Introduction
Over the last few years what has become rather acute to the digitized platform is the series of cyber attacks on companies and individuals. These security breaches have cost great financial loss, jobs, and data on a large scale. Facebook admitted that the data of over 87 million users was compromised. Further British Airways faced the data breach that amounted to 3.8 lakh transactions. In August an international group accessed passwords, personal information, billing amounts of over 2 million consumers of T- mobile.
It is not only the magnitude of the attacks that make them so unnerving but also the frequency with which they occur. In 2017 alone over 918 attacks occurred. It has also been determined by the National Cyber Security center that there is a strong threat to National infrastructures in the coming time. The shortage of workforce in cybersecurity to counter such attacks increases the vulnerability of firms. Small enterprises are in greater threat than the larger firms due to their insufficient resources to counter breaches. Further with GDPR in place, the small businesses can easily be bankrupt with the fines and losses. Such has been the case that over sixty percent of small scale businesses had to shut down in 2017 after the series of cyber attacks.
Security Breaches & the Cyber Attacks
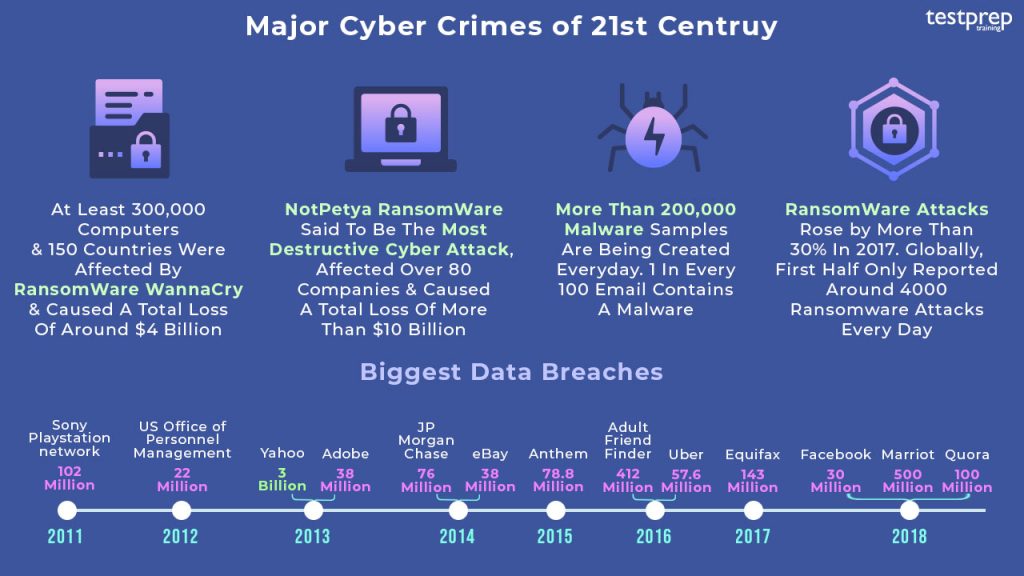
In 2017 two major ransomware attacks caused a global upheaval. These were the WannaCry and NotPetya attacks. The WannaCry ransomewareattack that occurred in May 2017 targeted 300,000 systems in 150 countries. The exploit targeted the systems without the latest patch of Microsoft windows. Their data was encrypted and ransom payment was demanded in Bitcoin Cryptocurrency. The National Health Service in England and Scotland marked as the major institutional victims of the attack. The NotPetya attack used a variant of Petya, an encrypting ransomeware that was first discovered in March 2016. The manipulated version used the same EternalBlue exploit to target systems that was used in the Wanna Cry attack. This attack affected UK, US, Russia and majorly Ukraine so much so that over 80 companies in the country were victims which also included the National Bank of Ukraine.
Cybercrime is becoming a prominent and established business of its own and the necessity for cybersecurity has only increased. All possible industries from finance, defense, legal, political, media, and others are digitized and thereby in immediate need of cyber security.
Hackers are no more an elite group in the milieu. Anyone with sufficient knowledge can exploit systems and target companies.
Shortage of Cybersecurity Experts
Despite this alarming sense of the threat that exists, most companies lack an emergent response team to tackle potential attacks. It was determined by (ISC)2, the largest nonprofit organization that trains and certifies cybersecurity professionals, that staffs and IT professionals of most companies were devoid of the necessary training and knowledge in the field to account for the cyber security requirement (now a mandate by GDPR).
Reference Read – (ISC)2 report here

The budget that goes in for cyber security is minimal against other IT projects. There is no absolute assurance against cyber attack and breaches and this lack of guarantee discourages firms to invest in security. It is an understandable attitude because the hackers are constantly finding various ways to exploit systems. It has also been regarded that the data crimes conducted by insiders with complete accessibility are far more damaging than any external attack. This form of threat is unforeseen and there is no concrete sense in which it could be regulated. If one is to consider these factors cybersecurity may seem a wasteful investment because attacks cannot be stopped. What most firms fail to realize is that the fight against data breach is not one that aims at prevention of any possible attack alone but one that is quick to respond and mitigate the potential loss that can be incurred if nothing is done in the first place. According to a Ponemon Institute research, it takes 191 days in average for a firm to detect a breach let alone counter the attack. Such a long duration of negligence causes the breach of personal, financial and transactional data, risking customer base and a company’s reputation.
