The AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam is an entry-level certification exam that validates the candidate’s knowledge of the AWS Cloud platform. This exam is designed for individuals with little or no experience with AWS or cloud computing in general, and it serves as a foundation for other AWS certifications. Passing the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam requires a solid understanding of the AWS Cloud, its services, security, pricing, support, and architectures. The AWS Cloud Practitioner exam guide is an entry-level certification that is designed to validate your overall understanding of the AWS Cloud. To pass this exam, here are some tips:
- Understand the exam format: The exam consists of 65 multiple-choice and multiple-answer questions, and you have 90 minutes to complete it.
- Read the AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide: This guide outlines the topics covered in the exam, including AWS core services, security, compliance, and billing and pricing.
- Study the AWS Whitepapers: AWS offers a wide range of whitepapers on various topics related to cloud computing. Read the AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials whitepaper, AWS Overview whitepaper, and AWS Well-Architected whitepaper to get a better understanding of AWS services, security, and best practices.
- Take AWS Cloud Practitioner Training: AWS offers online training courses and labs that can help you prepare for the exam. The training covers topics such as AWS core services, security, pricing, and support.
- Practice with AWS sample exam questions: You can check your understanding and find areas to improve by trying out sample exam questions. AWS offers these sample questions in the exam guide.
- Use AWS services: Create an AWS account and use the services to get hands-on experience. This will help you understand the services and concepts better.
- Schedule your exam: Once you feel confident, schedule your exam. The exam can be taken online or in-person at a testing center.
Stay concentrated while taking the exam. Go through each question attentively and remove the wrong choices to improve your chances of selecting the correct answer. Wishing you the best of luck with your exam!
AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Difficulty
The difficulty of passing the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam can vary depending on your background and level of experience with AWS. However, the exam is designed to test your knowledge of the fundamental concepts of the AWS Cloud, so if you have a basic understanding of cloud computing and AWS services, you should be able to pass the exam with adequate preparation.
The test has 65 questions, including multiple-choice and multiple-response questions. You have 90 minutes to finish it. To pass, you need a score of 700 out of 1000 points. These questions are made to check your knowledge of AWS services, security, costs, support, and structures.
To give you an idea of the difficulty level, the AWS Cloud Practitioner exam is considered an entry-level certification, and it is often the first certification that professionals earn in their AWS certification journey. However, you should still prepare adequately to increase your chances of passing the exam. By studying the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide, reviewing AWS whitepapers and documentation, taking AWS training courses, using practice exams, and joining AWS communities, you can gain the knowledge and confidence you need to pass the exam.
AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Guide
Here are some official links to resources for the AWS Cloud Practitioner exam:
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide: https://d1.awsstatic.com/training-and-certification/docs-cloud-practitioner/AWS-Certified-Cloud-Practitioner_Exam-Guide.pdf
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Official Study Guide: https://www.amazon.com/Certified-Cloud-Practitioner-Official-Study/dp/1119490700
- Thirdly, AWS Cloud Practitioner Training and Certification: https://aws.amazon.com/training/path-cloudpractitioner/
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam Readiness Training: https://www.aws.training/Details/Curriculum?id=20686
- AWS Whitepapers and Guides: https://aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/
AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Tips and Tricks
Here are some tips and tricks to help you prepare for the AWS Cloud Practitioner exam:
- Firstly, read the AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide thoroughly and understand the exam format, topics, and structure.
- Take advantage of the official AWS Cloud Practitioner training resources, including the official study guide, sample exam questions, and exam readiness training.
- Next, practice with AWS Free Tier services to gain hands-on experience with AWS services and solutions.
- Familiarize yourself with the AWS console and command-line interface (CLI) to perform tasks and manage AWS resources.
- Review AWS whitepapers and guides related to the exam topics, such as the AWS Well-Architected Framework, AWS Best Practices, and AWS Pricing Overview.
- Utilize practice exams and quizzes to evaluate your understanding and pinpoint areas where you can enhance your knowledge.
- Focus on the core AWS services and their use cases, such as EC2, S3, RDS, VPC, and CloudWatch.
- Memorize key AWS concepts and terminology, such as regions, availability zones, elastic IPs, security groups, and roles.
- Manage your time effectively during the exam, and don’t spend too much time on a single question.
