Preparing for the Exam AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure is all about understanding and getting familiar with the concepts of Azure Hybrid Benefit. Where the Azure hybrid benefit service is a valuable feature that allows you to migrate your on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses with active Software Assurance or subscriptions to Azure. When you combine Azure Hybrid Benefit, reservation savings, and extended security updates, you can save up to 85%* on normal pay-as-you-go pricing and reach the lowest total cost of ownership.
But, how to start preparing for the Microsoft AZ-800 exam to get into the Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure. To help in this, we have prepared this guide to cover all the essential areas of the exam including the updated course objectives, training methods, and practice tests for passing the AZ-800 exam.
Guide to pass the Microsoft Azure AZ-800 exam
Microsoft AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure exam is designed for candidates with skills for administering core Windows Server workloads using on-premises, hybrid, and cloud technologies. These professionals have the ability for applying and managing on-premises and hybrid solutions, such as identity, management, compute, networking, and storage. They also know how to use administrative tools and technologies including Windows Admin Center, PowerShell, Azure Arc, and IaaS virtual machine management. Further, this exam needs significant knowledge of Windows Server operating systems.
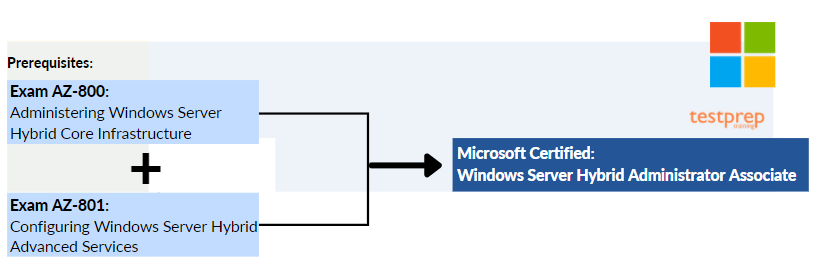
However, talking about the certifications, passing this exam will take you one step closer to becoming Microsoft Certified: Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate. Yes, the AZ-800 exam works as a prerequisite for this certification. Therefore to become Microsoft Certified: Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate, you have to pass:
- AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- AZ-801: Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
Microsoft Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate: Roles and Responsibilities
The Microsoft Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate is responsible for executing tasks like:
- Firstly, configuring and managing Windows Server on-premises, hybrid, and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) platform workloads.
- Secondly, managing Windows Server in on-premises networks and merging Windows Server systems with Azure services.
- Thirdly, controlling and maintaining Windows Server IaaS workloads in Azure, in addition to migrating and deploying workloads to Azure.
- Lastly, collaborating with,
- Azure administrators
- Enterprise architects
- Microsoft 365 administrators
- Network engineers.
Further, earning the Microsoft Certified: Windows Server Hybrid Administrator Associate certification will you get into the top job roles such as:
- Administrator
- Identity And Access Administrator
- Information Protection Administrator
- Network Engineer
- Security Engineer
- Support Engineer
- Technology Manager
Microsoft AZ-800 Exam Format
Microsoft Azure AZ-800 exam validates your skills for executing various tasks like:
- Firstly, Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) deployment and management in on-premises and cloud settings
- Secondly, in a hybrid environment, managing Windows Servers and workloads.
- Thirdly, managing virtual machines and containers
- Then, applying and controlling an on-premises and hybrid networking infrastructure
- Lastly, managing storage and file services.
However, the exam will have 40-60 questions for which the minimum passing score is 700. The exam can be taken in the English language and is available at the cost of $165 USD*.
Step 1. Getting familiar with the exam objectives
This is an important component of your preparation. Every examination has topics that are highly significant. It’s also important to go through each section to have a better knowledge of the subject. The Microsoft AZ-800 exam has various subjects, each having sections and subsections. Let’s have a look at them.