It was also discovered by ( ISC)2 that globally there was a gap of 3 million jobs in the field.
What most firms fail to realize is that the fight against data breach is not one that aims at prevention of any possible attack alone but one that is quick to respond and mitigate the potential loss that can be incurred if nothing is done in the first place
Job Opportunities in Cyber Security
Due to the high demand and insufficient workforce, a Cyber Security Careerwill pay a great amount.

- Chief Information Security Officer
This is a superior level job with leading all security initiatives & carrying the responsibility of overall security of the organization. The role requires strategizing & deploying information security technologies, auditing system, anticipating threats, surveilling & monitoring organization’s security, developing strategies to handle security breaches & attacks. Additionally it may also involve non-technical managerial responsibilities. The salary range for Chief Information Security Officer is $103,000 – $254,000. - Cryptographer & Cryptoanalyst
The responsibilities of a cryptographer are developing algorithms, ciphers & system to encrypt & secure information. A cryptoanalyst performs analysis & decryption of hidden/encrypted information. It is a cryptographer’s & cryptoanalyst’s responsibility to make sure that sensitive information is hidden & secured from any threat & breach. One can begin with a junior cryptoanalyst role & the starting salary for a junior cryptoanalyst can be between $40,000 to $60,000. The salary range of a cryptographer can be between $100,000 – $200,000. - Chief Security Engineer
The job would involve developing ways to build & maintain security solutions & software for the organization along with solving existing production issues for security A security engineer is also responsible for installing firewalls & intrusions detection systems, assessing risks, detecting vulnerabilities and managing a team of security experts. S/he would leverage automation, machine learning & AI to develop robust & reliable security systems. The salary ranges from $66,000 – $132,769 - Information Security Analyst
The job require of the analyst to develop plans and strategies that can be implemented for securing the firm from potential attacks. They have to secure information, maintain & protect data, conduct security audits, analyze security breaches & the root causes & vulnerability, and train other employees, monitor data access and create policies that shall be effective in preventing attacks. The salary of a security analyst ranges from $42,391 – $101,091. - Cyber Security Manager
A Security Manager’s job is to manage an organization’s security in every way, from developing plans for security solutions to implementing them, and providing training to the workforce. S/he would devise, execute & maintain security policies & procedures, lead the audits, investigations & procedures, and manage a team of security analysts, administrators & other IT professionals along with administering costs, budgets, & integration tasks. The salary of a security manager ranges from $74,283 – $154,794. - Cyber Security Consultant
The security consultant manage and negotiate all aspects of security including implementation of the database protection, talking to the team and heads to determine security issues, research and design robust security architectures by providing technical supervision. The salary of a security consultant can range from $50,636 – $149,000. - Penetration Tester / Ethical Hacker
Penetration Testing also called as Ethical Hacking requires regular probing and exploiting security vulnerabilities in applications, networks & systems . They identify flaws, vulnerabilities, loop holes & weak practices which could expose to security breaches & lead to cyber attacks. The salary of a security consultant can range from $49,205 – $133,135. - Network Security Engineer
A Network security engineer performs risk assessments for network security & is responsible for deploying, configuring, & administering different pieces of network, and security hardware & software. The tasks include installation of firewalls, routers, switches, network monitoring tools, and VPNs (virtual private networks). engineers also regularly. The salary ranges from $56,000 – $177,000. - Cyber Security Architect
A Cyber Security Architect oversees the designing, building and implementation of network & computer security for a company. S/he is responsible for making complex security architectures & infrastructures. The salary range for a security architecture is $84,295 – $168,334. - Information Security crime Investigator/ Forensic Expert
Forensic experts are responsible for investigating the cause of an attack. They further look into the hints and clues that an attacker would have left. This clarifies the causes and flaws that led to an attack. They also perform data recovery & examination tasks, draft technical reports, & compiler legal evidence for cases. The salary ranges for Digital Forensics Expert is $57,749 – $126,277. - Security Software Developer
A security software developer is responsible for developing security software & integrating security applications. S/he also develops the tools for detecting virus, spyware, malware, or any kind of intrusion & breach. The salary for a security software developer ranges from $46,886 – $106,932. - Security Administrator
A security administrator is basically responsible fto instal, administer and troubleshoot security solutions. He performs tasks like providing protection against unauthorized access, performing vulnerability assessments, scanning networks & monitoring it for any unusual activity. The salary range for a security administer is $42,806 – $95,771.
This list of job titles may vary and the roles & responsibilities may intersect, as a lot of security experts start from general IT & software-related jobs. Further, we’ll be discussing the career paths in cybersecurity & how you can get started or transition into a cybersecurity career. We’ll also look at various certifications & training available.
How to Build A Cyber Security Career

If you have an inclination for hacking and security then it is not necessary that you retain concrete formal qualification to get the job. Experience and strategic know how become skills of practical worth in the field. However, it would be of use for any aspiring learner to have a degree in Computer sciences or STEM degree.
