The AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional exam is surely a hard nut to crack. Given its vast syllabus and tricky questions, you need to really revise well. AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional certification exam is developed to verify a candidate’s technical knowledge of creating, running, and managing distributed application systems on the AWS platform. It verifies a candidate’s ability to –
- Firstly, Implement and manage continuous delivery systems and methodologies on AWS
- Secondly, Implement and automate security controls, governance processes, and compliance validation
- Thirdly, Define and deploy monitoring, metrics, and logging systems on AWSImplement systems that are highly available, scalable, and self-healing on the AWS platform
- Also, Design, manage and maintain tools to automate operational processes
The AWS DevOps Engineer Professional certification exam validates your expertise in provisioning, operating, and managing distributed application systems on the AWS platform. It requires a deep understanding of continuous delivery, automation, monitoring, and scalability.
Exam Details:
- Format: Multiple-choice, multiple-response
- Number of questions: 75
- Time allowed: 180 minutes
- Pass score: 750/1000
- Cost: $300
Recommended Knowledge:
Candidates who wish to appear for the exam must comply with the following AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional certification prerequisites:
- To begin with, Experience developing code in at least one high-level programming language
- Then, Experience building highly automated infrastructures
- Moreover, Understanding of modern development and operations processes and methodologies
- Also, Experience administering operating systems
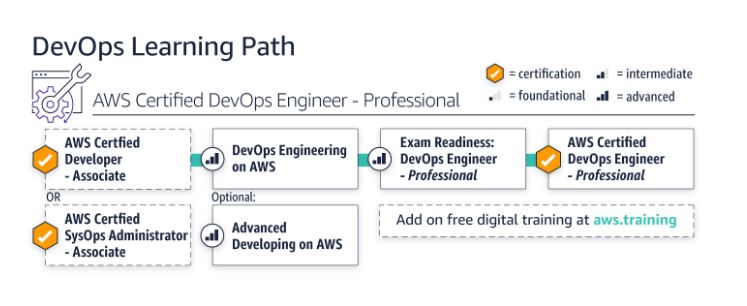
AWS Learning Path : AWS Certified DevOps Engineer-Professional
This learning path is designed for individuals who want to understand the process of creating, deploying, and managing apps in the AWS Cloud using popular DevOps practices. While pursuing AWS Certification, you’ll enhance your technical skills.
Services to Know for the AWS DevOps Engineer Professional exam:
- Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Use CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodePipeline, and CodeDeploy for version control, building, testing, and deploying code.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Use CloudFormation or Terraform to automate infrastructure deployment.
- Monitoring & Logging: Use CloudWatch for monitoring and logging, and integrate it with other AWS services such as EC2 and Lambda.
- Security: Implement security best practices using IAM policies and roles, VPCs, security groups, and network access control lists.
- Deployment Strategies: Know the difference between blue/green and rolling deployments, and when to use them.
- Load balancing: Use ELB or ALB for load balancing and ensure high availability and scalability.
- Containers: Use EC2 Container Service (ECS) or Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) for container management.
- Databases: Know the different database options available in AWS, such as RDS, DynamoDB, and Redshift.
- Disaster Recovery: Plan for disaster recovery by implementing backup and recovery strategies, such as cross-region replication.
- Microservices: Use AWS services such as Lambda, API Gateway, and SQS to build and deploy microservices.
Cheat Sheet | AWS Certified DevOps Engineer-Professional
When preparing for this certification exam, let your mind roam and devise a study plan that works for you. To succeed at this, one has to be calm, laser-focused, and knowledgeable about the AWS environment. For your convenience as you proceed toward certification, here is a cheat sheet provided by subject matter experts.

1. Review the Exam Objectives
Before taking the test, you should have enough hands-on expertise with pertinent AWS products and services. Visit the official website to become familiar with the exam domains. Making a study schedule based on exam topics will aid in your exam preparation. The following six domains are covered in the Professional Course for AWS Certified DevOps Engineers:
Module 1: Understanding SDLC Automation (22%)
1.1: Implement CI/CD pipelines.