AWS Cloud Practitioner Course Outline
The AWS Cloud Practitioner exam covers the following topics –
Domain 1: Cloud Concepts 24%
1.1: Define the benefits of the AWS Cloud.
Knowledge of:
- Value proposition of the AWS Cloud
Skills in:
- Understanding the economies of scale (for example, cost savings) (AWS Documentation: Understand the fundamentals of pricing)
- Understanding the benefits of global infrastructure (for example, speed of deployment, global reach) (AWS Documentation: Global infrastructure)
- Understanding the advantages of high availability, elasticity, and agility (AWS Documentation: High availability and scalability on AWS)
Task Statement 1.2: Identify design principles of the AWS Cloud.
Knowledge of:
- AWS Well-Architected Framework
Skills in:
- Understanding the pillars of the Well-Architected Framework (for example, operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, cost optimization, sustainability) (AWS Documentation: The pillars of the framework)
- Identifying differences between the pillars of the Well-Architected Framework
Task Statement 1.3: Understand the benefits of and strategies for migration to the AWS Cloud.
Knowledge of:
- Cloud adoption strategies
- Resources to support the cloud migration journey
Skills in:
- Understanding the benefits of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) (for example, reduced business risk; improved environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance; increased revenue; increased operational efficiency) (AWS Documentation: AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF), Benefits management, An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption)
- Framework
- Identifying appropriate migration strategies (for example, database replication, use of AWS Snowball) (AWS Documentation: Best practices for AWS Database Migration Service)
Task Statement 1.4: Understand concepts of cloud economics.
Knowledge of:
- Aspects of cloud economics
- Cost savings of moving to the cloud
Skills in:
- Understanding the role of fixed costs compared with variable costs (AWS Documentation: Key principles)
- Understanding costs that are associated with on-premises environments (AWS Documentation: AWS Outposts)
- Understanding the differences between licensing strategies (for example, Bring Your Own License [BYOL] model compared with included licenses) (AWS Documentation: Simplified Bring-Your-Own-License experience using AWS License Manager)
- Understanding the concept of rightsizing Tips for Right Sizing)
- Identifying benefits of automation (for example, provisioning and configuration management with AWS CloudFormation) (AWS Documentation: What is AWS CloudFormation?)
- Identifying managed AWS services (for example, Amazon RDS, Amazon Elastic Container Service [Amazon ECS], Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service [Amazon EKS], Amazon DynamoDB) (AWS Documentation: Choosing an AWS container service)
Domain 2: Security and Compliance 30%
2.1 Define the AWS shared responsibility model
Knowledge of:
- AWS shared responsibility model
Skills in:
- Recognize the elements of the Shared Responsibility Model (AWS Documentation: Shared Responsibility Model)
- Describe the customer’s responsibility on AWS
- Describe AWS responsibilities (AWS Documentation: Shared Responsibility Model)
- Describing responsibilities that the customer and AWS share
- Describing how AWS responsibilities and customer responsibilities can shift, depending on the service used (for example, Amazon RDS, AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2)
2.2 Understand AWS Cloud security, governance, and compliance concepts.
Knowledge of:
- AWS compliance and governance concepts
- Benefits of cloud security (for example, encryption)
- Where to capture and locate logs that are associated with cloud security
Skills in:
- Identifying where to find AWS compliance information (for example, AWS Artifact) (AWS Documentation: Viewing compliance information)
- Understanding compliance needs among geographic locations or industries (for example, AWS Compliance)
- Describing how customers secure resources on AWS (for example, Amazon Inspector, AWS Security Hub, Amazon GuardDuty, AWS Shield) (AWS Documentation: Security, identity, and compliance)
- Identifying different encryption options (for example, encryption in transit, encryption at rest) (AWS Documentation: Encrypting Data-at-Rest and Data-in-Transit)
- Recognizing services that aid in governance and compliance (for example, monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch; auditing with AWS CloudTrail, AWS Audit Manager, and AWS Config; reporting with access reports) (AWS Documentation: Logging and events)
- Recognizing compliance requirements that vary among (AWS Documentation: AWS services Compliance)
2.3 Identify AWS access management capabilities
Knowledge of:
- Identity and access management (for example, AWS Identity and Access Management [IAM])
- Importance of protecting the AWS root user account
- Principle of least privilege
- AWS IAM Identity Center (AWS Single Sign-On)
Skills in:
- Understanding access keys, password policies, and credential storage (for example, AWS Secrets Manager, AWS Systems Manager) (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Secrets Manager?)