The following would be relevant degrees to pursue in graduation if you intend to pursue cyber security in the future.
- Computer Science
- IT
- Forensic Computing
- Mathematics, Physics or any other STEM degree
- Network Engineering
- Networks and Security.
These courses could also be pursued in the post graduation level to account for eligibility in the field.
Transition to Security
If you are to transition from an IT field to a Cyber Security Career, then you must consider your field of interest and skills. Cyber Security Certifications are a great way to make a transition into the field. Your choice of certification would depend upon your current skill set, role, experience & your goal in cyber security career. It would be important since certifications can be functional in upgrading your skill set and job position.
Cyber Security is an overarching term that encapsulates various specialties and relevant certifications that validate those specialties. Also the jobs that come under cyber security can be highly interrelated. The job position in networking, software development, system engineering, financial and risk analysis, and security intelligence can be considered as beginning positions to enter into a specialty in security.
The job position in networking, software development, system engineering, financial and risk analysis, and security intelligence can be considered as beginning positions to enter into a specialty in security.
Thus, you must know which specialty would suit you. For instance, if you are more detail oriented, analytical, strategic then the job of the security analyst or Auditor would suit you more than that of the security engineer. Also you must know the interrelated jobs amongst the various security jobs. For instance, the security architects have the grasp of the work of the security engineers.
Learning and Training
As a learner in the field you must look into relevant online courses that concern with the fundamentals of networking and security. Likewise, books on crypto,TCP/IP, Linux, UDP, routing etc. would be a good start for knowledge and self study.
The field of cyber security undergoes rapid changes and innovations all the time. Thus certifications become handy in validating one’s familiarity with the emerging changes. They are also useful if one intends to get promoted.
There is not much that would be required of anyone entering into the field except some IT knowledge and cybersecurity certifications. Experience in the field, however, is highly valued.
Cyber Security Certifications
Various Cyber Security Certifications are offered by many well known organizations which are recognized & valued globally. Let’s take a look at these organizations & the useful cybersecurity certifications
ISC2 – The International Information System Security Certification Consortium
Regarded as world’s largest IT security organization, it offers following security certifications
- SSCP – System Security Certified Practitioner
This is an entry-level certification that can be of use to those with minimal experience. - CCSP – Certified Cloud Security Professional Certification
Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) Certification Exam imparts advanced technical skills and knowledge to design, manage and secure data, applications and infrastructure in the cloud. - CISSP – Certified Information Systems Security Professional
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification Exam imparts advanced knowledge in Access Control Systems, Cryptography, and Security Management Practices. Candidates who take this exam are typically network security professionals & system administrators having an experience of at least 4 years in two or more of the ten test domains.
CompTIA: Information Technology (IT) Industry & Association
- CompTIA Security+
Validates skills in installing & configuring systems to secure applications, networks, and devices; performing threat analysis and responding with appropriate mitigation techniques; participating in risk mitigation activities.Free Mock Test on CompTIA Security+ Certification exam is available here
- CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst
The only intermediate cybersecurity analyst certification that covers security analytics, intrusion detection and response.
Free Mock Test on CompTIA CyberSecurity Analyst is available here - CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner
A CASP-certified IT professional provide the best cybersecurity solutions and protection to an organization.
Free Mock Test on CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner
EC-Council
- CEH – Certified Ethical Hacker
Among the most desired security certification, The CEH is the first part of a 3 part EC-Council Information Security Track imparting hacking technologies.
ISACA
- CISM- Certified Information Security Manager
The certification concerns with governance, management, and compliance.
Free Mock Test on CISM - CISA- Certified Information System Auditor
The certification deals with surveilling, auditing, assessing, monitoring and regulating information system.
Free Mock Test on CISA
CISCO
- CCNP- Cisco Certified Network Professional Security
The certification validates the knowledge of network security and architecture. - CCNA – Cisco Certified Network Associate
The qualification concerns with securing network infrastructure, managing secure access, VPN encryption, firewalls, intrusion prevention, web and email security, network management.
More Security Certifications
- GIAC- Global Information Assurance Certification
The certification concerns with specialty hands-on technical abilities like forensic, intrusion detection etc. - CCSK- Cloud Computing Security Knowledge Certification
The certification involves a comprehensive teaching of cloud security. - Amazon Certified Security Specialty
AWS Certified Security – Specialty Certification validates experienced cloud security professionals on the knowledge of how to secure the AWS platform. - Microsoft Security Fundamentals Certification
This certification exam validates that a candidate has fundamental security knowledge and skills. It can serve as a stepping stone to the Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate (MCSA) exams.Free Mock Test on Microsoft Security Fundamentals Certification
The job gap in the cybersecurity space needs to be met and an aware social and professional environment that is security driven needs to become the norm for companies to tackle the breaches that occur. The environment that encourages more cybersecurity professionals in the educational sphere needs to be adopted for growth in the field. All in all the necessity is ample be it any industry in the present and its high time that cybersecurity is acknowledged as a significant field.
Give your feedback or ask any questions in the comments below

