Construction Professional in Built Environment Projects (PMI-CP)

The PMI-CP, known as the Construction Professional in Built Environment Projects, is a globally accepted certification providing a detailed education on the construction sector. This certification helps professionals, such as yourself, enhance their careers by training construction project managers to effectively lead, plan, and oversee contracts. It also ensures you’re well-prepared to handle challenges and stay up-to-date in this constantly changing field.
The PMI-CP test is a crucial step in getting certified professionally. It’s important that this exam accurately represents what construction professionals do. Qualified construction experts, holding PMI’s PMP certification, have carefully written and reviewed all the questions. These questions follow industry best practices and are matched with the PMI-CP Examination Content Outline to make sure the exam is fair and valid.
Why Earn the PMI-CP?
- Boost Your Leadership: PMI-CP enhances your communication, active listening, and commitment-based management skills, empowering you to enhance your leadership abilities.
- Foster Innovation and Sustainability: PMI-CP teaches the skills needed to adapt to current industry changes and meet sustainability requirements.
- Stay Updated in Your Field: PMI-CP provides the tools to keep you updated the latest technologies, materials, and communication methods in your industry.
- Secure Your Future Career: PMI-CP enables you to develop skills that future-proof your career, allowing you to thrive in the ever-changing construction environment.
Eligibility
To qualify for the PMI-CP certification, you need to fulfill specific professional experience criteria.
Work Experience:
- A minimum of 3 years of experience in the construction/built environment sector.
- The experience doesn’t have to be in a supervisory or leadership position.
- This experience should be within the past 10 years.
Further, the journey to your PMI-CP certification involves:
- Earning 3 micro-credentials
- Completing 4 eLearning courses
- Passing the PMI-CP capstone exam
Exam Details

The PMI-CP exam consists of 170 questions, with 20 of them being pretest questions. Pretest questions don’t affect your score; they’re used to test the validity of future exam questions. All questions are randomly placed in the exam.
You have 230 minutes to complete the center-based exam, but it might take less time. There are two 10-minute breaks during the PMI-CP exam. The first break is after questions 1-57, and the second break is after question 114, provided you’ve reviewed your answers.
It’s important to note that once you start a break after reviewing your answers, you can’t go back to the questions from the previous section of the exam.
The cost for getting the PMI-CP Certification is $499 USD, but it could vary based on membership and regional factors. You don’t have to be a member to get the PMI-CP. After your application is approved, you must pay the initial examination fees before scheduling your exam.
If you need to retake the exam within your eligibility period, you can do so at a discounted rate, which might depend on membership and regional pricing. Once you confirm and schedule an exam date, there may be cancellation or no-show fees.
Lastly, renewing your PMI-CP Certification will involve a payment, and the amount could be influenced by membership and regional considerations.
Retaking Exam:
If you don’t pass the first exam, we encourage you to keep studying and try again. You’re allowed to take the exam three times within a year. After three attempts, you must wait a year from the last exam before reapplying. This rule is to ensure exam security and prevent too much exposure of questions to one person. However, during that year, you can apply for any other PMI certification. If your one-year eligibility period ends without passing the exam, you need to reapply for certification.
Course Outline
Here, you’ll discover the layout of the PMI-CP Examination Content Outline. PMI has made changes to make the format simpler and more understandable based on feedback from customers and stakeholders.