- Identifying authentication methods in AWS (for example, multi-factor authentication [MFA], IAM Identity Center, cross-account IAM roles) (AWS Documentation: Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) in AWS)
- Defining groups, users, custom policies, and managed policies in compliance with the principle of least privilege (AWS Documentation: Security best practices in IAM)
- Identifying tasks that only the account root user can perform (AWS Documentation: Tasks that require root user credentials)
- Understanding which methods can achieve root user protection (AWS Documentation: Root user best practices for your AWS account)
- Understanding the types of identity management (for example, federated) (AWS Documentation: Overview of AWS identity management: Users)
2.4 Identify components and resources for security
Knowledge of:
- Security capabilities that AWS provides
- Security-related documentation that AWS provides
Skills in:
- Describing AWS security features and services (for example, security groups, network ACLs, AWS WAF) (AWS Documentation: Security group policies)
- Understanding that third-party security products are available from AWS Marketplace (AWS Documentation: Security Products in AWS Marketplace)
- Identifying where AWS security information is available (for example, AWS Knowledge Center, AWS Security Center, AWS Security Blog)
- Understanding the use of AWS services for identifying security issues (for example, AWS Trusted Advisor) (AWS Documentation: AWS Trusted Advisor)
Domain 3: Cloud Technology and Services 34%
3.1 Define methods of deploying and operating in the AWS Cloud
Knowledge of:
- Different ways of provisioning and operating in the AWS Cloud
- Different ways to access AWS services
- Types of cloud deployment models
- Connectivity options
Skills in:
- Deciding between options such as programmatic access (for example, APIs, SDKs, CLI), the AWS Management Console, and infrastructure as code (IaC) (AWS Documentation: Grant programmatic access)
- Evaluating requirements to determine whether to use one-time operations or repeatable processes
- Identifying different deployment models (for example, cloud, hybrid, onpremises) (AWS Documentation: Selecting the right cloud for workloads – differences between public, private, and hybrid)
- Identifying connectivity options (for example, AWS VPN, AWS Direct Connect, public internet) (AWS Documentation: Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Connectivity Options)
3.2 Define the AWS global infrastructure
Knowledge of:
- AWS Regions, Availability Zones, and edge locations
- High availability
- Use of multiple Regions
- Benefits of edge locations
- AWS Wavelength Zones and AWS Local Zones
Skills in:
- Describe the relationships among Regions, Availability Zones, and Edge Locations (AWS Documentation: Regions and Zones, Regions and Availability Zones)
- Describe how to achieve high availability through the use of multiple Availability Zones
- Describing when to use multiple Regions (for example, disaster recovery, business continuity, low latency for end users, data sovereignty) (AWS Documentation:Multi-Region Application Architecture)
- Describing at a high level the benefits of edge locations (for example, Amazon CloudFront, AWS Global Accelerator) (AWS Documentation:AWS for the Edge)
3.3 Identify AWS compute services
Knowledge of:
- AWS compute services
Skills in:
- Recognizing the appropriate use of different EC2 instance types (for example, compute optimized, storage optimized) (AWS Documentation: Compute optimized instances)
- Recognizing the appropriate use of different container options (for example, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS) (AWS Documentation: Choosing an AWS container service)
- Recognizing the appropriate use of different serverless compute options (for example, AWS Fargate, Lambda)
- Recognizing that auto scaling provides elasticity (AWS Documentation: Auto Scaling group for your Elastic Beanstalk environment)
- Identifying the purposes of load balancers (AWS Documentation: What is an Application Load Balancer?)
3.4 Identify AWS database services.
Knowledge of:
- AWS database services
- Database migration
Skills in:
- Deciding when to use EC2 hosted databases or AWS managed databases (AWS Documentation: Choosing between Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS)
- Identifying relational databases (for example, Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora) (AWS Documentation: What is Amazon Aurora?)
