The Certified Chief Information Security Officer (CCISO) certification is a prestigious credential that recognizes individuals who have demonstrated the highest level of expertise in cybersecurity leadership. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too does the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals. The CCISO certification is a testament to an individual’s ability to navigate complex security challenges, implement robust security strategies, and protect critical organizational assets. But is the CCISO exam truly worth the significant time and effort required to obtain it? In this blog post, we’ll enter into the intricacies of the CCISO certification, exploring its benefits, challenges, and suitability for different career paths.
Understanding the CCISO Certification
The Certified Chief Information Security Officer (CCISO) certification is the pinnacle of achievement for cybersecurity professionals aspiring to leadership roles. This prestigious credential, offered by the EC-Council, recognizes individuals who possess the strategic thinking, technical expertise, and managerial acumen necessary to effectively secure organizations in the digital age.
The CCISO program is designed to bridge the gap between technical knowledge and executive leadership, equipping certified professionals with the skills to navigate complex security landscapes, mitigate risks, and drive business objectives. To earn the CCISO certification, candidates must meet stringent eligibility requirements, including years of relevant experience and a deep understanding of information security principles. The exam itself is a rigorous test of knowledge and critical thinking, covering a wide range of topics such as risk management, governance, compliance, incident response, and cybersecurity frameworks.
Advantages of CCISO
- Provide candidates with information to help them manage the day to day duties of a CCISO
- Design to assist managers in obtaining senior executive positions
- Imparting comprehensive understanding of the five essential CCISO domains imparting useful expertise on the use of IS management concepts from a top level management viewpoint
- Preparing applicants to pass the CCISO exam on their first go
Target Audience
- Network engineers with a focus on security
- Knowledgeable IT specialists working in information security management
- Individuals who carry out CISO duties without holding a formal title
- Prerequisites for all professionals hoping to advance to top positions in the field of information security.
Job Profile and Responsibility of CISO
A C-Level is the chief information security officer. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) oversees the company’s security stance and guarantees that all vital data and IT systems are Shielded from any cyberattacks. A solid grasp of the IT infrastructure, good leadership and effective communication are necessary for becoming a chief information security officer The tasks of a CISO are as follows:
- Collaborating with the security teams and management to improve the organization’s security posture
- Hiring security professionals
- Makes certain that many departments work together to ensure cyber hygiene
- Planning initiatives to educate staff members about potential cyberattacks
- Organizing the organization’s security budget
- Confirming that all security tools and software are up to date analysis of security.
Exam Eligibility Application Verification
To be eligible for the CCISO exam, candidates must meet specific experience requirements. This involves demonstrating five years of experience in at least three of the five CCISO domains: Security Governance and Risk Management, Information Security Architecture and Engineering, Information Security Operations, Information Security Assurance and Compliance, and Information Security Incident Response and Disaster Recovery.
This experience is verified through the EC-Council’s exam eligibility application process, where candidates are required to provide detailed information about their professional roles, responsibilities, and the specific security domains they have worked in. Meeting these eligibility criteria ensures that CCISO certified professionals possess the requisite practical experience to excel in senior cybersecurity leadership positions.
Exam Details
The Chief Information Security Officer (CCISO) Exam is a rigorous evaluation designed for senior-level IT security professionals. The exam duration is two and a half hours and consists of 150 multiple-choice questions. To pass, candidates must achieve a score ranging between 60% and 85%, depending on the scoring criteria. This exam assesses a candidate’s expertise in information security leadership, strategy, and management, ensuring they are equipped to handle the responsibilities of a Chief Information Security Officer effectively.