Required Knowledge
- Software development lifecycle (SDLC) concepts, phases, and models
- Pipeline deployment patterns for single- and multi-account environments
Skills
- Configuring code, image, and artifact repositories
- Using version control to integrate pipelines with application environments
- Setting up build processes (for example, AWS CodeBuild)
- • Managing build and deployment secrets (for example, AWS Secrets Manager, AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store)
- Determining appropriate deployment strategies (for example, AWS CodeDeploy)
1.2: Integrate automated testing into CI/CD pipelines.
Required Knowledge
- Different types of tests (for example, unit tests, integration tests, acceptance tests, user interface tests, security scans)
- Reasonable use of different types of tests at different stages of the CI/CD pipeline
Skills
- Running builds or tests when generating pull requests or code merges (for example, AWS CodeCommit, CodeBuild)
- Running load/stress tests, performance benchmarking, and application testing at scale
- Measuring application health based on application exit codes
- Automating unit tests and code coverage
- Invoking AWS services in a pipeline for testing
1.3 Build and manage artifacts.
Required Knowledge
- Artifact use cases and secure management
- Methods to create and generate artifacts
- Artifact lifecycle considerations
Skills
- Creating and configuring artifact repositories (for example, AWS CodeArtifact, Amazon S3, Amazon Elastic Container Registry [Amazon ECR])
- Configuring build tools for generating artifacts (for example, CodeBuild, AWS Lambda)
- Automating Amazon EC2 instance and container image build processes (for example, EC2 Image Builder)
1. 4: Implement deployment strategies for instance, container, and serverless environments.
Required Knowledge
- Deployment methodologies for various platforms (for example, Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic Container Service [Amazon ECS], Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service [Amazon EKS], Lambda)
- Application storage patterns (for example, Amazon Elastic File System [Amazon EFS], Amazon S3, Amazon Elastic Block Store [Amazon EBS])
- Mutable deployment patterns in contrast to immutable deployment patterns
- Tools and services available for distributing code (for example, CodeDeploy, EC2 Image Builder)
Skills
- Configuring security permissions to allow access to artifact repositories (for example, AWS Identity and Access Management [IAM], CodeArtifact)
- Configuring deployment agents (for example, CodeDeploy agent)
- Troubleshooting deployment issues
- Using different deployment methods (for example, blue/green, canary)
Module 2: Understanding Configuration Management and IaC (17%)
2.1 Define cloud infrastructure and reusable components to provision and manage systems throughout their lifecycle.
Required Knowledge
- Infrastructure as code (IaC) options and tools for AWS
- Change management processes for IaC-based platforms
- Configurations management services and strategies
Skills
- Composing and deploying IaC templates (for example, AWS Serverless Application Model [AWS SAM], AWS CloudFormation, AWS Cloud Development Kit [AWS CDK])
- Applying AWS CloudFormation StackSets across multiple accounts and AWS Regions
- Determining optimal configuration management services (for example, AWS OpsWorks, AWS Systems Manager, AWS Config, AWS AppConfig)
- Implementing infrastructure patterns, governance controls, and security standards into reusable IaC templates (for example, AWS Service Catalog, CloudFormation modules, AWS CDK)
2.2 Deploy automation to create, onboard, and secure AWS accounts in a multiaccount/multi-Region environment.
Required Knowledge
- AWS account structures, best practices, and related AWS services
Skills
- Standardizing and automating account provisioning and configuration
- Creating, consolidating, and centrally managing accounts (for example, AWS Organizations, AWS Control Tower)
- Applying IAM solutions for multi-account and complex organization structures (for example, SCPs, assuming roles)
- Implementing and developing governance and security controls at scale (AWS Config, AWS Control Tower, AWS Security Hub, Amazon Detective, Amazon GuardDuty, AWS Service Catalog, SCPs)
2. 3: Design and build automated solutions for complex tasks and large-scale environments.