- Identifying NoSQL databases (for example, DynamoDB) (AWS Documentation: Types of NoSQL databases)
- Identifying memory-based databases
- Identifying database migration tools (for example AWS Database Migration Service [AWS DMS], AWS Schema Conversion Tool [AWS SCT]) (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Database Migration Service?)
Task Statement 3.5: Identify AWS network services.
Knowledge of:
- AWS network services
Skills in:
- Identifying the components of a VPC (for example, subnets, gateways) (AWS Documentation: What is Amazon VPC?)
- Understanding security in a VPC (for example, network ACLs, security groups) (AWS Documentation: Control traffic to subnets using network ACLs)
- Understanding the purpose of Amazon Route 53 (AWS Documentation: What is Amazon Route 53?)
- Identifying edge services (for example, CloudFront, Global Accelerator) (AWS Documentation: AWS services for edge computing)
- Identifying network connectivity options to AWS (for example AWS VPN, Direct Connect) (AWS Documentation: Network-to-Amazon VPC connectivity options)
Task Statement 3.6: Identify AWS storage services.
Knowledge of:
- AWS storage services
Skills in:
- Identifying the uses for object storage (AWS Documentation: Amazon S3 objects overview)
- Recognizing the differences in Amazon S3 storage classes (AWS Documentation: Using Amazon S3 storage classes)
- Identifying block storage solutions (for example, Amazon Elastic Block Store [Amazon EBS], instance store) (AWS Documentation: Storage options for your Amazon EC2 instances)
- Identifying file services (for example, Amazon Elastic File System [Amazon EFS], Amazon FSx) (AWS Documentation: What is Amazon Elastic File System?)
- Identifying cached file systems (for example, AWS Storage Gateway) (AWS Documentation: Managing local disks for your gateway)
- Understanding use cases for lifecycle policies (AWS Documentation: Managing your storage lifecycle)
- Understanding use cases for AWS Backup
Task Statement 3.7: Identify AWS artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) services and analytics services.
Knowledge of:
- AWS AI/ML services
- AWS analytics services
Skills in:
- Understanding the different AI/ML services and the tasks that they accomplish (for example, Amazon SageMaker, Amazon Lex, Amazon Kendra) (AWS Documentation: Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI))
- Identifying the services for data analytics (for example, Amazon Athena, Amazon Kinesis, AWS Glue, Amazon QuickSight) (AWS Documentation: Overview of Amazon Web Services)
Task Statement 3.8: Identify services from other in-scope AWS service categories.
Knowledge of:
- Application integration services of Amazon EventBridge, Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS), and Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS)
- Business application services of Amazon Connect and Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES)
- Customer engagement services of AWS Activate for Startups, AWS IQ, AWS Managed Services (AMS), and AWS Support
- Developer tool services and capabilities of AWS AppConfig, AWS Cloud9, AWS CloudShell, AWS CodeArtifact, AWS CodeBuild, AWS CodeCommit, AWS CodeDeploy, AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeStar, and AWS X-Ray
- End-user computing services of Amazon AppStream 2.0, Amazon WorkSpaces, and Amazon WorkSpaces Web
- Frontend web and mobile services of AWS Amplify and AWS AppSync
- IoT services of AWS IoT Core and AWS IoT Greengrass
Skills in:
- Choosing the appropriate service to deliver messages and to send alerts and notifications (AWS Documentation: Mobile text messaging (SMS))
- Choosing the appropriate service to meet business application needs (AWS Documentation: Business applications)
- Choosing the appropriate service for AWS customer support (AWS Documentation: Getting started with AWS Support)
- Choosing the appropriate option for business support assistance
- Identifying the tools to develop, deploy, and troubleshoot applications (AWS Documentation: Developer tools)
- Identifying the services that can present the output of virtual machines (VMs) on end-user machines (AWS Documentation: Compute services)
- Identifying the services that can create and deploy frontend and mobile services (AWS Documentation: Front-end web and mobile services)
- Identifying the services that manage IoT devices (AWS Documentation: Managing devices with AWS IoT)
Domain 4: Billing and Pricing 12%
Task Statement 4.1: Compare AWS pricing models.