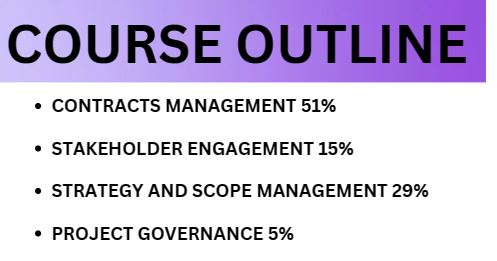
Domain I Contracts Management—51%
Task 1
Manage risks and the risk process for Construction and Built Environment Projects
- Recognize positive risk and use it to improve project outcomes
- Manage the risk process throughout the project and gain input from the required
stakeholders - Apply the different risk classifications appropriately
- Identify and evaluate risks for better allocation, avoidance, and management of risks
- Manage the risk prioritization process during Front End Planning and conduct
frequent reviews to the prioritization matrix - Identify and overcome the barriers that built environment companies face when
implementing innovative solutions - Determine the impact and risk of technology decisions or lack thereof, on the project
throughout the lifecycle and apply corrective actions
Task 2
Determine how to apply risk tools appropriately
- Use the Integrated Project Risk Assessment (IPRA) tool to improve how risk are managed
- Apply risk management tools and techniques to drive a better risk process (Monte Carlo simulations, probabilistic risk management techniques, and risk registers)
- Mobilize a risk management framework process at the project outset
Task 3
Manage the claims process
- Use lessons learned and previous project data to identify problematic areas on projects that result in claims
- Recognize how contract types and delivery methods selected impact the frequency of claims
- Utilize the claims process and key intervention points to reach early resolution
- Distinguish the difference between change/variation orders and claims
- Apply best practices to prevent claims and disputes (i.e. FEP, DRB, Documentation, communication, etc.)
- Utilize the risk management framework effectively to reduce claims
- Determine the root cause of claims and areas that require greater attention on the front end of projects
- Apply the different dispute resolution techniques available to be used
Task 4
Manage the contract lifecycle effectively
- Oversee the full contract lifecycle from discovery to close out
- Utilize Lean Integrated Project Delivery and IFOA to help resolve some of the industries contracting pain
- Utilize important clauses present in built environment contracts to support project delivery
- Advise senior stakeholders on the delivery method and contract structure that best fits the needs of the project
- Utilize the various delivery methods and contract structures available for built environment project covering risk apportionment, roles and responsibilities, and project delivery
- Apply innovation & technology requirements up-front in the tendering process (RFI/ RFP)
- Recognize the potential for communication gaps caused by contractual arrangements found in capital projects
- Apply knowledge to support senior leadership throughout the contract lifecycle
Task 5
Plan the Materials and Procurement Management processes accurately
- Plan and trace the cash flow of materials, its controls and debt service to improve planning and cost accuracy
- Implement the end-to-end materials management process with all of its stages: Strategy, Planning & Engineering, Ordering, Delivery, Storing, Managing Goods,
Closing & Handing Over, and Managing Waste - Leverage the new and emerging industry trends such as prefabicates or modularization
- Assess and determine the impact of critical path and lead times in materials management
- Recognize the different stages of the materials lifecycle and utilize the best practices
- Efficiently plan all stages of the material delivery process
- Apply methods for quantity planning, budgeting, and estimation
Task 6
Perform the Materials and Procurement Management activities accurately
- Identify the pitfalls involved in on-site and off-site handling, transportation, and tracking of materials
- Apply the benefits of the economies of scale role in managing procurement and supply chain processes
- Apply waste management practices to a project and integrate materials and suppliers with the schedule
- Apply best practices for ordering and managing materials in the project construction phase
- Apply methods for inspecting damaged goods, stock control, storage, and warehouse placement
Task 7
Implement the Interface Management process efficiently
- Establish and plan all the interface points (IPs) between the different packages
- Classify the different interfaces found in mega projects
- Recognize and use the industry leading frameworks and systems for implementing Interface Management
- Apply and design effective Interface Management practices
- Identify and apply the important principles and proper timing to guide the implementation of Interface Management throughout the project life cycle
- Apply the defined skills needed to effectively lead an interface management plan and monitor this effectively throughout the project
- Develop strong communication skills, relationship management skills, and negotiation skills
- Utilize the common language, definitions, and elements of Interface Management
Domain II Stakeholder Engagement—15%
Task 1
Utilize Communication Tools Appropriately to engage stakeholders and maintain proper communication
- Utilize PMIS to improve communication and project decisions
- Incorporate a central communication platform for the project
- Utilize Obeya/Big Room to enhance program activities
- Recognize the common pitfalls of Obeya/Big Room