Topic 1: Deploy and manage Azure Directory Domain Services (AD DS) in on-premises and cloud environments (30–35%)
Deploy and manage AD DS domain controllers
- deploy and manage domain controllers on-premises (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy and manage Azure IaaS Active Directory domain controllers in Azure)
- deploying and managing domain controllers in Azure (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy AD DS in an Azure virtual network)
- deploying read-only domain controllers (RODCs) (MicrosoftDocumentation: AD DS: Read-Only Domain Controllers)
- troubleshoot flexible single master operation (FSMO) roles (MicrosoftDocumentation: Active Directory FSMO roles in Windows)
Configure and manage multi-site, multi-domain, and multi-forest environments
- configuring and manage forest and domain trusts (MicrosoftDocumentation: How trust relationships work for resource forests in Azure Active Directory Domain Services)
- configure and manage AD DS sites (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create and configure an Azure Active Directory Domain Services managed domain)
- configure and manage AD DS replication (MicrosoftDocumentation: Active Directory Replication Concepts)
Create and manage AD DS security principals
- create and manage AD DS users and groups (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create and configure an Azure Active Directory Domain Services managed domain)
- manage users and groups in multi-domain and multi-forest scenarios (MicrosoftDocumentation: Multiple forests with AD DS and Azure AD)
- implement group managed service accounts (gMSAs) (MicrosoftDocumentation: Group Managed Service Accounts Overview)
- Join Windows Servers to AD DS, Microsoft Entra Domain Services, and Microsoft Entra
Implement and manage hybrid identities
- Integrate Microsoft Entra ID, AD DS and Microsoft Entra Domain Services
- implement Microsoft Entra Connect
- manage Microsoft Entra Connect Synchronization
- implement Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync
- manage Microsoft Entra Domain Services
- managing Microsoft Entra Connect Health
- manage authentication in on-premises and hybrid environments (MicrosoftDocumentation: Microsoft 365 integration with on-premises environments)
- configure and manage AD DS passwords (MicrosoftDocumentation: Password and account lockout policies)
Manage Windows Server by using domain-based Group Policies
- implement Group Policy in AD DS (MicrosoftDocumentation: Administer Group Policy in an Azure Active Directory Domain Services managed domain)
- implementing Group Policy Preferences in AD DS (MicrosoftDocumentation: Group Policy Preferences)
- implement Group Policy in Microsoft Entra Domain Services
Topic 2: Manage Windows Servers and workloads in a hybrid environment (10–15%)
Manage Windows Servers in a hybrid environment
- deploy a Windows Admin Center Gateway server (MicrosoftDocumentation: Install Windows Admin Center)
- configure a target machine for Windows Admin Center Gateway server (MicrosoftDocumentation: Troubleshooting Windows Admin Center)
- configuring PowerShell Remoting (MicrosoftDocumentation: Enable-PSRemoting)
- configure Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP) or Kerberos Delegation for 2nd Hop Remoting (MicrosoftDocumentation: Making the second hop in PowerShell Remoting)
- configure Just Enough Administration (JEA) for PowerShell Remoting (MicrosoftDocumentation: Just Enough Administration)
Manage Windows Servers and workloads by using Azure services
- manage Windows Servers by using Azure Arc (MicrosoftDocumentation: What is Azure Arc-enabled servers?)