Knowledge of:
- Compute purchasing options (for example, On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances, Savings Plans, Dedicated Hosts, Dedicated Instances, Capacity Reservations)
- Data transfer charges
- Storage options and tiers
Skills in:
- Identifying and comparing when to use various compute purchasing options (AWS Documentation: Instance purchasing options)
- Describing Reserved Instance flexibility (AWS Documentation: How Reserved Instances are applied)
- Describing Reserved Instance behavior in AWS Organizations (AWS Documentation: Reserved Instances)
- Understanding incoming data transfer costs and outgoing data transfer costs (for example, from one Region to another Region, within the same Region) (AWS Documentation: Understanding data transfer charges)
- Understanding different pricing options for various storage options and tiers
Task Statement 4.2: Understand resources for billing, budget, and cost management.
Knowledge of:
- Billing support and information
- Pricing information for AWS services
- AWS Organizations
- AWS cost allocation tags
Skills in:
- Understanding the appropriate uses and capabilities of AWS Budgets, AWS Cost Explorer, and AWS Billing Conductor (AWS Documentation: Cloud Financial Management)
- Understanding the appropriate uses and capabilities of AWS Pricing Calculator (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Pricing Calculator?)
- Understanding AWS Organizations consolidated billing and allocation of costs (AWS Documentation: Consolidated billing for AWS Organizations)
- Understanding various types of cost allocation tags and their relation to billing reports (for example, AWS Cost and Usage Report) (AWS Documentation: Using AWS cost allocation tags)
Task Statement 4.3: Identify AWS technical resources and AWS Support options.
Knowledge of:
- Resources and documentation available on official AWS websites
- AWS Support plans
- Role of the AWS Partner Network, including independent software vendors
and system integrators - AWS Support Center
Skills in:
- Locating AWS whitepapers, blogs, and documentation on official AWS websites
- Identifying and locating AWS technical resources (for example AWS Prescriptive Guidance, AWS Knowledge Center, AWS re:Post) (AWS Documentation: AWS Prescriptive Guidance Patterns)
- Identifying AWS Support options for AWS customers (for example, customer service and communities, AWS Developer Support, AWS Business Support, AWS Enterprise On-Ramp Support, AWS Enterprise Support)
- Identifying the role of Trusted Advisor, AWS Health Dashboard, and the AWS Health API to help manage and monitor environments for cost optimization (AWS Documentation: AWS Trusted Advisor)
- Identifying the role of the AWS Trust and Safety team to report abuse of AWS resources
- Understanding the role of AWS Partners (for example AWS Marketplace, independent software vendors, system integrators) (AWS Documentation: What is AWS Marketplace?)
- Identifying the benefits of being an AWS Partner (for example, partner training and certification, partner events, partner volume discounts) (AWS Documentation: Benefits for AWS Specialization Partners)
- Identifying the key services that AWS Marketplace offers (for example, cost management, governance and entitlement)
- Identifying technical assistance options available at AWS (for example, AWS Professional Services, AWS Solutions Architects)
AWS Cloud Practitioner Glossary
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – A cloud platform that offers various cloud services like storage, computing power, and databases, all online.
- Cloud Computing: The delivery of computing resources like storage, processing power, and applications over the internet.
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): A web service that provides scalable computing power in the cloud, allowing users to manage virtual machines.
- Simple Storage Service (S3): A web-based cloud storage service for data storage and retrieval.
- Relational Database Service (RDS): A web service for setting up, operating, and scaling relational databases in the cloud.
- DynamoDB: A fully managed NoSQL database service for fast and scalable data storage.
- Elastic Block Store (EBS): High-performance block storage for use with EC2 instances.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): A service to launch AWS resources in a user-defined virtual network.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): A service for controlling access to AWS resources.
- Simple Notification Service (SNS): A pub/sub messaging service for sending and receiving messages.
- Simple Queue Service (SQS): A message queuing service for decoupling and scaling microservices.
- Lambda: A serverless computing service for running code in response to events.
- Elastic Beanstalk: A service for deploying and managing applications without worrying about infrastructure.
- CloudFormation: A service for defining and managing AWS infrastructure as code.
- Route 53: A scalable cloud Domain Name System (DNS) service.
- CloudFront: A content delivery network (CDN) service for faster content delivery.
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB): Automatically distributes application traffic across multiple targets.
- Auto Scaling: Automatically adjusts capacity to maintain performance and reduce costs.
