principles.
- Experience of five years with two years of work experience in Quality Management Audit activities and a total of 300 hours in MS audit/assessment experience.
What you will learn?
Upon completion of this, the participant will have the capability to:
- Clarify the fundamental concepts and principles of a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001.
- Interpret ISO 9001 requirements for a QMS as viewed by an auditor.
- Assess QMS conformity to ISO 9001 requirements using essential audit concepts and principles.
- Strategically plan, execute, and conclude an ISO 9001 compliance audit in line with ISO/IEC 17021-1 standards, ISO 19011 guidelines, and other auditing best practices.
- Effectively manage an ISO 9001 audit program.
Exam Details

The ISO 9001 Lead Auditor exam consists of a total of 80 questions. The exam is available in multiple-choice. This assesses candidates’ understanding of both simple and complex concepts. It includes stand-alone questions and scenario-based questions. Stand-alone questions are independent, while scenario-based questions are context-dependent, requiring candidates to read a scenario and answer five related questions. Answers involve applying concepts from the training course, analyzing problems, and evaluating alternatives. Each multiple-choice question presents three options: one correct response (keyed response) and two incorrect responses (distractors).
This is an open-book exam, allowing candidates to use:
- A hard copy of the ISO 9001 standard
- Training course materials (accessed through the PECB Exams app and/or printed)
- Personal notes from the training course (accessed through the PECB Exams app and/or printed)
- A hard-copy dictionary
To pass the exam, you need a score of at least 70%. Make sure to arrive at least 30 minutes before the exam begins; late arrivals won’t get extra time and might not be allowed to take the exam. Bring a valid ID (national ID, driver’s license, or passport) and show it to the invigilator. For those taking paper-based exams, additional time may be given if you’re taking the exam in a non-native language:
- 10 extra minutes for Foundation exams
- 20 extra minutes for Manager exams
- 30 extra minutes for Lead exams
PECB offers two exam formats:
- Paper-based: No electronic devices are allowed, and the exam is supervised by an approved invigilator.
- Online: Conducted via the PECB Exams application, supervised remotely by a PECB Invigilator using a camera.
You can take the exam without attending the training course, and the fees are as follows:
- Lead Exam: $1000
- Manager Exam: $700
- Foundation Exam: $500
- Transition Exam: $500
The certification application fee is $500.
Course Outline
The content of the exam is as follows:
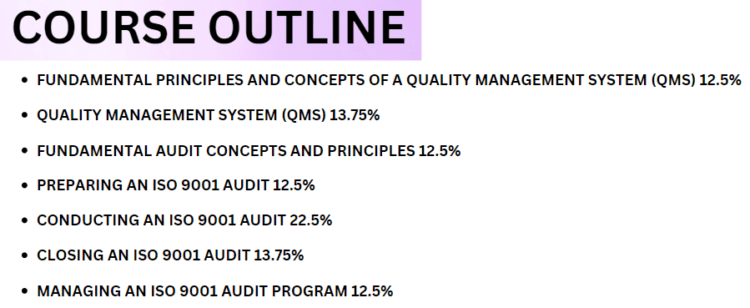
Domain 1: Understand the fundamental principles and concepts of a quality management system (QMS)
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate can explain and apply ISO 9001 principles and concepts.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Describe the applicability and scope of ISO 9001
- Explain the connection between ISO 9001 and other ISO standards, such as ISO 9001, ISO/TS 9002, ISO 9004, etc.