Exam Overview
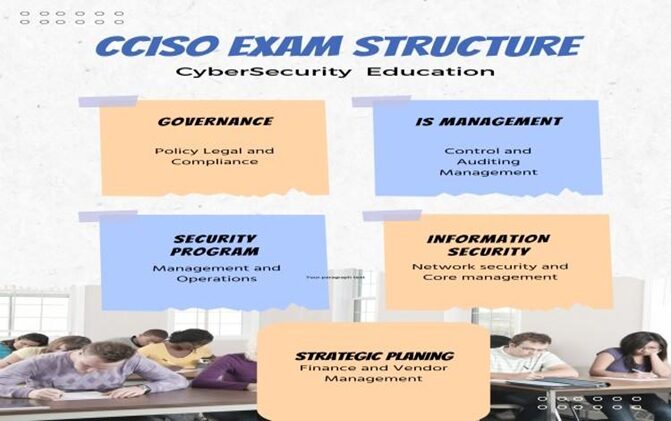
The purpose of the CCISO exam is to assess a candidate’s proficiency in five essential areas of information security management, it’s crucial to understand the CCISO Body of Knowledge”s content and the exam’s objectives before starting to study for it. This will enable you to concentrate on your studies and make sure you have covered every subject in the exam. The five key domains are:
1. Governance, Risk and Compliance(GRC)
- Define , implement ,Manage and maintain an information security governance program that includes Organizational structures and leadership
- Align the organization’s objectives and governance including standards, policies leadership style, philosophy and values with information security governance framework
- Create a structure for information security management
- Create a framework for evaluating information security governance that takes ROI and cost/benefit evaluations of measures into account
- Examine all external laws,rules, guidelines and best practices that the company may be subject to Recognize the various legal provision that impact organizational security including those found in the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act,Family educational Rights and privacy Act, Federal Information Security Management Act,Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Clinger-Cohen Act Privacy Act,Sarbanes-Oxley and others
- Learn about various standards including the Federal Information processing Standards(FIPS)and the ISO 27000 series
- Evaluate the main enterprise risk factors for compliance
- Coordinate the application of information security plans, policies and procedure to reduce regulatory risk
- Recognize the significance of regulatory information security organizations and the relevant industry groups,forums and stakeholders
- Comprehend the federal and organization-specific published documents to manage operations in a computing environment
- Handle enterprise compliance program controls
2. Information Security Controls and Auditing Management (IS Management)
- Controls for information security management
- Determine the operating procedure, goals and degree of risk tolerance of the company
- Create information systems controls that are in line with the objectives and needs of operations and test them before putting them into use to make sure they work well
- Determine and pick the resources needed to apply and manage information system controls in an efficient manner,information, infrastructure, architecture(e.g,.platforms, operating systems, network, databases and applications), and human capital are examples of such resources
- Design and put into place controls for information systems to reduce risk
- Metrics and key performance indicators are identified and measured in order to track and record the effectiveness of information security control in achieving organizational goals
- Create and carry out information that it complies with the policies, standards and procedures of the organization
- Assess and play tools and techniques by automate information systems control procedures
- Design and implement processes to correct inadequacies appropriately
- Evaluate problem management strategies to ensure that errors are reported, examined and reminded in a timely manner
- Create information systems control status reports and distribute them with pertinent stakeholders to facilitate executive decision- making . These reports verify that the organization’s strategies and objectives are met by the information systems, operating, maintenance and support procedures.
3. Management Auditing
- Execute the audit process in accordance with established standards and interpret results against defined criteria to ensure that the information systems to protected controlled and effectively supporting the organization’s objectives
- Recognize the IT audit process and to be familiar with IT audit standards
- Apply information systems audit principles, skills and techniques in reviewing and testing information system technology and applications to design and implement a thorough risk- based IT audit strategy
- To make sure that the information systems are secure, under control and capable of achieving the goals of the company, carry out the audit process in compliance with set standards and evaluate the findings in light of predetermined standards
- Assess audit results efficiently considering the viewpoint,correctness and relevance of conclusions in relation to the total audit evidence
- Determine the exposure brought on by inadequate or absent control procedures and create a workable , affordable plan to address those areas
- Make sure that the required adjustments based on the audit findings are successfully implemented in a timely manner
- Create an IT audit documentation process and provide reports to pertinent stakeholders as the foundation of decision making.