- Trusted Advisor: Provides guidance to optimize AWS infrastructure.
- CloudTrail: Monitors, logs, and audits AWS infrastructure by recording API calls and events.
- Cost Explorer: Analyzes AWS usage and costs.
- AWS Well-Architected Tool: Framework for designing reliable, secure, and cost-effective systems.
- AWS Organizations: Manages multiple AWS accounts with centralized billing and management.
- CloudWatch: Monitors AWS resources, collects metrics, and provides alarms and notifications.
- Glacier: It’s like a low-cost storage freezer for rarely used data. You can securely keep lots of data and retrieve it when you need, although it might take a little time.
- Kinesis: Think of it as a real-time data stream catcher. It helps you collect, process, and analyze data as it flows in from various sources like websites, sensors, or mobile devices.
- Elastic MapReduce (EMR): This service makes handling big data easier. It helps you process large amounts of data using powerful frameworks like Hadoop and Spark. You can launch and manage clusters of virtual computers and run various data processing tools.
- Amazon Redshift: It’s like a super-fast, massive warehouse for data. You can analyze huge amounts of structured and semi-structured data using standard SQL queries.
- AWS Direct Connect: This service gives you a super highway for your data between your own data centers and AWS. It’s like having a dedicated, high-speed road that avoids the regular internet.
- AWS Snowball: Imagine a secure courier service for moving large amounts of data between your place and AWS. They send you a rugged device, you load your data onto it, and they transport it safely to or from AWS.
- Amazon WorkSpaces: It’s like having your computer in the cloud. You can access your applications and data from anywhere using any device securely.
- AWS IoT: This helps you manage and connect all your smart devices securely and efficiently. It also allows you to collect, process, and analyze the data these devices generate.
- Amazon GuardDuty: Think of it as your security watchdog. It continuously watches over your AWS accounts and workloads, alerting you to any suspicious activity or threats.
- AWS WAF: It’s like a shield for your web applications. It protects them from common online attacks like injecting malicious code or trying to trick your website into doing bad things.
- AWS Certificate Manager: It’s like a certificate manager for your website’s security. You can easily get, control, and use secure certificates for your website or other systems to keep your data safe during online transactions.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS): Think of it as a key keeper for your data. You can create and manage encryption keys to lock and unlock your data using strong encryption methods.
- AWS Glue: It’s like a data mover and organizer. You can use it to smoothly transfer data between different sources and destinations, and get it ready for detailed analysis.
- Amazon SageMaker: Imagine having a personal trainer for your machine learning models. It helps you build, teach, and deploy machine learning models on a large scale, and it comes with pre-built tools and techniques.
Learning Path with AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide

Step 1 : AWS Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide and Learning
To begin your learning journey, you can sign up for free AWS digital training. This will provide you with a strong starting point for building your AWS skills. The free digital training can be accessed on the following link:
Free Digital Training: AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
Once you complete the free digital training you can test your knowledge with our free AWS cloud practitioner practice tests on the following link:
https://www.testpreptraining.com/aws-cloud-practitioner-exam-questions
Then you can proceed with your training
The free cloud practitioner essentials course above covers the following essential concepts. We have also added additional practice material and exercises for you to make your learning as solid as possible. You can follow the path laid out below:
1. Introduction to AWS and the interface:
1. Begin with AWS Overview and learn about core services, aws platform and global infrastructure
2. Learn about AWS Well Architected Framework
Start with learning about the basic cloud computing services, concepts and the AWS interface. You can start with making an AWSs free tier account.
What is an AWS free tier account?
2. Core AWS services
First you will start learning about the following core aws services:
- Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2),
- Secondly, Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS),
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3),
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and
- Security Groups.
Additional practice and learning exercises:
Amazon EC2:
Amazon EC2 is the virtual application server provider which are known as instances, to host your web application or website. Further, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud gives you the ability to scale up your computing capacity. It eliminates your need to buy hardware and helps you in increasing the speed of developing and deploying your application. You can learn and practice amazon EC2 on the following links.
Know about EC2 instance categories
User guide for linux instances
User guides for windows instances
Amazon EBS:
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is not so difficult to use, but high performance block storage which has been designed to be used with Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for intensive workloads at any scale. You can learn and practice amazon EBS on the following links.