- Create and assign Azure Policy that uses guest configuration extension
- deploy Azure services using Azure VM extensions on non-Azure machines (MicrosoftDocumentation: Virtual machine extensions and features for Windows)
- manage updates for Windows machines (MicrosoftDocumentation: Update Management overview)
- integrate Windows Servers with Log Analytics (MicrosoftDocumentation: Install Log Analytics agent on Windows computers)
- Integrate Windows Servers with Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- manage IaaS VMs in Azure that run Windows Server (MicrosoftDocumentation: Administer and manage Windows Server IaaS Virtual Machine remotely)
- implement Azure Automation for hybrid workloads (MicrosoftDocumentation: Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker overview)
- create runbooks to automate tasks on target VMs (MicrosoftDocumentation: Manage runbooks in Azure Automation)
- Implement Azure Automation State Configuration to prevent configuration drift in IaaS machines (MicrosoftDocumentation: Azure Automation State Configuration overview)

Topic 3: Manage virtual machines and containers (15–20%)
Manage Hyper-V and guest virtual machines
- enable VM enhanced session mode (MicrosoftDocumentation: Enable enhanced console session in VMM)
- Manage VM using PowerShell remoting, PowerShell Direct and Secure Shell (SSH) Direct for Linux VMs
- configure nested virtualization (MicrosoftDocumentation: Run Hyper-V in a Virtual Machine with Nested Virtualization)
- configuring VM memory (MicrosoftDocumentation: Configure virtual machine settings in the VMM compute fabric)
- configure Integration Services (MicrosoftDocumentation: Install Integration Services (SSIS))
- configuring Discrete Device Assignment (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy graphics devices using Discrete Device Assignment)
- configure VM Resource Groups (MicrosoftDocumentation: Manage Azure Resource Manager resource groups by using the Azure portal)
- configuring VM CPU Groups (MicrosoftDocumentation: Virtual Machine Resource Controls)
- configure hypervisor scheduling types (MicrosoftDocumentation: Managing Hyper-V hypervisor scheduler types)
- manage VM Checkpoints (MicrosoftDocumentation: Enable or disable checkpoints)
- implement high availability for virtual machines (MicrosoftDocumentation: Availability options for Azure Virtual Machines)
- manage virtual hard disk (VHD) and virtual hard disk v2 (VHDX) files (MicrosoftDocumentation: Manage Virtual Hard Disks (VHD))
- configure Hyper-V network adapter (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create a virtual switch for Hyper-V virtual machines)
- configuring network interface card (NIC) Teaming (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create a new NIC Team on a host computer or VM)
- configure Hyper-V switch
Create and manage containers
- create Windows Server container images (MicrosoftDocumentation: Container Base Images)
- manage Windows Server container images
- configure Container networking (MicrosoftDocumentation: Windows container networking)
- managing container instances (MicrosoftDocumentation: What is Azure Container Instances?)
Manage Azure Virtual Machines that run Windows Server
- manage data disks (MicrosoftDocumentation: Introduction to Azure managed disks)
- resize Azure VM (MicrosoftDocumentation: Change the size of a virtual machine)
- configure connections to VMs (MicrosoftDocumentation: How to connect and sign on to an Azure virtual machine running Windows)
- manage Azure VM network configuration (MicrosoftDocumentation: Virtual networks and virtual machines in Azure)
Topic 4: Implement and manage an on-premises and hybrid networking infrastructure (15–20%)
Implement on-premises and hybrid name resolution
- integrate DNS with AD DS (MicrosoftDocumentation: DNS and AD DS)
- create and manage DNS zones and records (MicrosoftDocumentation: Overview of DNS zones and records)
- configure DNS forwarding/conditional forwarding (MicrosoftDocumentation: Forwarders and conditional forwarders resolution timeouts)
- integrate Windows Server DNS with Azure DNS private zones (MicrosoftDocumentation: Azure Private Endpoint DNS configuration)
- implement Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) (MicrosoftDocumentation: Overview of DNSSEC)
Manage IP addressing in on-premises and hybrid scenarios
- implement and manage IP Address Management (IPAM) (MicrosoftDocumentation: IP Address Management (IPAM))
- implement and configure the Dynamic Host Configuration protocol (DHCP) server role (on-premises only) (MicrosoftDocumentation: How To Install and Configure a DHCP Server in a Workgroup)
- resolve IP address issues in hybrid environments (MicrosoftDocumentation: Troubleshoot migration issues in Exchange Server hybrid environment)
- create and manage DHCP scopes
- create and manage IP reservations (MicrosoftDocumentation: Managing IP Address Space)
- implementing DHCP high availability (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy DHCP Failover)
Implement on-premises and hybrid network connectivity
- implementing and managing the Remote Access role (MicrosoftDocumentation: Manage Remote Access)
- implement and manage Azure Network Adapter (MicrosoftDocumentation: Connect standalone servers by using Azure Network Adapter)
- implementing and managing Azure Extended Network (MicrosoftDocumentation: What is Azure Virtual Network?)