Required Knowledge
- AWS services and solutions to automate tasks and processes
- Methods and strategies to interact with the AWS software-defined infrastructure
Skills
- • Automating system inventory, configuration, and patch management (for example, Systems Manager, AWS Config)
- • Developing Lambda function automations for complex scenarios (for example, AWS SDKs, Lambda, AWS Step Functions)
- Automating the configuration of software applications to the desired state (for example, OpsWorks, Systems Manager State Manager)
- Maintaining software compliance (for example, Systems Manager)
Module 3: Understanding Resilient Cloud Solutions (15%)
3.1 Implement highly available solutions to meet resilience and business requirements.
Required Knowledge
- Multi-AZ and multi-Region deployments (for example, compute layer, data layer)
- SLAs
- Replication and failover methods for stateful services
- Techniques to achieve high availability (for example, Multi-AZ, multi-Region)
Skills
- Translating business requirements into technical resiliency needs
- Identifying and remediating single points of failure in existing workloads
- Enabling cross-Region solutions where available (for example, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon RDS, Amazon Route 53, Amazon S3, Amazon CloudFront)
- Configuring load balancing to support cross-AZ services
- Configuring applications and related services to support multiple Availability Zones and Regions while minimizing downtime
3.2 Implement solutions that are scalable to meet business requirements.
Required Knowledge
- Appropriate metrics for scaling services
- Loosely coupled and distributed architectures
- Serverless architectures
- Container platforms
Skills
- Identifying and remediating scaling issues
- Identifying and implementing appropriate auto scaling, load balancing, and caching solutions
- Deploying container-based applications (for example, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS)
- Deploying workloads in multiple AWS Regions for global scalability
- Configuring serverless applications (for example, Amazon API Gateway, Lambda, AWS Fargate)
3.3 Implement automated recovery processes to meet RTO/RPO requirements.
Required Knowledge
- Disaster recovery concepts (for example, RTO, RPO)
- Backup and recovery strategies (for example, pilot light, warm standby)
- Recovery procedures
Skills
- Testing failover of Multi-AZ/multi-Region workloads (for example, Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Route 53, CloudFront)
- Identifying and implementing appropriate cross-Region backup and recovery strategies (for example, AWS Backup, Amazon S3, Systems Manager)
- Configuring a load balancer to recover from backend failure
Module 4: Monitoring and Logging
4.1 Configure the collection, aggregation, and storage of logs and metrics.
Required Knowledge
- How to monitor applications and infrastructure
- Amazon CloudWatch metrics (for example, namespaces, metrics, dimensions, and resolution)
- Real-time log ingestion
- Encryption options for at-rest and in-transit logs and metrics (for example, client-side and server-side, AWS Key Management Service [AWS KMS])
- Security configurations (for example, IAM roles and permissions to allow for log collection)
Skills
- Securely storing and managing logs
- Creating CloudWatch metrics from log events by using metric filters
- Creating CloudWatch metric streams (for example, Amazon S3 or Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose options)
- Collecting custom metrics (for example, using the CloudWatch agent)
- Managing log storage lifecycles (for example, S3 lifecycles, CloudWatch log group retention)
- Processing log data by using CloudWatch log subscriptions (for example, Kinesis, Lambda, Amazon OpenSearch Service)
- Searching log data by using filter and pattern syntax or CloudWatch Logs Insights
- Configuring encryption of log data (for example, AWS KMS)