- Apply Commitment based Management (CbM) to your own teams and across projects to drive effective outcomes
- Utilize the Compass tool to highlight communication deficiencies
- Assess data collected to infer meaningful insights and take action
Task 2
Prevent communication issues from occuring and ensure stakeholders are engaged
- Apply approaches to increase stakeholder buy in and alignment from the project outset
- Develop an effective communication strategy to ensure all project communication needs are identified and met
- Craft messaging that drives greater understanding for tailored audiences
- Utilize nuanced communication methods to engage multiple parties on a deeper level
- Prevent the effects of poor communication in capital projects from a completion and financial prospective
Task 3
Mitigate communication issues effectively as they emerge
- Implement feedback loops to highlight gaps and introduce changes to resolve communication gaps
- Apply approaches to overcome resistance and secure support through high impact communication
- Develop action plans to resolve communication gaps
- Identify and address culture issues as they emerge
Task 4
Manage stakeholders effectively
- Cooperate with project stakeholders to identify and select the best technology
solutions - Recognize what needs to be done, identify the appropriate specialists, and bring the
required skills in to do the work - Support the project team when implementing technology
- Identify and assess stakeholders to help establish an effective communication
strategy - Recognize the rule of culture and the impact on communication with stakeholders
- Make appropriate project team organizational recommendations for AWP
implementation - Recognize how culture impacts innovation
Domain III Strategy and Scope Management—29%
Task 1
Manage Scope Effectively
- Determine the factors to be considered when developing a technology
implementation plan - Define scope and drive projects by focusing on project outcomes or missions
- Implement scope revisions in order to achieve an accurate and mature project scope
- Identify the different ways to innovate (process innovation, product and services
innovation, project delivery innovation) and ensure they lead to better project
outcomes during implementation - Select the correct metrics and KPIs
- Apply Agile practices in construction
- Apply concepts including constraint management and continuous improvement
appropriately - Recognize and handle problematic Hot Spots within construction and commissioning
phases - Build a successful performance management strategy
Task 2
Implement and Manage the Change Order Process effectively and deliver project benefits and value
- Create a robust change order process
- Finalize the change process in the appropriate part of the project lifecycle
- Design agile processes to deal with change orders in an efficient and rapid way
- Recognize the benefits and downfalls to using technology to manage scope and
change orders - Evaluate all scope changes in relation to the core outcomes
Task 3
- Develop and apply methods, tools and techniques to develop and manage project scope
- Apply a decision-making framework for technology implementation
- Use scope evaluation tools to identify gaps in scope
- Apply scope management tools as a means of managing and pivoting scope (value
engineering and cost benefit analysis) - Establish an effective project measurement reporting process
- Implement engineering (technical design deliverable) as a critical element of the
planning process
Task 4
Implement the Advanced Work Packaging model and tools effectively
- Recognize the Advanced Work Packaging (AWP) implementation model and apply it
appropriately across the project lifecycle - Recognize and implement the different stages, process steps, activities, and
deliverables of the AWP implementation model - Utilize AWP tools, including templates and checklists appropriately
- Apply the principles of Lean and the Last Planner System to the planning of projects
- Apply the Commissioning and Startup (CSU) activity model and its tools correctly
- Utilize the 5 Connect conversations correctly
Task 5
Implement and utilize innovative planning tools on projects, adhering to best practices
- Apply Lean Deployment Planning Guide core principles
- Recommend latest technologies and their value potential to drive productivity and
its efficiency within projects - Demonstrate the importance of integrated technology platforms to realize the
benefits of technology solutions to drive collaboration - Apply the methods to support innovation on projects
Domain IV Project Governance—5%
Task 1
Implement governance models to drive project outcomes
- Develop governance structures for capital projects
- Apply project structures, appropriate practices and leadership tone to foster innovation
Task 2
Set up scope governance structures and practices on built environment projects
Task 3
Leverage scope governance structures to protect project scope and foster efficient decision making
Construction Professional in Built Environment Projects (PMI-CP) FAQs
Construction Professional in Built Environment Projects (PMI-CP) Study Guide
Getting ready for the PMI-CP exam is important, even if you’re already experienced in construction project management. The best way to prepare is by gaining relevant knowledge through learning modules or instructor-led training. This preparation is also a requirement to qualify for the PMI-CP exam application.

