Store Google Professional Data Engineer GCP
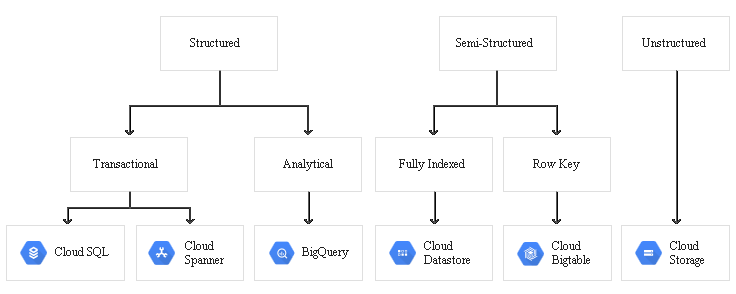
Data is of various types as
Object Storage
Tools for object storage are listed.
Cloud Storage
- A managed object storage service
- Durable and highly-available storage for structured and unstructured data
- Can store
- log files
- database backup
- export files
- images
- binary files.
- Files organized by project into individual buckets.
- Buckets can support either custom ACLs or IAM controls.
- Logging by Cloud Logging.
- Use cases
- Data backup and disaster recovery
- Content distribution – store and deliver media files
- Storing ETL data
- Storing data for MapReduce jobs
- Storing query data
- Seeding machine learning
- Archiving cold data
- Multiple storage classes offered
- Standard Storage has highest availability, low-latency access for frequently accessed data, like serving website content, interactive storage workloads, data supporting mobile and gaming apps, data-intensive computations and big data processing.
- Nearline Storage is low-cost, highly durable storage if data is accessed once a month. Gives sub-second response times and apt for data archiving, online backup, or disaster recovery.
- Coldline Storage is a very-low-cost, highly durable storage for one a quarter data access. Gives sub-second response times, and apt for data archiving, online backup, and disaster recovery.
- Archive Storage is lowest-cost, highly durable storage for once a year data access. Gives fast access with sub-second response times and suitable for data archiving, online backup, and disaster recovery.
Cloud Storage for Firebase
- Scalable storage service for mobile app developers
- Designed to scale with user base.
- Also good for storing and retrieving assets such as images, audio, video, and other user-generated content in mobile and web apps.
- Firebase SDKs for uploads and downloads
- It stores files in a Cloud Storage bucket,
- Can do server-side processing like image filtering or video transcoding
Storing database data
Tools for databases, both RDBMS and NoSQL, are listed.
Cloud SQL
- A managed service giving MySQL and PostgreSQL engine
- built-in support for replication
- Provides low-latency, transactional and relational database workloads
- Supports standard APIs for connectivity.
- Has built-in backup and restoration, high availability, and read replicas.
- Supports RDBMS workloads up to 30 TB for both MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- Accessible from apps running on App Engine, GKE, or Compute Engine.
- Also supports standard connection drivers and app frameworks (like Django, Ruby on Rails) Data stored is encrypted in transit and at rest.
- Also has built-in support for access control, using network firewalls.
- Use cases for Cloud SQL OLTP
- Financial transactions
- User credentials
- Customer orders
- Also suitable for OLAP workloads or data needing dynamic schemas on a per-object basis.
- For dynamic schemas, use Datastore and for OLAP use BigQuery and for wide-column schemas, use Bigtable. Use Dataflow or Dataproc for ETL
Bigtable
- A managed service for wide-column NoSQL
- Designed for terabyte- to petabyte-scale workloads.
- Built on Google’s internal Bigtable database infrastructure
- Provides consistent, low-latency, and high-throughput storage for large-scale NoSQL data. Supports real-time app serving and large-scale analytical workloads.
- Use a single-indexed row key associated with a series of columns
- queries are based on row key
- Schemas are structured as tall or wide
- The style of schema is dependent on the downstream use cases and it’s important to consider data locality and distribution of reads and writes to maximize performance.
- Tall schemas used for time-series events, as data is keyed by a timestamp, with relatively fewer columns per row.
- Wide schemas, a simplistic identifier as the row key along with a large number of columns.
- Use cases
- Real-time app data
- Stream processing
- IoT time series data
- Adtech workloads
- Data ingestion
- Analytical workloads
- Apache HBase replacement
- No support for multi-row transactions, SQL queries or joins.
Spanner
- A horizontally scalable relational database service
- Has strong consistency, high availability, and global scale.
- Has ease of use and familiarity of a RDBMS with the scalability of a NoSQL database.
- Spanner supports
- Schemas
- ACID transactions
- SQL queries (ANSI 2011)
- Scales horizontally in regions and can scale across regions
- Perform automatic sharding and give millisecond latencies.
- Security includes data-layer encryption, audit logging, and Cloud IAM integration.
- Use cases
- Financial services
- Ad tech
- Retail and global supply chain
Firestore
- A flexible, scalable NoSQL database service
- stores JSON data
- JSON data can be synchronized in real time to connected clients
- Firestore API lets app persist data to a local disk
- Has a flexible, expression-based rules language
- Firestore Security Rules for authentication
- Use cases
- Chat and social media
- Mobile games
Ecosystem databases
- Can deploy own database software on Compute Engine VMs
- Traditional RDBMS supported like EnterpriseDB and Microsoft SQL Server
- NoSQL database systems like MongoDB and Cassandra
Storing data warehouse data
A data warehouse stores large quantities of data for query and analysis instead of transactional processing. For data-warehouse workloads, Google Cloud provides BigQuery.
BigQuery
- A managed data warehouse service
- Supports ingestion by web interface, command line tools, and REST API calls.
- Bulk loading in CSV, JSON, or Avro files.
- For streaming data, use Pub/Sub and Dataflow
- Can also stream data directly into BigQuery
Google Professional Data Engineer (GCP) Free Practice TestTake a Quiz