Requirements Analysis and Design Definition
The tasks that business analysts perform to structure and organize requirements discover during elicitation activities, specify and model requirements and designs, validate and verify information, identify solution options that meet business needs, and estimate the potential value that could realize for each solution option are in the Requirements Analysis and Design Definition knowledge area. From the original concept and study of the requirement through the transformation of those needs into a specific proposed solution, this knowledge area comprises incremental and iterative processes. Business analysts utilize both requirements and designs as tools to specify and steer change.
Understanding the difference between requirements and designs:
- The major distinction between needs and designs is in how and by whom they are employed. The needs of one individual may differ from those of another.
- Requirements and designs might be high-level or highly specific. This depends on the needs of individuals who will be using the information.
- The function of the business analyst in modeling needs, requirements, designs, and solutions. This is critical for complete analysis and communication with other stakeholders.
- The environment, audience, and goal all influence the form, amount of detail, and what is being modeled. Both requirements and designs are evaluated for their potential value by business analysts.
- Business analysts create solution possibilities that may be reviewed in partnership with implementation subject matter experts in order to suggest the best solution option that fits the demand and adds the greatest value.
- As business analysis operations advance from offering prospective value to producing actual value, the following image depicts the value spectrum.
The Requirements Analysis and Design Definition knowledge area includes the following tasks:
- Specify and Model Requirements: describes a set of requirements or designs in detail using analytical techniques.
- Verify Requirements: ensures that a set of requirements or designs has been developed in enough detail to be usable by a particular stakeholder, is internally consistent, and is of high quality.
- Validate Requirements: ensures that a set of requirements or designs delivers business value and supports the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Define Requirements Architecture: structures all requirements and designs so that they support the overall business purpose for a change and that they work effectively as a cohesive whole.
- Define Solution Options: identifies, explores, and describes different possible ways of meeting the need.
- Analyze Potential Value and Recommend Solution: assesses the business value associated with a potential solution and compares different options, including trade-offs, to identify and recommend the solution option that delivers the greatest overall value.
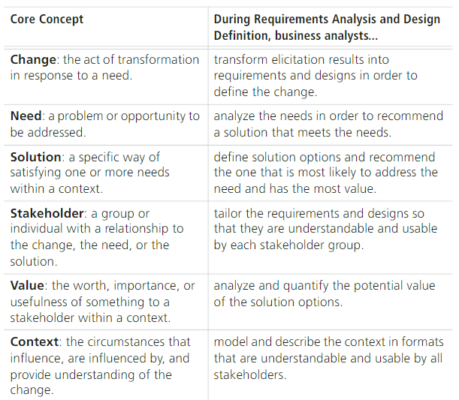
Core Concept Model in Requirements Analysis and Design Definition
The links between the six core ideas are described by the Business Analysis Core Concept ModelTM (BACCMTM). Each of the key principles is described and applied in the context of Requirements Analysis and Design Definition below.