1. Complete Seven Course Module
Begin your preparation by finishing 7-course modules:
Achieve 3 micro-credentials (earned by completing the eLearning course and passing an exam):
- Built Environment Project Communication Pro
- Learn the basics of successful communication, including ways to overcome cultural differences in communication.
- Built Environment Technology and Innovation Pro
- Discover how to introduce technology and innovation in different teams and organizational settings.
- Built Environment Performance and Materials Management Pro
- Implement processes focused on metrics to enhance transparency, decrease waste, and proactively tackle global supply chain issues.
Complete 4 eLearning courses:
- Interface Management in the Built Environment PDUs:
- Gain expertise in handling communications, relationships, and project deliverables, a crucial skill.
- Scope and Change Order Management in the Built Environment:
- Develop the ability to manage scope changes and handle change orders efficiently in significant projects.
- Contract and Risk Management in the Built Environment:
- Learn how to prioritize project risks to effectively manage high-impact risks.
- Execution Planning in the Built Environment
- Explore new planning and execution strategies to enhance project outcomes.
Each self-paced module requires a commitment of 4-6 hours. They also provide a chance to earn PDUs, which can be used for certification renewals.
2. Gain Work Experience
To be eligible for the PMI-CP, you must have 3 years of work experience in construction or built environment projects within the last 10 years. Ensure you meet this requirement before applying. PMI-CP courses fulfill the necessary training for applying for the PMI-CP certification. If you prefer self-study or need a review, PMI-CP courses are an ideal choice for you!
3. PMI-CP Instructor-Led Training
Get in touch with a PMI Authorized Training Partner to take instructor-led courses that meet the training requirement for PMI-CP certification. The course content aligns with the PMI-CP exam outline, and you can use the following:
- Collaborating with a PMP-certified instructor who has significant experience in the construction field.
- Studying with a group of peers who share similar goals, helping each other succeed.
- Choosing a program that fits your schedule and establishes a well-organized exam preparation routine.
4. Use PMBOK Guide
The PMBOK Guide – Seventh Edition has been updated to address current challenges, aiming to make you more proactive, innovative, and agile. The Seventh edition of the PMBOK Guide:
- Encompasses all development approaches (predictive, traditional, adaptive, agile, hybrid, etc.).
- Includes a dedicated section on customizing the approach and processes.
- Introduces an expanded list of tools and techniques, featuring a “Models, Methods, and Artifacts” section.
- Emphasizes project outcomes alongside deliverables. Collaborates with PMIstandards+ for extra guidance on applying the PMBOK Guide in real-world situations.
5. Join Study Groups
Being part of study groups brings a lot of advantages! It gives you the opportunity to exchange knowledge, get different viewpoints, and receive support. Additionally, studying alongside others can add a fun element to the learning process. So, consider joining study groups—it’s not just about studying; it’s about making learning a shared and enjoyable experience! Connect, learn, and make the most out of your educational journey.
6. Take Practice Tests
Engaging in practice tests is a smart move! It allows you to familiarize yourself with the exam format, identify areas for improvement, and build confidence. Practice tests simulate the real exam experience, helping you manage time effectively and refine your test-taking skills. So, don’t skip this valuable step—take practice tests to enhance your preparation and boost your chances of success!