- Communicate the advantages of implementing a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Counterargument common misconceptions about ISO 9001
- Explain what a management system is
- Define what quality management system is
- Describe ISO’s quality management principles
- Explain what an integrated management system is and how it can help an organization
- Describe the determinants of product and service quality
- Explain the process approach and its role in a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Describe the role of Plan-Do-CheckAct (PDCA) cycle and risk-based thinking in a QMS based on ISO 9001
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- ISO 9001 scope and its applicability
- Relationship between ISO 9001 and other ISO standards
- Advantages of implementing a QMS based on ISO 9001
- Common misconceptions about ISO 9001
- Components of a management system
- Main concepts and terminology related to QMS and ISO 9001
- Principal characteristics of an integrated management system
- Seven ISO quality management principles
- Determinants of product and service quality
- Process approach and its inclusion in the ISO 9001 requirements for a QMS
- Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle and risk-based thinking and their role in a QMS based on ISO 9001
Domain 2: Learn about Quality management system (QMS) and ISO 9001 requirements
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate can identify and explain the requirements for a quality management system based on ISO 9001.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Understand the ISO 9001 requirements and the structure of the standard
- Describe the standard’s requirements with regard to the context of the organization, interested parties, and QMS scope (clause 4)
- Validate the degree to which the top management has demonstrated leadership and commitment, analyze the quality policy,and ability to identify the separation of the roles and responsibilities related to the QMS (clause 5)
- Identify risks and opportunities and to validate the appropriateness of quality objectives (clause 6)
- Analyze whether sufficient resources are available to implement, operate, and maintain the QMS (clause 7)
- Determine the effectiveness of the processes and controls established as part of the QMS (clause 8)
- Use monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation to support the effective management of the QMS (clause 9)
- Determine if appropriate actions were taken when nonconformities occurred and to analyze the actions taken to continually improve the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the QMS (clause 10)
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Requirements of ISO 9001 for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a QMS
- Common external and internal issues that affect the context of an organization and approaches to establishing the scope
- Requirements with regard to top management’s involvement in the QMS, establishment of the quality policy, and definition of roles and responsibilities
- Approaches used in risk management and strategies used in establishing objectives
- Required resources, competences, awareness, and documented information for an effective QMS
- Requirements for operational planning and control
- Approaches, techniques, and methods used for the monitoring, measurement, analysis, evaluation, internal audits, and management reviews
- Requirement and approaches to dealing with nonconformities and initiating corrective actions, as well as the methods to continually improve a QMS
Domain 3: Basic audit concepts and principles
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate has skills for interpreting and applying the main concepts and principles related to a QMS audit.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Understand, explain, and illustrate the application of the audit principles in a QMS audit
- Differentiate between first, second, and third party audits
- Identify and judge situations that would discredit the professionalism of the auditor and violate the PECB Code of Ethics
- Identify and judge ethical issues considering the obligations related to the audit client, auditee, law enforcement, and regulatory authorities
- Determine and evaluate the level of materiality and apply a risk-based approach during the different stages of a QMS audit
- Judge the appropriate level of reasonable assurance needed for a QMS audit
- Understand the legal implications related to any irregularities committed by the auditee
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Main audit concepts and principles as described in ISO 19011
- Differences between first, second, and third party audits
- Principles of auditing: integrity, fair presentation, due professional care, confidentiality, independence, evidencebased approach, and risk-based approach
- Auditor’s professional responsibility and the PECB Code of Ethics
- Risk-based approach to an audit and the different types of risks related to audit activities, such as inherent risk, control risk, and detection risk
- Concept of materiality and its application to an audit
- Concept of reasonable assurance and its application to an audit
- Laws and regulations applicable to the auditee and the country it operates in, etc.