4. Security Program Management and Operations
- Create a precise project scope statement for each information system project that is in line with corporate goals
- Create ,administer and oversee the information system program budget, estimate and regulate the expenses of particular projects
- Identify the task require to carry out the information systems program successfully assess their duration and create a schedule and staffing plan
- Determine bargain for obtain and oversee the resources (people,infrastructure and architecture) required for the information systems program’s effective design and implementation
- Gather, cultivate and oversee the information security project team
- To guarantee efficient performance and responsibility, clearly define the job responsibilities of information security workers and offer ongoing training
- Oversees information security staff and facilitate teamwork and communication between the information systems team and other security related staff members(such as technical support, incident, management and security engineering)identify, negotiate and manage vendor agreements and the community
- Collaborate with vendors and stakeholders to review and assess suggested solutions,identify inconsistencies, difficulties or problems with proposed solutions
- Assess project management practices and controls to determine whether business requirements are met in an economical way while minimizing risk to the organization
- Identify stakeholders, manage their expectations and communicate clearly to report progress and performance
- Create a plan to continuously measure the effectiveness of information systems projects to ensure optimal system performance
- Ensure that required modifications and enhancements to the information systems processes are implemented as needed.
5. Information Security Core Competencies
Access Control:
- Determining the Needs for mandatory and Discretionary Access Control
- Understand the various factors that assist control implementation, creating and maintaining an access control plan in consistency with the fundamental principles that Guide Access control Systems, such as Need- to- know
- Recognize various access control mechanism, including Biometrics and ID cards
- Recognize the significance of warning banners when putting access restrictions in to practice
- Create policies to make sure users of the system are aware of their information security obligations before allowing them to access to the systems
- Recognize the different social engineering concepts and how they relate to insider attacks.
- Create strategies to prevent social engineering attacks and plan of action for handling identity theft incidents
- Determine the worth of physical assets and the consequences of their unavailability
- Identify standards, processes , directives, policies, regulations and laws of pertaining to physical security
- Establish goals for personnel security to ensure alignment with enterprise’s overall security objectives
- Identify resources required to implement a physical security plan effectively design implement and oversee a cohesive coordinated and holistic physical security plan to ensure overall organizational security
- Create a system for measuring the performance of physical security, manage , audit and update issues.
Risk Management:
- Recognize the procedure for risk treatment and mitigation, comprehend the idea of acceptable risk
- Establish an organized and methodical risk assessment process
- Collaborate with stakeholders to create an IT security risk management program that adheres to standards and procedures and in organizational goals and objectives
- Determine the resources needed to implement the risk management plan
- Forage connections between the incident response team and other internal( like legal department) and external ( like law enforcement agencies, vendors and public relations specialist) groups
- Recognize the information infrastructure’s residual risk to detect security risk,evaluate threats, then update any relevant security measures on a regular basis
- Recognize modifications to risk management procedures and policies and make sure the program is up to date.
6. Study Network Security Principles including Firewalls
- Based on IT portfolio and security data access how well security controls and procedures are integrated into the investment planning process
- Planning for business continuity and disaster recovery , create , carry out and oversee business continuity plans
- Determine the capabilities and responsibilities of the various business continuity stakeholders. The ability to comprehend perimeter defense systems , such as access control lists and grid sensors on routers, firewalls and other network devices , an understanding of network segmentation of DMZs , VPNs, and telecommunication technologies such as VoIP and PBX, the ability to identify vulnerabilities in networks and investigate security controls such as the use of SSL and TLS for transmission security
- The ability to support , monitor , test and troubleshoot issues with hardware and software,and manage accounts network rights and access to systems and equipment
- The ability to recognize vulnerabilities and attacks related to wireless networks as well as manage various wireless network security tools threats from viruses, Trojans and malware best practices for secure coding and securing Web Applications evaluate the danger Comprehend different system engineering practices
- Install and operate IT systems in test configuration that does not modify program code or jeopardize security measures
Benefits of Obtaining the CCISO Certification
The CCISO certification offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance your career trajectory and professional standing. By obtaining this prestigious credential, you can unlock new opportunities, elevate your expertise, and position yourself as a sought-after leader in the cybersecurity field.
Career Advancement:
- Enhanced Credibility: The CCISO certification is globally recognized as a symbol of excellence in cybersecurity leadership. It validates your knowledge, skills, and experience, making you more credible and respected in the industry.
- Increased Earning Potential: Certified CISOs often command higher salaries and receive more lucrative compensation packages compared to their non-certified counterparts. Your certification demonstrates your value and can lead to significant salary increases and bonuses.