- implement and manage Network Policy Server role (MicrosoftDocumentation: Network Policy Server (NPS))
- implementing Web Application Proxy (MicrosoftDocumentation: Web Application Proxy in Windows Server)
- implement Azure Relay (MicrosoftDocumentation: What is Azure Relay?)
- implementing site-to-site VPN (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create a Site-to-Site connection in the Azure portal)
- implement Azure Virtual WAN (MicrosoftDocumentation: What is Azure Virtual WAN?)
- implement Microsoft Entra Application Proxy
Topic 5: Manage storage and file services (15–20%)
Configure and manage Azure File Sync
- create Azure File Sync service (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy Azure File Sync)
- creating sync groups
- create cloud endpoints (MicrosoftDocumentation: az storagesync sync-group cloud-endpoint)
- register servers (MicrosoftDocumentation: Register Servers)
- create server endpoints (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create a service endpoint)
- configure cloud tiering (MicrosoftDocumentation: Cloud tiering overview)
- monitor File Sync (MicrosoftDocumentation: Monitor Azure File Sync)
- Migrate Distributed File System (DFS) to Azure File Sync
Configure and manage Windows Server file shares
- configure Windows Server file share access (MicrosoftDocumentation: Overview of file sharing using the SMB 3 protocol in Windows Server)
- configuring file screens (MicrosoftDocumentation: Create a File Screen)
- configure file server resource manager (FSRM) quotas (MicrosoftDocumentation: File Server Resource Manager (FSRM) overview)
- configure BranchCache
- implement and configure Distributed File System (DFS) (MicrosoftDocumentation: Distributed File System (DFS) Functions)
Configure Windows Server storage
- configure disks and volumes (MicrosoftDocumentation: Overview of Disk Management)
- configuring and managing Storage Spaces (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy Storage Spaces Direct)
- configure and manage Storage Replica (MicrosoftDocumentation: Storage Replica overview)
- configuring Data Deduplication (MicrosoftDocumentation: Install and enable Data Deduplication)
- Configure Server Message Block (SMB) direct (MicrosoftDocumentation: SMB Direct)
- configuring Storage QoS (MicrosoftDocumentation: Storage Quality of Service)
- configure file systems (MicrosoftDocumentation: Deploy Network File System)
Step 2. Exploring Microsoft Study Resources
Microsoft offers a variety of resources to assist applicants in studying for the AZ-800 exam. This includes the following:
– Microsoft Learning Path
Microsoft provides new methods for grasping the topics. That is, Microsoft offers a range of study paths for each examination, each of which covers the exam’s subjects in modules. These include all relevant data as well as useful reference links for every topic. Furthermore, you may acquire in-depth information on test subjects by using the sections provided with a bonus quiz at the end of each module to help you prepare for the exam.
– Microsoft Documentation
Microsoft documentation aids in the comprehension and familiarisation of topics. You will learn about the many ways to administer basic Windows Server workloads utilizing on-premises, hybrid, and cloud technologies for the Microsoft AZ-800 exam. You’ll also improve your skills in using and administering on-premises and hybrid systems including identity, management, computing, networking, and storage. You may also use the Azure Hybrid documentation to learn more about the service.
– Microsoft Instructor-led Training
Microsoft provides courses in the form of Instructor-led Training. This training offers short-term courses covering all the relevant concepts, modules, details, and tests that will lead you towards passing the exam. And, the major benefit of this instructor-led training is that you can study on your own time, at your own speed, and in your own place, you just have to choose a classic classroom training scenario.