Amazon Elastic Block Store
Creating an Amazon EBS volume
Attaching an Amazon EBS volume to an instanceDeep dive on amazon EBS elastic volumes
Amazon simple storage (S3):
Amazon simple storage as the name tells is a cloud storage service by aws. It provides secure, durable, and highly-scalable cloud storage making web based high scale computing easier for developers.You can learn and practice amazon S3 on the following link.
Learn Amazon S3
Amazon virtual private cloud :
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) is a virtual network service to make you able in launching AWS resources into a your own virtual network. Closely resembling your at premise network the benefit it brings is the scalability of infrastructure of AWS.
Amazon VPC concepts
3. AWS integrated services
Now as you have studied and practiced the basic aws services, you will proceed to learn about some of the integrated services that are part of the AWS Cloud: You can learn about them through the following links
Load Balancing:
Elastic Load Balancing is used to handle network traffic workloads. It distributes incoming network traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, in multiple Availability Zones. A load balancer distributes network workloads across multiple compute resources and increases the availability and fault tolerance of your applications.
AWS Elastic load balancing,
AWS Application Load Balancer
Auto Scaling:
In events of surge in traffic or demands auto scaling helps you to automatically scale up or down the number of compute resources needed for your application at any given time
Auto Scaling
Amazon Route 53:
The main functions of amazon route 53 are: domain registration, DNS routing, and health checking. Used separately or in any combination
Amazon Route 53
Amazon RDS:
Easily scale, operate and setup relational databases with amazon RDS
Amazon Relational Database Services (RDS)
AWS Lamba:
A serverless computing service lets you execute a code to automate the scaling as per the need
Other important Integrated services:
AWS Lambda
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS)
Next, Amazon CloudWatch
Amazon CloudFront, and
AWS CloudFormation.
4. AWS Architecture
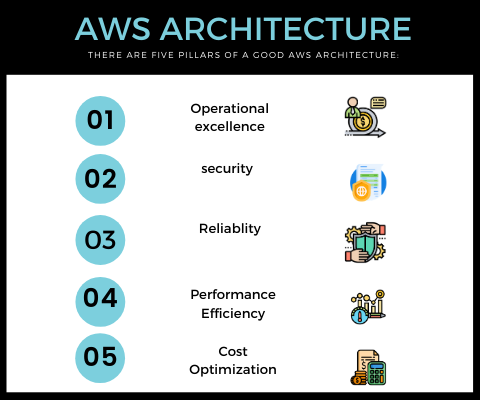
It is important to know the practice of implementing well-architected framework in aws

The following resources will help.
AWS well architected tool
AWS well architected framework
Fault tolerance and high availability
Web hosting on aws cloud
5. Next, AWS Security
Firstly, AWS Overview of security Process
Next, AWS Security Service
6. AWS Pricing Support
It is time to take the practice tests again to check your progress:
https://www.testpreptraining.com/aws-cloud-practitioner-exam-questions
Step 2 : AWS Whitepapers and learning resources
Now as you have finished your lessons, it is time to practice your learning with use cases, hands on exercises and not to forget go through the aws whitepapers.
1. AWS Cloud Practitioner White Papers
Cloud best practices – AWS Well Architected Framework
AWS Pricing overview
Compare aws support plans
2. AWS hands on exercises:
You can find all the hands on exercises on the following link. You can practice the relevant exercises.
https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/hands-on/
3. Others Learning Resources
All whitepapers:
https://aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/?whitepapers-main.sort-by=item.additionalFields.sortDate&whitepapers-main.sort-order=desc
Learning Library:
https://www.aws.training/LearningLibrary?&search=&tab=view_all
AWS complete documentation:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/
Step 3: Evaluate yourself with Practice tests
Now before finally sitting for the exam, it is essential to practice and prepare for AWS Cloud Practioner exam question. Moreover, it is essential to take practice tests to check your learning so far and polish those skills. This step is very crucial because it forces you into the actual scenario of giving an exam and here you can find out about your weaknesses. You can go back to the learning stage to revise anything you feel you have no solid grasp.
Link for practice tests again
https://www.testpreptraining.com/aws-cloud-practitioner-exam-questions
That’s it, now you are ready to sit for the exam. All the best.