4.2 Audit, monitor, and analyze logs and metrics to detect issues.
Required Knowledge
- Anomaly detection alarms (for example, CloudWatch anomaly detection)
- Common CloudWatch metrics and logs (for example, CPU utilization with Amazon EC2, queue length with Amazon RDS, 5xx errors with an Application Load Balancer)
- Amazon Inspector and common assessment templates
- AWS Config rules
- AWS CloudTrail log events
Skills
- Building CloudWatch dashboards and Amazon QuickSight visualizations
- Associating CloudWatch alarms with CloudWatch metrics (standard and custom)
- Configuring AWS X-Ray for different services (for example, containers, API Gateway, Lambda)
- Analyzing real-time log streams (for example, using Kinesis Data Streams)
- Analyzing logs with AWS services (for example, Amazon Athena, CloudWatch Logs Insights)
4.3 Automate monitoring and event management of complex environments.
Required Knowledge
- Event-driven, asynchronous design patterns (for example, S3 Event Notifications or Amazon EventBridge events to Amazon Simple Notification Service [Amazon SNS] or Lambda)
- Capabilities of auto scaling a variety of AWS services (for example, EC2 Auto Scaling groups, RDS storage auto scaling, DynamoDB, ECS capacity provider, EKS autoscalers)
- Alert notification and action capabilities (for example, CloudWatch alarms to Amazon SNS, Lambda, EC2 automatic recovery)
- Health check capabilities in AWS services (for example, Application Load Balancer target groups, Route 53)
Skills
- Configuring solutions for auto scaling (for example, DynamoDB, EC2 Auto Scaling groups, RDS storage auto scaling, ECS capacity provider)
- Creating CloudWatch custom metrics and metric filters, alarms, and notifications (for example, Amazon SNS, Lambda)
- Configuring S3 events to process log files (for example, by using Lambda), and deliver log files to another destination (for example, OpenSearch Service, CloudWatch Logs) Configuring EventBridge to send notifications based on a particular event pattern
- Installing and configuring agents on EC2 instances (for example, AWS Systems Manager Agen [SSM Agent], CloudWatch agent)
- Configuring AWS Config rules to remediate issues
- Configuring health checks (for example, Route 53, Application Load Balancer)
Module 5: Incident and Event Response
5.1 Manage event sources to process, notify, and take action in response to events.
Required Knowledge
- AWS services that generate, capture, and process events (for example, AWS Health, EventBridge, CloudTrail, CloudWatch Events)
- Event-driven architectures (for example, fan out, event streaming, queuing)
Skills
- Integrating AWS event sources (for example, AWS Health, EventBridge, CloudTrail, CloudWatch Events)
- Building event processing workflows (for example, Amazon Simple Queue Service [Amazon SQS], Kinesis, Amazon SNS, Lambda, Step Functions)
5.2 Implement configuration changes in response to events.
Required Knowledge
- Fleet management services (for example, Systems Manager, AWS Auto Scaling)
- Configuration management services (for example, AWS Config)
Skills
- Applying configuration changes to systems
- Modifying infrastructure configurations in response to events
- Remediating a non-desired system state
5.3 Troubleshoot system and application failures.
Required Knowledge
- AWS metrics and logging services (for example, CloudWatch, X-Ray)
- AWS service health services (for example, AWS Health, CloudWatch, Systems Manager OpsCenter)
- Root cause analysis
Skills
- Analyzing failed deployments (for example, AWS CodePipeline, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, CloudFormation, CloudWatch synthetic monitoring)
- Analyzing incidents regarding failed processes (for example, auto scaling, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS)
Module 6: Security and Compliance
6.1 Implement techniques for identity and access management at scale.
Required Knowledge
- Appropriate usage of different IAM entities for human and machine access (for example, users, groups, roles, identity providers, identity-based policies, resource-based policies, session policies)
- Identity federation techniques (for example, using IAM identity providers and AWS Single Sign-On)
- Permission management delegation by using IAM permissions boundaries
- Organizational SCPs
Skills
- Designing policies to enforce least privilege access
- Implementing role-based and attribute-based access control patterns
- Automating credential rotation for machine identities (for example, Secrets Manager)
- Managing permissions to control access to human and machine identities (for example, enabling multi-factor authentication [MFA], AWS Security Token Service [AWS STS], IAM profiles)