– Online Study Groups
Candidates can benefit from online study groups while studying for exams. Joining study groups, in other words, will allow you to keep in touch with experts and professionals who are already on this route. You may also use this group to discuss your test-related question or concern, as well as take the AZ-800 exam study notes. Furthermore, these groups will help you gain confidence by talking and connecting with those professionals who have already passed the AZ-800 exam. This will help you get clarity about what you have to do next to earn your dream job role.
– Assess yourself using Practice tests
It is important to take practice examinations in order to improve your preparation. You will learn about your weak and strong areas by testing yourself with Microsoft AZ-800 practice exams. Furthermore, you will be able to enhance your answering abilities, which will allow you to save a significant amount of time during the exam. However, taking the AZ-800 exam practice tests after completing a whole topic is the wise way to go. This can also help you revise effectively. So, go online and look for the greatest practice exam tests to prepare for the Microsoft AZ-800 certification exam.
Why learn Azure Hybrid Benefit?
The Azure Hybrid Benefit is a licensed benefit that helps you in saving the cost of operating your workloads over the cloud. It works by allowing you to utilize your Windows Server and SQL Server licenses that are Software Assurance-enabled on-premises on Azure. This benefit now extends to RedHat and SUSE Linux subscriptions as well.
However, let’s understand the concept of Azure hybrid in SQL Server, Window Server, and Linux.
1. SQL Server
- Firstly, use Azure Hybrid Benefit to save money on both Windows Server and SQL Server workloads.
- Secondly, in the platform as a service (PaaS) settings, you can use current SQL Server licenses.
- Thirdly, apply to the SQL Server 1 to 4 vCPUs exchange: You receive 4 vCPUs of SQL Managed Instance or Azure SQL Database general purpose and Hyperscale tiers or 4 vCPUs of SQL Server Standard Edition on Azure VMs for every 1 core of SQL Server Enterprise Edition.
- Then, with Azure Dedicated Host, you can fulfill compliance needs with unlimited virtualization.
- Lastly, get 180 days of on-premises and Azure dual-use rights.
2. Windows Server
In this, using Azure you can:
- Firstly, assign Windows Server licenses in the cloud.
- Secondly, get 180 days of on-premises and cloud dual-use rights.
- Thirdly, get the most out of your Windows Server licences while saving up to 40%* on virtual machines with Azure Hybrid Benefit.
- Lastly, hav access to each Datacenter or Standard edition with two-processor license or bundle of 16-core licenses includes two instances of up to 8 cores or one instance of up to 16 cores.
- Datacenter edition licenses enable on-premises and Azure usage at the same time.
- Standard edition licences may be used on-premises or on Azure. However, you’ll get 180 days of concurrent use rights while switching servers.
3. Linux
On Azure, you can use your current on-premises Red Hat or SUSE software subscriptions. You can only do the following on Azure:
- Firstly, pay exclusively for the charges of your VM infrastructure. Moreover, your existing subscription already covers the software charge, which applies to all Azure Marketplace Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server pay-as-you-go images.
- Secondly, save time by avoiding production redeployment with seamless post-deployment conversions.
- Thirdly, automatic image maintenance, updates, and patches can help you save money in the long run.
- Moreover, take advantage of the Azure Portal and CLI’s seamless user interface integration, as well as scalable batch conversions.
- Lastly, with just one ticket, you can get the cloud’s only co-located technical assistance from Azure, Red Hat, and SUSE.
Final Words
To begin in a stepwise manner, the details of the Microsoft AZ-800 test, as well as the main study guide, have been discussed above. This examination will put your knowledge, competence, and collaborative abilities to the test. As a result, in order to increase your preparation, you must focus on all of the essential areas. Take the time to create a study plan and pattern based on the material you’ve been provided, and then begin the preparation process step by step. Also, we have gone through the Azure hybrid service by learning about some of its areas. So, don’t forget to review by taking practice exams and evaluations. Just take the test and pass it!