- Expanded Career Opportunities: The CCISO certification opens doors to a wide range of high-level cybersecurity leadership positions, including CISO, Chief Security Officer, and other executive roles. Your certification makes you a highly competitive candidate for top-tier organizations.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills:
- Comprehensive Cybersecurity Expertise: The CCISO certification program covers a broad spectrum of cybersecurity topics, including risk management, governance, compliance, incident response, and strategic planning. By completing the certification, you gain a deep understanding of these critical areas.
- Strategic Thinking and Leadership Abilities: The CCISO certification emphasizes the development of strategic thinking and leadership skills. You learn how to align security initiatives with business objectives, make informed decisions, and effectively communicate with stakeholders at all levels.
- Continuous Professional Development: The CCISO certification encourages ongoing learning and professional development. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices, you can maintain your competitive edge and adapt to the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Networking Opportunities:
- Global Community of Cybersecurity Professionals: The CCISO certification connects you with a global network of cybersecurity leaders. You can collaborate with peers, share knowledge, and learn from experienced professionals.
- Access to Industry Insights and Trends: By participating in CCISO forums, conferences, and online communities, you gain access to the latest industry insights, emerging threats, and innovative solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
While the CCISO certification offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges and considerations associated with pursuing this rigorous credential.
Time Commitment:
- Rigorous Study Schedule: Preparing for the CCISO exam requires a significant time investment. Candidates must dedicate numerous hours to studying the extensive body of knowledge and mastering the concepts.
- Balancing Work and Personal Life: Balancing work, family, and personal commitments while dedicating time to study can be challenging. Effective time management and prioritization are crucial for success.
Financial Cost:
- Exam Fees and Study Materials: The CCISO exam involves significant financial costs, including exam fees, study materials, and potential training courses.
- Opportunity Cost: The time spent studying for the exam represents an opportunity cost, as it takes away from other professional and personal pursuits.
Exam Difficulty:
- Comprehensive Exam Coverage: The CCISO exam covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics, requiring a deep understanding of complex concepts and real-world applications.
- High-Stakes Exam: The rigorous nature of the exam and the potential impact on your career can create additional stress and pressure.
Maintaining Certification:
- Continuous Learning: To maintain the CCISO certification, individuals must meet ongoing continuing professional education (CPE) requirements. This involves staying up-to-date with the latest industry trends and advancements.
- Recertification Process: The recertification process requires additional time and effort to complete the necessary requirements.
Is the CCISO Exam Right for You?
Determining whether the CCISO exam is the right fit for you requires careful self-assessment and consideration of your career goals. It’s essential to evaluate your current knowledge, skills, and aspirations to make an informed decision.
Self-Assessment:
- Current Knowledge and Skills: Assess your current understanding of cybersecurity concepts, risk management, governance, compliance, and incident response. Evaluate your experience in leading security teams and making strategic decisions.
- Career Goals and Aspirations: Consider your long-term career aspirations. If you aim for C-suite positions or aspire to become a CISO, the CCISO certification can significantly enhance your credibility and open doors to new opportunities.
Considering the Costs and Benefits:
- Time Investment: Evaluate your ability to dedicate significant time to study and prepare for the exam. Consider your work-life balance and prioritize your study schedule accordingly.
- Financial Investment: Assess the financial implications of the exam fees, study materials, and potential training courses. Weigh the potential return on investment in terms of career advancement and salary increases.
Seeking Guidance from Mentors and Peers:
- Consult Experienced Cybersecurity Professionals: Seek advice from experienced CISOs and security leaders who can provide insights into the challenges and rewards of the CCISO certification.
- Discuss with Colleagues and Mentors: Talk to your colleagues and mentors about their experiences with certifications and career advancement.
Conclusion
Certified Chief Information Security Officer (CCISO) certification is a highly respected credential that can significantly elevate your career in cybersecurity. It offers numerous benefits, including increased earning potential, enhanced job security, and recognition as a cybersecurity leader. However, it also comes with significant challenges, such as the time commitment required for preparation, the financial costs involved, and the rigorous nature of the exam itself.
Ultimately, the decision to pursue the CCISO certification is a personal one. By carefully assessing your current knowledge, skills, and career goals, you can determine whether the potential rewards outweigh the challenges. If you are passionate about cybersecurity, have the necessary experience, and are willing to invest the time and effort, the CCISO certification can be a valuable asset in your professional journey.