6.2 Apply automation for security controls and data protection.
Required Knowledge
- Network security components (for example, security groups, network ACLs, routing, AWS Network Firewall, AWS WAF, AWS Shield)
- Certificates and public key infrastructure (PKI)
- Data management (for example, data classification, encryption, key management, access controls)
Skills
- Automating the application of security controls in multi-account and multi-Region environments (for example, Security Hub, Organizations, AWS Control Tower, Systems Manager)
- Combining security controls to apply defense in depth (for example, AWS Certificate Manager [ACM], AWS WAF, AWS Config, AWS Config rules, Security Hub, GuardDuty, security groups, network ACLs, Amazon Detective, Network Firewall)
- Automating the discovery of sensitive data at scale (for example, Amazon Macie)
- Encrypting data in transit and data at rest (for example, AWS KMS, AWS CloudHSM, ACM)
6.3 Implement security monitoring and auditing solutions.
Required Knowledge
- Security auditing services and features (for example, CloudTrail, AWS Config, VPC Flow Logs, CloudFormation drift detection)
- AWS services for identifying security vulnerabilities and events (for example, GuardDuty, Amazon Inspector, IAM Access Analyzer, AWS Config)
- Common cloud security threats (for example, insecure web traffic, exposed AWS access keys, S3 buckets with public access enabled or encryption disabled)
Skills
- Implementing robust security auditing
- Configuring alerting based on unexpected or anomalous security events
- Configuring service and application logging (for example, CloudTrail, CloudWatch Logs)
- Analyzing logs, metrics, and security findings
2. Discover Learning Resources
Amazon offers a wide variety of learning resources to all its candidates. These resources are truly beneficial for your preparations. Here are some highly suggested resources you must explore:
– Refer Whitepapers
Candidates preparing for the AWS can also take the help of amazon whitepapers for preparation. These are the authentic study resources that we can surely vouch for. These are basically the pdf formats of the topics which you can find on the official page of amazon certifications. Whitepapers not only strengthen your preparation process but also helps you build a strong strategy to lay your focus on.

– Learn from Books
Professional AWS DevOps Engineer Training Books are a never-ending source of knowledge. You may discover a variety of books for the security specialized test online or at libraries. You can arm yourself with the following books:
- Firstly, AWS Automation Cookbook by Nikit Swaraj
- Secondly, Continuous Delivery and DevOps – Quickstart by Paul Swartout
- Also, Implementing DevOps on AWS by Veselin kantsev
- Then, Effective DevOps with AWS by Nathenial Felson
– Online Tutorials and Study Guide
The best way to enhance your knowledge is by referring Online Tutorials. These Tutorials provide in depth understanding about the exam and its concepts. Also, following a Study Guide is key to success. These resources will enrich your learning and will result in strengthening your preparation.
3. Stay Updated
AWS regularly enhances its services and tools, making it crucial to stay informed about the latest changes. Keep yourself updated by using AWS blogs, forums, and social media channels to stay informed about the latest news and updates from AWS.
4. Hands-on Practice
Hands-on experience with AWS services and tools is essential for passing the exam. Set up a test environment using AWS to practice and experiment with different configurations and scenarios. Use AWS services like AWS CloudFormation, AWS CodeDeploy, AWS CodePipeline, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk to gain practical experience with continuous delivery and process automation.
5. Join AWS Community
The AWS community is a great resource for learning and sharing knowledge about AWS services and tools. Join AWS forums, discussion groups, and meetups to interact with other AWS professionals and learn from their experiences.
6. Practice your way ahead!
Use as many practice tests and test series as you can to evaluate your readiness level and how much further study is needed. To finish your revision, pick the most reputable and reliable practice test among the many that are offered online. Exam practice can help you assess yourself and boost your confidence. These tests also provide you the chance to evaluate your own performance. Let’s Start Practising Now!
Remember, practical experience is key to passing the AWS DevOps Engineer Professional exam. It is important to have hands-on experience in deploying and managing infrastructure and applications on the AWS platform.