Domain 4: Learn how to prepare an ISO 9001 audit
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate can prepare a quality management system audit.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Understand and illustrate the steps and activities to prepare a QMS audit considering the specific context of the audit
- Explain and compare evidence types and their characteristics
- Determine and justify the type and amount of evidence required in a QMS audit
- Understand and explain the roles and responsibilities of the audit team leader, audit team members, and technical experts
- Determine and evaluate the level of materiality during the different stages of a QMS audit
- Determine the audit feasibility
- Determine, evaluate, and confirm the audit objectives, criteria, and scope for a QMS audit
- Explain, illustrate, and define the characteristics of the terms of the audit engagement and apply the best practices to
establish the initial contact with an auditee - Develop audit working papers and elaborate appropriate audit test plans in a QMS audit
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Main responsibilities of the audit team leader and audit team members
- Roles and responsibilities of technical experts
- Audit objectives, scope, and criteria
- Difference between a QMS scope and the audit scope
- Factors to take into account during the audit feasibility study
- Cultural aspects to consider in an audit
- Characteristics of terms of the audit engagement and the best practices to establish initial contact with an auditee
- Audit plan preparation procedure
- Preparation and development of audit working papers
- Different types of audit evidence: physical, mathematical, confirmative, technical, analytical, documentary, and verbal
- Best practices for the creation of audit test plans
Domain 5: Understand methods for conducting an ISO 9001 audit
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate know how to conduct a QMS audit.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Conduct the stage 1 audit, taking into account the documented information evaluation criteria
- Organize and conduct an opening meeting
- Conduct the stage 2 audit by appropriately following the procedures that this stage entails
- Apply the best practices of communication to collect the appropriate audit evidence
- Consider the roles and responsibilities of all the interested parties involved
- Explain, illustrate, and apply evidence collection procedures and tools
- Explain, illustrate, and apply the main audit sampling methods
- Gather appropriate evidence from the available information during an audit and evaluate it objectively
- Explain, illustrate, and apply the audit evidence approach in a QMS audit
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Objectives and the content of the opening meeting in an audit
- Difference between stage 1 audit and stage 2 audit
- Stage 1 audit requirements, steps, and activities
- Documented information evaluation criteria and ISO 9001 requirements
- Stage 2 audit requirements, steps, and activities
- Best communication practices during an audit
- Roles and responsibilities of guides and observers during an audit
- The different conflict resolution techniques
- Evidence collection procedures and tools, such as interview, documented information review, observation, analysis, sampling, and technical verification
- Evidence analysis techniques (i.e., corroboration and evaluation)
- Main concepts, principles, and evidence collection procedures used in an audit
- Advantages and disadvantages of using audit checklists
Domain 6: Learn about closing an ISO 9001 audit
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate can conclude a QMS audit and conduct audit follow-up activities.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Explain and apply the evidence evaluation process: drafting audit findings and preparing audit conclusions
- Understand, explain, and illustrate the concept of the benefit of the doubt
- Report appropriate audit observations in accordance with audit rules and principles
- Conduct quality reviews to audit documentation
- Draft and present audit conclusions
- Complete audit working documents
- Organize and conduct a closing meeting
- Write an audit report and justify the recommendation for certification
- Conduct the activities following an initial audit, including the evaluation of action plans, audit follow-ups, and surveillance activities
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- The evidence evaluation process: to draft audit findings and to prepare audit conclusions
- Characteristics and differences between the concepts of conformity, minor nonconformity, major nonconformity, anomaly, and observation
- Guidelines and best practices to draft nonconformity reports
- Guidelines and best practices to draft and report audit observations
- Benefit of the doubt and its application in the management system audits
- Guidelines and best practices to complete audit working documents and perform a quality review
- Guidelines and best practices to present audit findings and conclusions to the management of an audited organization
- Possible recommendations an auditor can give during the certification audit
- Guidelines and best practices to evaluate action plans
- Audit follow-ups, surveillance audits, and recertification audit requirements, steps, and activities
- Conditions for the modification, extension, suspension, or withdrawal of an organization’s certification
Domain 7: Learn about managing ISO 9001 audit program
Main objective: Ensuring that the candidate can establish and manage a QMS audit program.
Competencies:
- Ability to:
- Understand and explain the establishment of an audit program and the application of the PDCA cycle into an audit program
- Explain the importance of protecting the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of audit records and the auditors’ responsibilities in this regard
- Understand the documented information management process
- Understand the process of evaluating the efficiency of the audit program by monitoring the performance of each auditor and audit team member
- Demonstrate the application of the personal attributes and behaviors
Knowledge statements:
- Knowledge of:
- Application of the PDCA cycle in the management of an audit program
- Requirements, guidelines, and best practices regarding audit resources, procedures, and policies
- Requirements, guidelines, and best practices regarding the management of audit records
- Management of combined audits
- Personal attributes and behaviors of a professional auditor
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Exam FAQs
Exam Policies
Some of the PECB Exam policies are:
Exam Results:
The communication of exam results is done through email. The timeframe for receiving results is within three to eight weeks for essay-type exams and two to four weeks for multiple-choice paper-based exams, starting from the exam date. Online multiple-choice exam results are instantly provided. Successful candidates can apply for one of the credentials in the respective certification scheme. For those who don’t pass, the email includes a list of domains where improvement is needed to guide preparation for a retake.
Exam Retake Policy:
Candidates can retake the exam without a set limit, but there are time constraints. After the first attempt, a 15-day waiting period is required before the next attempt (1st retake). If a candidate fails the first attempt after completing a training course with a partner, they can retake the exam for free within 12 months (the training course fee covers the first attempt and one retake). Otherwise, retake fees apply. PECB recommends attending a training course for better preparation after a failed retake.
Renewing the Certification:
PECB certifications are valid for three years. Certified professionals must meet requirements related to the designated credential, including fulfilling the required number of continual professional development (CPD) hours and paying an annual maintenance fee of $120 to maintain their certification.
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Study Guide

1. Use the ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Training Course:
The PECB ISO 9001 Lead Auditor training equips you to conduct quality management system (QMS) audits effectively. You’ll learn essential audit principles, procedures, and techniques following ISO/IEC 17021-1 and ISO 19011 standards. The course integrates these with auditing best practices to create a comprehensive methodology for planning, executing, and concluding ISO 9001 conformity assessment audits.
Beyond theory, the training includes practical elements like examples, exercises, and quizzes. These cover crucial aspects of conformity assessment audits such as interpreting ISO 9001 requirements in an audit context, auditing principles, applying audit methods, evidence collection and verification, leading audit teams, creating nonconformity reports, and preparing final audit reports.
Upon completing the course, an exam follows. A successful exam result allows you to apply for the “PECB Certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor” credential. This UKAS-accredited and globally recognized certificate attests to your professional competence, confirming your ability to audit a QMS based on ISO 9001 standards.
5- Day Training Course Objective:
- Day 1: Getting Started with the Quality Management System (QMS) and ISO 9001
- Day 2: Understanding Audit Principles and Preparing for and Starting an Audit
- Day 3: Conducting On-Site Audit Activities
- Day 4: Wrapping Up the Audit
- Day 5: Certification Exam
What you will get in the course?
- The cost of the training course covers both certification and examination fees.
- Participants will receive extensive training material, comprising over 450 pages filled with information and practical examples.
- Upon completion of the course, participants will receive an attestation of course completion, which is valued at 31 CPD (Continuing Professional Development) credits.
- If a candidate doesn’t pass the exam, they have the opportunity to retake it once for free within 12 months from the initial exam date.
2. Use PECB eLearning
PECB eLearning training courses are tailored to cater to individual needs, breaking free from spatial and temporal constraints. The goal is to provide an exceptional learning experience that transcends physical barriers, offering engaging and high-quality courses across various fields.
Why opt for PECB eLearning training courses?
- Enhanced Accessibility and Learning Flexibility:
- With eLearning, you have the flexibility to learn anything at your own pace and on your own schedule.
- Personalized Learning Experience:
- Choose training courses based on your preferences and needs, allowing you to advance at a pace that suits you.
- Unrestricted Access to Premium Training:
- Gain limitless access to online resources, training materials, and relevant information.
- Interactive Courses by Multiple Experts:
- Experience interactive and premium-quality content delivered by different experts in the field.
- Cost Savings through Reduced Travel and Materials:
- Lower your costs by taking the training course from the comfort of your chosen environment, eliminating the need for travel and reducing material expenses.
3. Use ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Handbook
Gain all the exam-related information using the candidate handbook provided for the ISO 9001 Lead Auditor exam. This handbook is your key source to explore the core of the exam from details, pattern, format, topics, and rules to taking the exam, you can get all the information in one place.
4. Take Practice Tests
Taking practice tests for the ISO 9001 Lead Auditor exam is a smart and effective way to prepare for the real test. These practice exams replicate the actual exam conditions, familiarizing you with the format, types of questions, and time constraints. They enable you to identify your strengths and areas that need improvement, allowing you to concentrate your study efforts where they are most beneficial. Answering practice questions helps enhance your understanding of key concepts and assess your readiness for the actual exam.
Moreover, these tests instill confidence and alleviate anxiety about the exam, providing insight into what to expect on the actual day. Make the most of this valuable resource to enhance your exam preparedness, boost your familiarity with the material, and enhance your chances of success in the ISO 9001 Lead Auditor exam.



